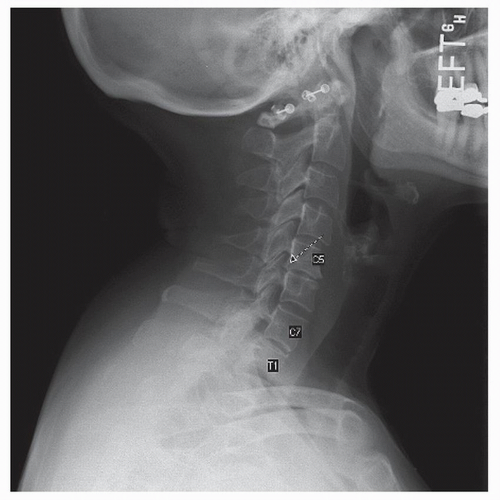
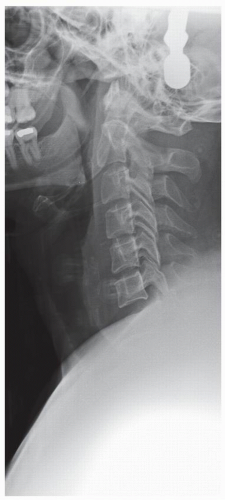
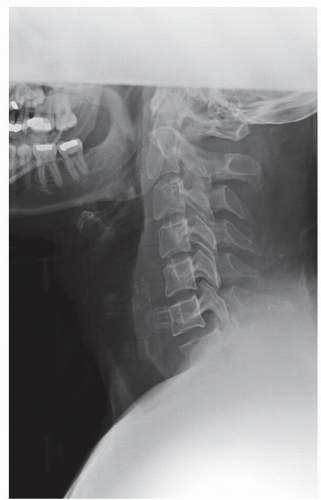
by the occiput and mandible. The spinous processes and facet joints should be symmetric and well aligned. Any abnormal rotation of a single spinous process can indicate a unilateral facet dislocation and rotational malalignment to the side of the injury. Attention should be paid to any abnormalities in bony architecture. The intervertebral disk and facet joints should be symmetric and preserved. Look for evidence of asymmetry in the paravertebral soft tissues (3). Evaluate the uncovertebral joints for any signs of degeneration including loss of joint space, sclerosis, and lateral spurring.
distance with flexion and extension indicates fusion at the levels in question. These images should be used cautiously in the case of suspected trauma. CT or MRI may be safer and of greater utility in this situation.
any substantial return of neurologic function. The conclusion of this study was that patients with a PADI of 14 mm or less should undergo operative stabilization (7).
TABLE 23.1 Normal Prevertebral Soft Tissue Width | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree