CHAPTER 8 COMA AND BRAIN DEATH
Assessing the level of consciousness and diagnosing the cause of coma are fundamental aspects of medical practice. Consciousness consists of two main components: the level of alertness or arousal and the content of thought. Impairment of arousal is a continuum from drowsiness to stupor and then to coma. In stupor, the patient awakens briefly in response to stimulation and then slips back into a sleeplike state. There is no verbal response. Coma is the inability of the patient to be aroused (i.e., to obey commands, speak, or open the eyes in response to painful stimuli). This is obviously different from a sleep state from which the individual can be aroused. Stupor and coma of recent onset are medical emergencies. Speedy diagnosis and treatment are imperative for achieving the optimal outcome; however, a discussion of the treatment of the many causes of coma is beyond the scope of this chapter.
CONSCIOUSNESS
Qualia are the high-order perceptions of qualities, such as the warmth of warm or the redness of red, that are experienced in the normal conscious state.1 Free will, conscience, meta-memory (knowledge and beliefs about the functioning of one’s own memory systems), the analysis of one’s own thoughts, and imagination are all integral components of human higher order consciousness that remain mysterious. Much of the planning and execution that humans perform is unconscious or preconscious in the “zombie mode.” An example is sensory processing and gating. The automatisms of complex partial seizures are an extended pathological example of this. Penfield (1937) showed that electrical stimulation of the cortex could alter the content of consciousness and produce “experiential responses” that the patient usually realized were unreal. The “déjà vu” phenomenon is a natural example of this.
The neural correlates of consciousness are slowly yielding to the study of individual and group neuronal electrical activity, through the use of surface cortical electrodes and implanted microelectrodes, and to functional brain imaging. Although there is a modularity to brain function, it is the integration of all the modules that is necessary for consciousness. There also seems to be competition between different cortical areas and neurons to choose the best fit for a set of perceptual inputs. There are “essential nodes” for particular perceptions such as face recognition or color perception. Clearly, multiple nodes and regions of the brain, functioning in concert, are necessary for consciousness to exist.2,3
Both the cerebral cortex and subcortical structures such as the thalamus are involved in consciousness. Dandy described temporary loss of consciousness after removal of both frontal lobes with sacrifice of the anterior cerebral arteries at the genu of the corpus callosum and speculated that the striatal damage was responsible for the coma.4 The reticular nucleus that surrounds the thalamus acts as a switch or “gate” to particular thalamic nuclei. It results in different patterns of activity of the thalamic nuclei and therefore in different weighting of sensory input. The intralaminar nucleus of the thalamus sets thresholds for the cortical response to the thalamic input. Thalamic gating is also influenced by feedback from the prefrontal cortex.5 The filtering of sensory information is done at a preconscious level so that attention is selectively directed, although it can also be altered at will.
Moruzzi and Magoun6 in 1949 produced electroencephalographic arousal by stimulating the brainstem reticular formation rostral to the mid-pons. They termed this system, including its rostral projection, the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS). This is an alerting or arousal system that also indirectly influences sensory processing in the cerebral cortex. It projects rostrally through the midline, intralaminar nucleus, and other nuclei of the thalamus, and via these structures to the cerebral cortex. Attention enables an awake and alert individual to select a task or a stimulus to process from a number of alternatives and to select a cognitive strategy to carry it out.5 The ARAS is thought to facilitate this process by enhancing the perception of differences between competing stimuli. The anterior cingulate gyrus is involved in a wide range of attentional and discriminatory activity and is involved in higher order motor control of many tasks. The parietal cortex is involved in attention in the visual field and the pulvinar of the thalamus is involved in selecting information for attention. The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex is also involved in attention, intention, and working memory; working memory is the term applied to the holding and manipulation of the current content of consciousness. The hippocampal system—including the fornices, the mammillary bodies and mammillothalamic tracts, the amygdala, the anterior thalamic nuclei, the medial dorsal thalamic nuclei, and the entorhinal cortex—are all involved with establishing new anterograde episodic memory. The amygdala, hippocampus, and associated limbic and nonlimbic structures are involved in the generation of internal feelings, emotions, and motivation.5
The γ-amino butyric acid (GABA) inhibitory neurons are widely dispersed throughout the central nervous system and are involved with the selection of sensory information. Barbiturates increase GABAergic activity in the ARAS. Glutamate and aspartate are the excitatory neurotransmitters that play a key role in cortical interplay.5 The N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor may be the main target for the action of general anesthetic agents that produce a pharmacological coma. The corollary, that the NMDA receptor is essential for consciousness, constitutes the Flohr hypothesis, about which there is considerable debate.7 Clearly, many other peptides and receptors are also involved in cortical function and consciousness.
Single neurons in the human entorhinal cortex have very specific responses (e.g., only to faces or only to different types of animal), and some temporal lobe neurons function at a different hierarchical level by responding to the extensively processed perception or imagining of an object and not to the raw retinal input.2 Different components of consciousness therefore seem to exist from the level of individual neurons to that of different brain regions and, indeed, that of the whole brain.
Edelman (2004) proposed a theory called neural Darwinism, or neuronal group selection, to explain consciousness, as opposed to an instructive model in which the brain has computer-like properties with a set of programs and algorithms. The three tenets of neural Darwinism are that (1) developmental selection leads to a highly diverse group of circuits, (2) experiential selection leads to changes in the connection strength of synapses, and (3) reentrant mapping occurs, in which brain maps are coordinated in space and time through reentrant signaling across reciprocal connections. This coordination leads to widespread synchronization of widely dispersed neuronal groups, which integrates information such as the color and orientation of visual objects and which Edelman proposed is central to the understanding of consciousness. This is a possible solution to the binding problem, which is the seamless reintegration of separately processed aspects of a sensory percept at a preconscious level. According to neural Darwinism, the brain is a selectional system. Other examples of such systems in nature are evolution and the immune system. Another important characteristic of the brain is degeneracy, in which different elements of the brain can perform the same function and one element can carry out different functions in different neuronal networks at different times. This creates great diversity of brain function. There is no need in the theory of neural Darwinism for a homunculus in the head directing the brain and being the seat of consciousness.1
The principal neural structures of consciousness according to Edelman’s (2004) theory are the cerebral cortex, the thalamus, and the reentrant loops between the two, which he called the dynamic thalamocortical core. He proposed that this neural activity generates the qualia of consciousness. The gamma, or 40-Hz, rhythm of the electroencephalogram (EEG) is believed to be produced by thalamocortical circuits during attention and sensory processing tasks. Attention is directed partly by the reticular nucleus of the thalamus and partly by the relationship of the basal ganglia to the frontal and parietal cortices. Higher order consciousness is based in part on episodic memory, which depends on the hippocampi, and in part on semantic and linguistic ability, which depend on the language cortices of Broca and Wernicke and associated areas (for further reading, see Edelman, 2004; Jasper et al, 1998; John, 2002; Metzinger, 2002; Young et al, 1998; Zeman, 2001).
COMA
The Etiology of Coma
The fundamental causes of coma are structural, including the mechanical deformation or disruption of neural tissue and ischemia, and metabolic or toxic derangement of neural tissue, inducing hypoxia. A detailed list of the causes is presented in Table 8-1. A detailed history from bystanders or relatives is vital in determining the cause of the coma.
ADEM, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis; PaO2, partial pressure of arterial oxygen; PVS, persistent vegetative state.
The Anatomy and Pathophysiology of Coma
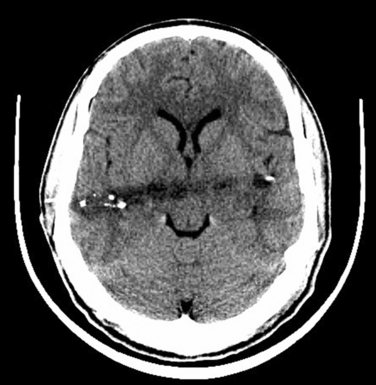
Diffuse lesions of both cerebral hemispheres (cortical and subcortical white matter) may cause coma. Bilateral diencephalic damage (especially to the paramedian dorsal thalamus) may also cause coma (Fig. 8-1). The extension of the thalamic lesions into the midbrain tegmentum has an even greater propensity for causing coma or severe neurological deficit, apathy, and impaired attention. Damage to the paramedian gray matter anywhere from the posterior hypothalamus to the tegmentum of the lower pons causes coma.8,9 When the respiratory centers in the lower medulla are damaged, apnea ensues. The testing of brainstem reflexes and for apnea is the clinical means of confirming the destruction of theses critical areas. The irreversible destruction of critical brainstem areas usually follows catastrophic supratentorial events that cause brain herniation and subsequent compression and ischemia of the brainstem.
The sequence of cardiovascular changes resulting from progressive mechanical compression and/or ischemia of the brainstem begins with vagal stimulation, which causes decreases in heart rate, mean arterial pressure, and cardiac output. As the pons becomes ischemic, sympathetic stimulation occurs, which results in hypertension with persistence of the bradycardia (Cushing’s reflex). As the medulla becomes ischemic, there is unopposed sympathetic stimulation with tachycardia, increased mean arterial pressure, and increased cardiac output. This sequence has been called an “autonomic storm” and has not been well recognized in intensive care unit patients, partly because it may have occurred by the time the patient is admitted to intensive care unit and may be affected by treatment or the presence of other injuries.10
Clinical Assessment of the Comatose Patient
A full neurological and general examination of the patient must be undertaken. Some of the pertinent components of the examination are described as follows.5,9
Assessment of the Conscious State
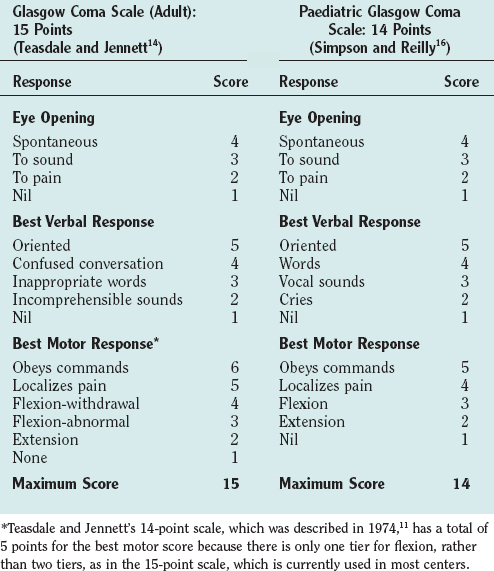
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) was devised to provide a simple, reliable, and reproducible method of assessment of conscious state so as to avoid misinterpretation and blurring of terms such as stupor, semicoma, and confusion.11 It has become a universally accepted scale for neurological observation, prognostication, and grading severity and has been found to have good interrater reliability. It was originally a 14-point scale but has been extended to 15 points by splitting limb flexion into two tiers: flexion-withdrawal and flexion-abnormal. Abnormal flexion is defined as any two elements of stereotyped flexion posture, extreme wrist flexion, adduction of the upper arm, and fisting of the fingers over the thumb.12,13 The 15-point scale is the preferred scale for research studies. The GCS is scored on the best response in each of the three categories: eye opening, vocalization, and limb movement (Table 8-2). Testing nail bed pressure with a pencil is the recommended method of applying a painful stimulus. Patients who do not open their eyes, do not speak, and are not obeying commands are said to be comatose. Many clinicians regard a maximum GCS score of 8 as the cutoff for coma. Some limitations to the usefulness of the GCS do exist, however. For example, periorbital swelling and endotracheal intubation, both common conditions in the trauma patient, prevent the accurate assessment of eye opening and verbal response, respectively. Some centers record a “T” next to the score when the patient is intubated and the verbal score cannot be assessed. The GCS is commonly used to monitor neurological progress, and a drop in the GCS of 2 points or more is a sensitive measure of neurological deterioration and necessitates action to halt the progression. Age and depth of coma are the principal predictors of poor outcome or death after traumatic brain injury. Repeated GCS assessments and the recognition of confounding factors are required for any confidence in prediction of outcome.
The conscious state is more difficult to assess in infants and young children, and special pediatric coma scales have been devised.14 The Paediatric Glasgow Coma Scale is a simple system based on the GCS with age-related norms for verbal and motor responses (see Table 8-2).15
Respiratory Pattern
Pupil Examination
Eye Motion: Extraocular Muscle Function (Fig. 8-2)
Deviation of the Ocular Axes
 Frontal lobe lesion (frontal center for contralateral gaze): the eyes look toward the side of the lesion.
Frontal lobe lesion (frontal center for contralateral gaze): the eyes look toward the side of the lesion. Downward deviation: thalamic or midbrain pretectal lesions, metabolic cause (especially barbiturates).
