Fig. 43.1
Diffuse AACE inhibitor induced angioedema. Axial contrast-enhanced CT image shows circumferential mucosal pharyngeal swelling (arrows) and diffuse stranding of the parapharyngeal and subcutaneous fat bilaterally
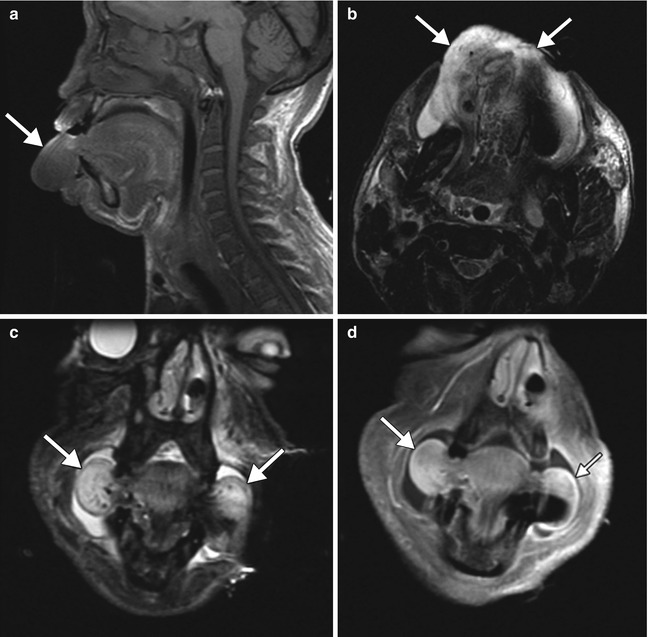
Fig. 43.2
Focal ACE inhibitor angioedema. Sagittal T1-weighted (a), axial (b) and coronal T2-weighted (c), and coronal post-contrast T1-weighted (d) MR images show diffusely massive tongue edema (arrows)
43.4 Differential Diagnosis
Several other drugs, such as rituximab, alteplase, fluoxetine, laronidase, lepirudin, and tacrolimus, can also cause angioedema. Otherwise, the imaging differential diagnosis for angioedema includes infection, longus coli calcific tendonitis, vascular malformations (Fig. 43.5), and neoplasms (Fig. 43.6).
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

Phlegmon appears as ill-defined areas of hypoattenuation and swelling on CT, while abscess is characterized by a rim-enhancing fluid collection (Fig. 43.3). Clinical parameters, such as fever and elevated white blood cell count, are typically present.
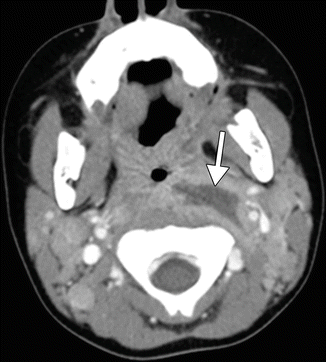
Fig. 43.3
Retropharyngeal abscess. Axial contrast-enhanced CT image shows a discrete rim-enhancing fluid collection in the left retropharyngeal space (arrow), consistent with abscess
Longus colli calcific tendonitis can present with prevertebral space edema. Identifying a calcification on CT along the course of the tendon helps to make the diagnosis (Fig. 43.4). Patients can present with neck pain and fever.
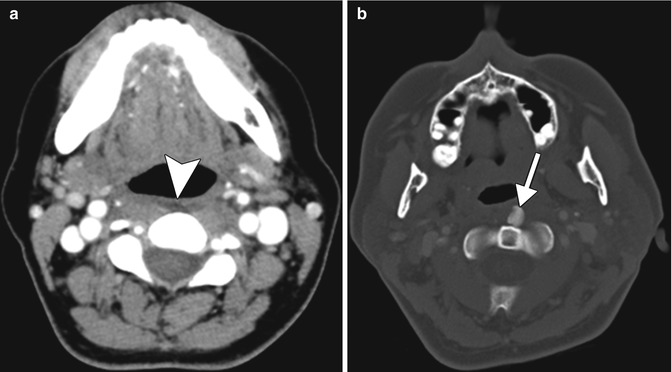
Fig. 43.4
Longus colli calcific tendonitis. Axial contrast-enhanced CT images in the soft tissue (a) and bone (b) windows obtained at different levels show an effusion in the prevertebral space (arrowhead) and a rounded calcification in the left longus colli tendon (arrow)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








