Fig. 4.1
In vitro evaluation of the ER stress response in cultured cells. The percentage of C6 glioma cells positive for GRP78 and Annexin V/PI (AP) after treatment with 24–72 h of the following: (a) 3 μg/ml, (b) 6 μg/ml, and (c) 12 μg/ml tunicamycin, (d) 10 mM l-glutamate, and (e) 40 mM l-glutamate. The number of AP-positive apoptotic cells increased significantly following treatment with 3, 6, and 12 μg/ml tunicamycin for 48–72 h, 10 mM l-glutamate for 72 h, and 40 mM l-glutamate for 48–72 h compared with control cells (p < 0.05). The number of GRP78-positive cells increased significantly following treatment with 6 and 12 μg/ml tunicamycin for 48–72 h, and with 40 mM of l-glutamate for 72 h compared with control cells (p < 0.05)
These results showed that the upregulation of GRP78 occurs when stress by tunicamycin and l-glutamate reaches a certain level.
4.2.2 Overexpression of GRP78 Protects C6 Glioma Cells from ER Stress
4.2.2.1 Methods
Using the Neon™ transfection system, C6 glioma cell line cells were transfected with a vector designed to induce transfected cells to transiently express green fluorescent protein (GFP) and GRP78. Twenty-four hours after transfection, GFP-positive and GFP-negative cells were sorted by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). Proteins were extracted from the sorted cells and GRP78 was detected using Immobilon Western Chemiluminescent HRP, which was quantified through densitometric scans of the films. In order to evaluate the cytoprotective characteristic of GFP78, GFP-positive and GFP-negative cells were cultured together and subjected to the same stress conditions as 4.2.1.1 and the number of Annexin V/PI-positive cells was quantified.
4.2.2.2 Results
Twenty-four hours after transfection, 41 % of the cells were positive for GFP. The level of GRP78 in GFP-positive cells was significantly higher than either GFP-negative cells or control cells without gene transfection (Fig. 4.2a). For the cells that received tunicamycin treatment, the number of Annexin V/PI-positive cells was significantly lower in the GFP-positive cells at 72 h after 3 μg/ml treatment and at 24–72 h after 6 and 12 μg/ml treatments when compared with GFP-negative cells (Fig. 4.2b–d). For the cells that received l-glutamate treatment, the number of Annexin V/PI-positive cells was significantly lower in the GFP-positive cells at 72 h after 10 mM treatment and at 24–72 h after 40 mM treatment (Fig. 4.2e, f).
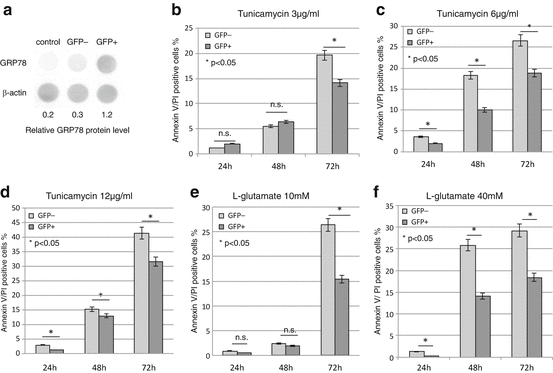