Downward deviation: thalamic or midbrain pretectal lesions, metabolic cause (especially barbiturates).Unilateral outward deviation with dilated pupil (nerve III palsy)
Unilateral inward deviation (nerve VI palsy)
Reflex Eye Movement
Oculocephalic reflex (doll’s-eye reflex)
In the awake patient, the eyes follow the movement of the head or, if the movement is performed slowly, there is contraversive conjugate eye movement if the eyes fixate on a stationary target. In the comatose patient with intact brainstem and cranial nerves, the reflex is preserved and the eyes move in the opposite direction when the head is turned laterally or the neck flexed and extended; that is, the conjugate eye movement is contraversive. When the brainstem is damaged, the reflex is lost, and the eyes follow the head movement. Cervical spine injury should be ruled out before this test is performed.
Herniation Syndromes (Coning)
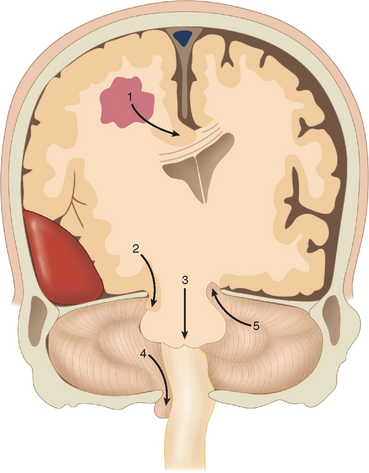
Cerebral herniation is the displacement of cerebral tissue as a result of intracranial mass lesions. This displacement may disturb the conscious state by direct or indirect pressure on the diencephalon and brainstem. Indirect pressure means displacement of tissue at a distance from the mass. Coning is the name given to progressive cerebral herniation with secondary compression of the brainstem and resultant deepening coma. Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging have helped significantly to elucidate the anatomy of herniation. Plum and Posner (1982) in their classic treatise described progressive and predictable stages of herniation with cephalad-caudal progression. There are five types of supratentorial and infratentorial herniation (Fig. 8-3), described as follows.
Supratentorial Herniation
Central (Transtentorial) Herniation
The classic description is of a sequential rostral-caudal failure from diencephalon to the midbrain, the pons, and finally the medulla. Central herniation is often caused by a tumor in the frontal, parietal, or occipital lobes that reaches the point of decompensation. The diencephalon may herniate through the tentorial incisura, damaging the pituitary stalk and causing diabetes insipidus. Vertical downward shift of the brainstem may be a critical factor in the development of the features of central herniation.16 The brainstem may become ischemic as a consequence of shearing of perforating arteries from the basilar artery. Resultant hemorrhages in brainstem are called Duret hemorrhages. CT may show a downward displacement of the pineal gland and effacement of the perimesencephalic (ambient) cisterns. The posterior cerebral arteries may be kinked at the tentorial edge as they pass onto the inferior surface of the occipital lobe, which results in occipital infarction and cortical blindness. This may further increase the intracranial pressure.
The clinical stages of central herniation are outlined in Table 8-3. It is difficult to discern these various stages (and those of the other types of coning) in many patients because of the speed of deterioration, the tendency of the stages to merge, and the mixed and complex pathology that may affect the supratentorial and infratentorial compartments, and because patients often receive early intervention with paralysis, endotracheal intubation, and ventilation that obscures or retards the clinical progression. Nevertheless, it is useful to think conceptually in these terms in contemplating the patient’s condition and the appropriate treatment.
TABLE 8-3 Stages of Central Herniation
| Diencephalon Stage | May be caused by displacement or ischemia of the diencephalon |
| This stage is reversible | |
| Consciousness | Altered alertness is first sign |
| Usually lethargy is present | |
| Some patients have agitation | |
| Later stupor, then coma | |
| Respiration | Sighs, yawns, occasional pauses |
| Pupils | Small (1-3 mm), reacting |
| Oculomotor | Conjugate or slightly divergent roving eyes |
| Doll’s-eye reflex present | |
| Parinaud’s syndrome with impaired upward gaze may be present | |
| Conjugate ipsilateral response to cold water calorics | |
| Motor | Early: appropriate response to painful stimulus |
| Contralateral hemiparesis may worsen | |
| Bilateral Babinski reflex; later, grasp reflexes | |
| Decorticate (contralateral to the lesion initially) | |
| Midbrain–Upper Pons Stage | Prognosis is very poor when midbrain signs have developed; <5% having a good outcome if treatment is undertaken |
| Respiration | Cheyne-Stokes respiration → sustained tachypnea |
| Pupils | Moderately dilated: midposition (3-5 mm), fixed |
| Oculomotor | Doll’s-eye reflex impaired |
| May be disconjugate | |
| May be internuclear ophthalmoplegia with medial moving eye moving less than the laterally moving eye) | |
| Response to calorics impaired | |
| Motor | Decorticate → bilaterally decerebrate |
| Lower Pons–Medulla Stage | |
| Respiration | Regular, shallow, and rapid (20-40/minute) |
| Pupils | Midposition (3-5 mm), fixed |
| Oculomotor | No doll’s-eye reflex |
| Response to calorics absent | |
| Motor | Flaccid, bilateral Babinski reflex |
| May be lower limb flexion in response to pain | |
| Medullary Stage (Terminal Stage) | |
| Respiration | Slow, irregular; sighs, gasps, occasional hyperpnea alternating with apnea |
| Pupils | Widely dilated and fixed |
Adapted from Greenberg MS: Coma. In Greenberg MS, ed: Handbook of Neurosurgery, 5th ed. New York: Thieme, 2001, pp 118-127. Also see Plum and Posner (1982).
