Fig. 4.1
Patient who experienced cardiac arrest responsible for low output state. Cerebral ischaemia involving all border zones of the brain (1 border zone between anterior and middle cerebral arteries, 2 border zone between middle and posterior cerebral arteries)
Aetiology
Low cardiac output (resuscitation after cardiocirculatory arrest or shock regardless of the cause, severe heart failure) or severe extracranial (Fig. 4.2) or intracranial arterial stenosis (Fig. 4.3) or atherosclerotic occlusion or dissection.
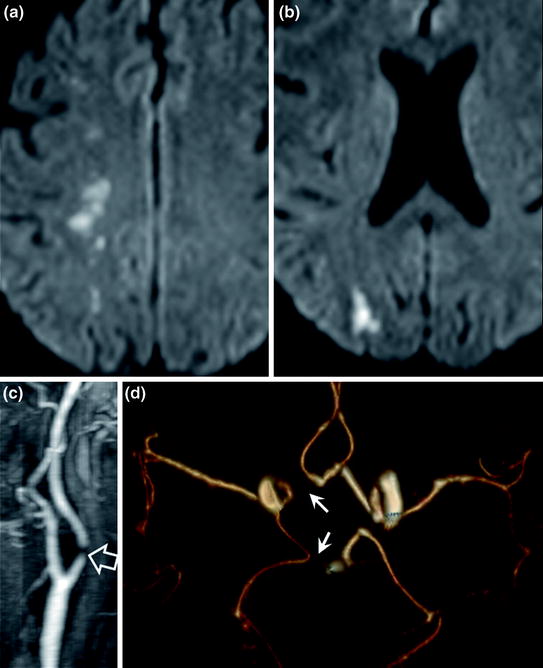
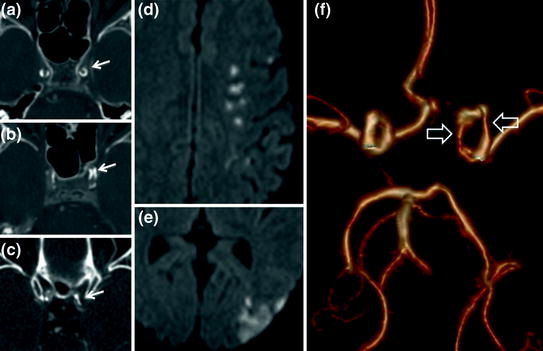

Fig. 4.2
Right anterior (a) and posterior (b) watershed infarction (a) secondary to sub-occlusive carotid artery stenosis (c hollow arrow). Brain TOF MR angiography (d) reveals a normal variant with hypoplasia of the first segment of the right anterior and posterior cerebral arteries (d arrows) accounting for absence of collateral flow to the right internal carotid artery via the Circle of Willis

Fig. 4.3
Left watershed infarction secondary to intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis. Brain CT angiography (a, b, c) demonstrates internal carotid artery calcifications predominantly on the left (single arrows) causing serial stenoses. MRI diffusion-weighted images (d and e) show hyperintensities related to cerebral ischaemia in the anterior (d) and posterior (e) watershed territories. Intracranial MR angiography (f TOF sequence, bottom view) visualizes major stenoses of the cavernous left internal carotid artery (hollow arrows)
A low output state can cause bilateral multifocal lesions (especially in the carotid/vertebrobasilar watershed territory), while arterial occlusion causes elongated subcortical ischaemic lesions in the watershed territory of two adjacent arteries. The most common form of watershed infarction consists of frontoparietal lesions between the anterior cerebral artery territory and the middle cerebral artery territory.
Diagnosis
Radiological: ischaemia in the watershed zone of two adjacent arteries.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