Fig. 4.2
Overexpression of GRP78 protects C6 glioma cells from ER stress. (a) Analysis of protein extracts from GFP-positive, GFP-negative, and untransfected control C6 cells confirms the expression of GRP78 in GFP-positive cells (p < 0.05). (b)–(f) The percentage of GFP-negative and GFP-positive cells that labeled positive for AP. 24 h after transfection, the cells were treated with 24–72 h of the following: (b) 3 μg/ml, (c) 6 μg/ml, and (d) 12 μg/ml tunicamycin, (e) 10 mM l-glutamate, and (f) 40 mM l-glutamate. The survival rate of GFP-positive, GRP78-overexpressing cells was significantly higher than the GFP-negative cells following treatments with 3 μg/ml of tunicamycin for 72 h, 6 and 12 μg/ml tunicamycin for 24–72 h, 10 mM l-glutamate for 72 h, and 40 mM l-glutamate for 24–72 h (p < 0.05)
The results show a higher survival rate under stress conditions for GFP-positive cells compared with GFP-negative cells, suggesting that overexpression of GRP78 protects cells from ER stress-induced apoptosis.
4.3 In Vivo Evaluation of the ER Stress Response in the Injured Spinal Cord and the Effect of Amiloride
The ER stress response of each cell type in the injured spinal cord (neurons, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and OPCs) was investigated. With the same SCI model, the effect of amiloride against SCI was investigated. Amiloride is a potassium-sparing diuretic used to treat hypertension in the United States that has recently been reported to have neuroprotective effects against multiple neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis.
4.3.1 ER Stress Response in a Rat SCI Model
4.3.1.1 Methods
A moderate contusive SCI was induced in Sprague–Dawley rats using an IH impactor. The sham group received a laminectomy without SCI.
Rats were sacrificed at 1, 3, 5, 7, and 14 days post injury (n = 5 for each group). Using five adjacent spinal cord sections 8 mm distal from the lesion epicenter, the expression ratio of GRP78 and CHOP was evaluated in neurons, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and OPCs using double immunohistochemical staining. Quantitative evaluation of GRP78 and CHOP expression was performed in the anterior horn area for neurons and in the dorsal column white matter for the remaining cell types.
4.3.1.2 Results
Compared with the sham group, significantly higher GRP78 expression was observed in the contused spinal cord at 5 days after injury, followed by a gradual decrease in expression. GRP78 expression was highest in astrocytes and lowest in OPCs. In contrast, CHOP expression within the damaged spinal cord gradually increased over time and showed a significantly higher expression compared with the sham group at 7 days after injury. CHOP expression was significantly higher in OPCs compared to astrocytes at 5, 7, and 14 days after injury. These results showed that the ER response varies according to cell type, with the greatest response in astrocytes and the lowest in OPCs.
4.3.2 Amiloride Reduces Apoptosis and Expansion of Secondary Injury After SCI
A moderate contusive SCI was induced in Sprague–Dawley rats using an IH impactor. Daily intraperitoneal injections of amiloride (10 mg/Kg body weight) or PBS were performed for 28 days (n = 6 for each group), during which hind limb locomotor function was assessed using the Basso, Beattie, and Bresnahan (BBB) scale. At 3, 7, and 14 days after injury, the rats were anesthetized, and a sample of the injured spinal cord was resected for western blot analysis of GRP 78 and CHOP expression. For histological analysis, the spinal cords were resected from another group of rats, and apoptosis was assessed using the TUNEL assay. Immunostaining for GRP78, NG2 for OPCs, and GFAP for astrocytes was also performed, and the percentages of positive cells in the dorsal funiculus were assessed.
4.3.2.1 Results
BBB scores were significantly higher in the amiloride group after 11 days after injury (Fig. 4.3a). Western blot analyses revealed that GRP78 expression was highest at 3 days after injury in both groups but subsequently showed a declining trend. Compared with the PBS group, GRP78 expression was significantly higher at 3 days after injury, while CHOP expression was significantly lower at 7 days after injury in the amiloride group. A decrease in apoptosis was observed in the amiloride group, with significantly fewer TUNEL-positive cells at 3 days after injury and significantly smaller TUNEL-positive area at 7 days after injury (Fig. 4.3b). Quantification of all cell types in the dorsal funiculus revealed that the ratio of NG2-positive OPCs gradually decreased over time in both groups with higher values in the amiloride group at all time points. In particular, at 14 days after injury, the ratio of OPCs was significantly higher in the amiloride group (Fig. 4.3c). In contrast, while the ratio of GFAP-positive astrocytes gradually increased, there was no significant difference observed between the two groups. These results indicate that amiloride treatment reduces apoptosis and expansion of secondary injury after SCI, leading to improved survival of OPCs.
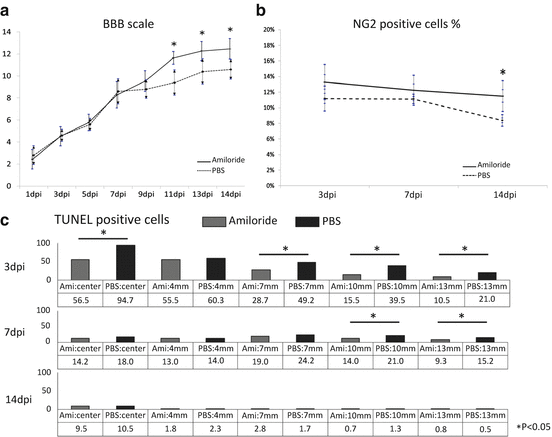

Fig. 4.3




In vivo evaluation of the ER stress response in the injured spinal cord and the effect of amiloride. (a) BBB hind limb motor function scores were significantly higher in the amiloride group compared to the PBS group after post injury day 11 (p < 0.05). (b) Although the percentage of NG2-positive cells gradually decreased in both groups, the amiloride group had a significantly higher rate compared to the PBS group on post injury day 14 (p < 0.05), suggesting that the NG2-positive cells were preferentially spared by amiloride treatment. (c) The percentage of TUNEL-positive apoptotic cells was significantly lower on post injury day 3 and the expansion of TUNEL-positive area was significantly reduced in the amiloride group on post injury day 7 (p < 0.05)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








