Fig. 16.1
Schematic of experimental design. Shown are the steps using phMRI to identify common brain activity in drugs at risk, and those for treating suicidal ideation and self-harm. Finding the difference between the two drug conditions identifies the vulnerable neural circuit
The three candidate drugs with black box warnings are shown in Table 16.1 and highlighted for their indication, mechanism of action, and chemical structure. Each drug was given i.v. in a single dose (rimonabant 1 mg/kg; venlafaxine 10 mg/kg; gabapentin 10 mg/kg). These drugs were compared to two test drugs used to treat suicidal ideation (clozapine 3 mg/kg) and aggressive behavior (buspirone 10 mg/kg) shown in Table 16.2. Clozapine was chosen because it is approved for the treatment of suicidal ideation in schizophrenics. Busprione was chosen because it is used to treat inappropriate aggressive behavior (Kavoussi et al. 1997), considered to be a risk factor for suicidal behavior. In fact, approximately 21 % of highly aggressive men diagnosed with Intermittent Explosive Disorder commit suicide (McCloskey et al. 2008).
Table 16.1
Drugs with black box warnings for suicidal ideation and self-harm
Drugs with black box warnings for suicidal ideation and self-harm | |
|---|---|
Venlafaxine—used to treat depression. Functions as a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor | 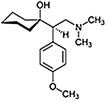 |
Rimonabant—used to treat obesity. Functions as an inverse agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB1 | 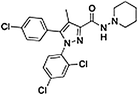 |
Gabapention—used to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Functions as a GABA analog acting on voltage-dependent calcium channels | 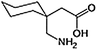 |
Table 16.2
Drugs used to treat suicidal ideation and aggression
Drugs used to treat suicidal ideation and self-harm | |
|---|---|
Colzapine—used to treat schizophrenia. Functions as an atypical antipsychotic acting on multiple signaling systems. FDA approved for the treatment of suicide risk inschizophrenics |  |
Buspirone—used primarily to treat anxiety. Also, indicated for treatment of aggression associated with head injury. Functions as serotonin 5-HT1A partial agonist |  |
All animals were imaged continuously for 35 min starting with a 5 min baseline followed by 30 min post i.v. injection of test drugs.
Figure 16.2 shows 3D activation maps for each of the test drugs. The red is the average significant positive BOLD signal change in over 16,000 voxels from the sample size shown beneath each figure. Starting with 154 brain areas that comprise the rat atlas, 67 were found to be common, or not significantly different from one another. Those areas that were common to clozapine and buspirone (data not shown) were compared to the 67 brain areas of the black box drugs. Seventeen brain areas were identified in the risk drugs that were not found in the treatment drugs. These areas constitute the putative neural circuit that has the potential when activated to arouse thoughts of suicide and self-harm.
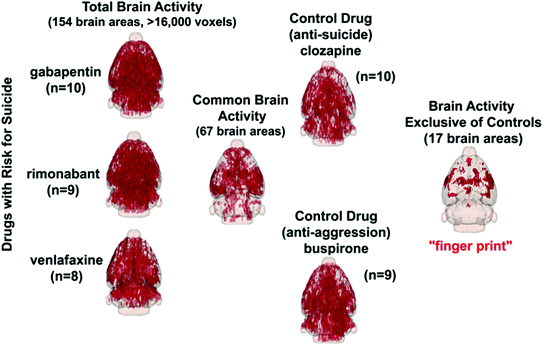

Fig. 16.2
Brain activity in the whole brain for each test drug shown are glass brains for each test drug and the location of the average significant change in BOLD signal from 154 brain areas and over 16,000 voxels. The parenthesis beneath each shows the sample size. Finding brain areas that were not significantly different between drugs at risk reduced the possible areas to 67. Identifying areas not common to the treatment drugs clozapine and buspirone reduced the brain areas to 17
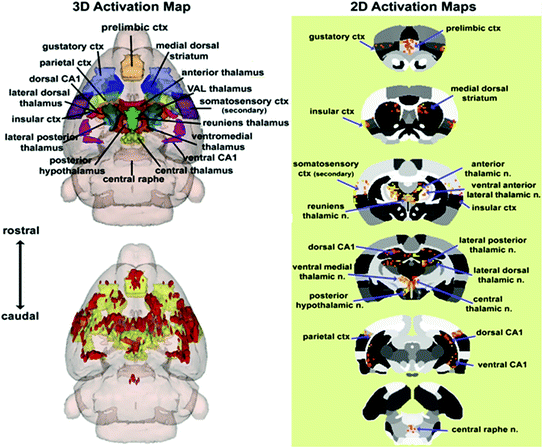
This pattern of brain activity was generated, reconstructed as an integrated neural circuit, and visualized as a 3D volume of activation and 2D activation maps as shown in Fig. 16.3. The 3D localization of these brain areas are shown in color with labels. These areas were coalesced into a single volume shown in yellow in the glass brain below. The average significant change in BOLD signal in these areas is shown in red using the rimonabant data as the example. These same data are presented in 2D activation maps to the right showing the localization of activated voxels within axial sections of the rat brain atlas.