♦ Preoperative
Overview
- Hemispherectomy refers to a variety of operations that functionally isolate the cerebral cortex of one hemisphere from the rest of the nervous system.
- Modern functional hemispherectomy procedures aim at greater degree of disconnection and less resection than original anatomic hemispherectomies.
Operative Planning and Preoperative Work-up
- In addition to intractable epilepsy, these patients typically present with a contralateral spastic hemiparesis.
- Because no portion of the hemisphere is to be spared functionally, preoperative or functional localization has no specific role; however, confirmation of transfer of language and motor function into the nonaffected hemisphere will affect risks of surgery.
- Structural neuroimaging (especially magnetic resonance imaging) plays an integral role in preoperative evaluation and may reveal malformations, vascular or posttraumatic hemispheric injury, from atrophy to porencephalic cysts, or other disease-specific imaging findings.
- Electroencephalography should lateralize disease to the radiographically abnormal hemisphere (lateralization, not intrahemispheric localization, is important).
- Hemispherectomy is not employed if less extensive surgical therapy (callosotomy or focal or multilobar resection) may be similarly effective.
- Older children with dominant hemisphere disease and some preserved language function should undergo assessment of lateralization of language (e.g., with the intracarotid amobarbital [Wada] test–lack of transfer to healthy hemisphere constitutes a contraindication to surgery).
- Timing of surgery determined by severity of epilepsy, the age of the patient, the natural history of the disease, and the adequacy of therapeutic trials of anticonvulsant medications
Patient Preparation and Anesthetic Issues
- Antiepileptic drugs are not withdrawn and are given the day before surgery.
- In hemimegalencephaly cases or cases with a near normal brain volume, dexamethasone (4 mg, six times daily) is given starting 1 to 2 days before surgery and tapered within 4 to 6 days after surgery.
- Premedication with midazolam (0.5 mg/kg) is followed by induction with thiopental (5 to 7 mg/kg); anesthesia is maintained with remifentanil (0.2 to 0.3 mcg/kg/min) and isoflurane or sevoflurane.
- At least two intravenous lines are placed and an intra-arterial line is placed in the radial or femoral artery; a central venous line is not used routinely but is useful in small infants with expected larger blood loss (e.g., hemimegalencephaly).
♦ Intraoperative (Fig. 62.1)
Overview
- Primary goal of hemispherectomy is to achieve seizure control via complete disconnection of the cortex of the epileptogenic abnormal hemisphere from the “good” hemisphere.
- Many variations of hemispherectomy have been described; this chapter describes the surgical technique for transsylvian functional hemispherectomy, which entails four steps:
- Linear incision and small craniotomy
- Transsylvian exposure and mesial temporal resection (uncoamygdalohippocampectomy)
- Transventricular callosotomy
- Frontobasal disconnection and transsylvian-transventricular occipitoparietal mesial disconnection
- Linear incision and small craniotomy
Positioning
- Patient either in a lateral decubitus position or supine with the shoulder elevated
- Head is placed in three-point Mayfield pin fixation and turned so that the frontotemporal region is parallel to the floor and the vertex is tilted down slightly.
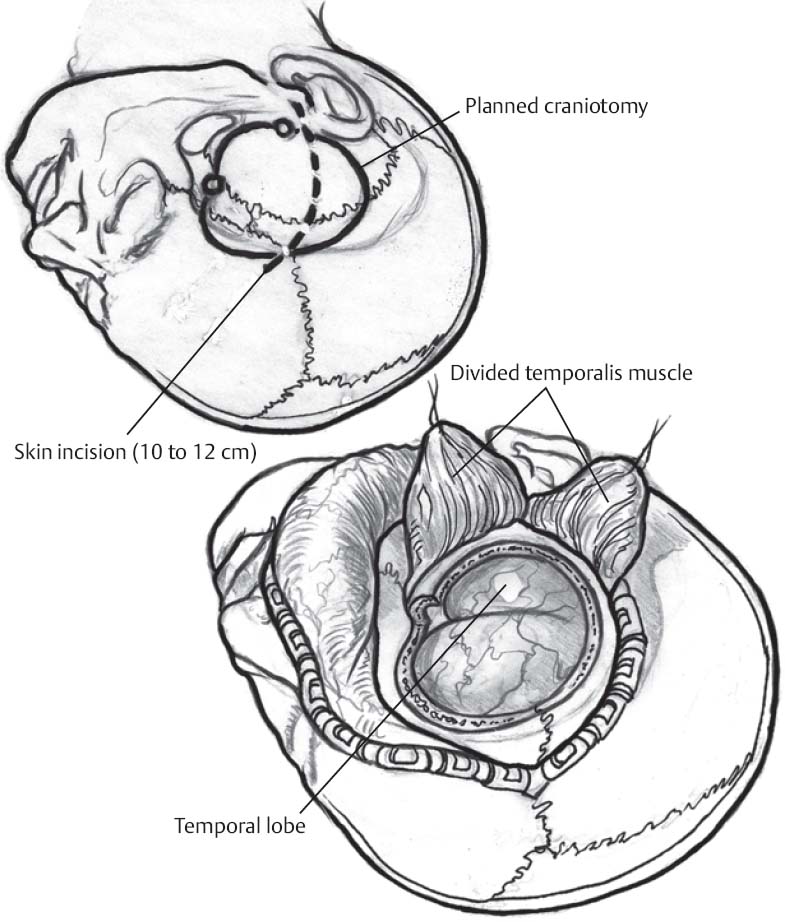
Skin Incision and Craniotomy
- Slightly curved incision (10 to 12 cm) is marked from just anterior to the tragus to the superior frontal area short of midline.
- Incision is opened, Raney clips placed, temporalis fascia/muscle split along incision and retracted
- Bone flap is planned with the following approximate borders:
- Anterior: limen insulae
- Superior: corpus callosum
< div class='tao-gold-member'>Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
- Anterior: limen insulae

Full access? Get Clinical Tree