Uncal herniation
The uncus of the temporal lobe herniates over the free edge of the tentorium, compressing the midbrain and the oculomotor nerve. This is usually caused by a rapidly expanding middle cranial fossa epidural, subdural, or intratemporal lobe hematoma. The earliest sign of uncal herniation is the ipsilateral dilation of the pupil. A depressed state of consciousness is not a reliable early sign, but the patient may be confused or agitated. Once the brainstem is compromised, the conscious state may deteriorate rapidly to a deep coma. The mass lesion causing the uncal herniation usually causes a contralateral hemiparesis, but as the pressure increases, the opposite cerebral peduncle is compressed against the tentorium, which causes an ipsilateral hemiparesis (Kernohan’s sign). This is recognized at autopsy as Kernohan’s notch. As in central herniation, the posterior cerebral arteries may be compressed against the edge of the tentorium, which may cause occipital lobe infarcts. The early CT findings of uncal herniation are early unilateral encroachment on the suprasellar cistern and later brainstem displacement and flattening, flattening of the contralateral cerebral peduncle, and rotation of the midbrain. Contralateral hydrocephalus may occur. The clinical stages of uncal herniation are outlined in Table 8-4.
TABLE 8-4 The Stages of Uncal Herniation
| Early Third Nerve Stage | |
| Pupils | Unilateral dilating pupil, ipsilateral to lesion in 85% of patients; often sluggish |
| Oculomotor | Doll’s-eye reflex normal or disconjugate (failure of adduction of ipsilateral eye) |
| Caloric reflex may be disconjugate | |
| Respiration | Normal |
| Motor | Appropriate response to pain |
| Contralateral Babinski reflex may be present | |
| Late Third Nerve Stage | |
| Consciousness | Stupor → coma |
| Pupil | Fully dilated (unilateral) |
| Oculomotor | Complete third nerve palsy with pupil dilatation (>6 mm) and ophthalmoplegia |
| Respiration | Hyperventilation sustained; in rare cases, Cheyne-Stokes respiration |
| Motor | Usually contralateral weakness |
| If opposite cerebral peduncle is compressed against the tent, an ipsilateral hemiparesis (Kernohan’s sign) and then bilateral decerebrate posture develop | |
| Midbrain–Upper Pons Stage | |
| Pupils | Contralateral pupil dilates initially to midposition (5-6 mm) |
| Oculomotor | Palsy |
| Respirations | Sustained hyperpnea |
| Motor | Bilateral decerebrate rigidity |
Adapted from Greenberg MS: Coma. In Greenberg MS, ed: Handbook of Neurosurgery, 5th ed. New York: Thieme, 2001, pp 118-127. Also see Plum and Posner (1982).
The distinction between uncal and central herniation is difficult when the compression has reached the midbrain and below. Prediction of the location of the pathology on the basis of the type of herniation syndrome is unreliable, inasmuch as central and uncal herniation may occur together. Decrease in consciousness occurs early in the sequence of central herniation but later in the sequence of uncal herniation. Cushing’s reflex, consisting of hypertension, bradycardia, and respiratory irregularity, which is a feature of medullary compression, is often absent with slowly progressive supratentorial mass lesions. The cause of the coma and the third nerve palsy in cases of presumed uncal herniation is not always uncal compression, because the degree of uncal herniation on imaging or at autopsy may not be correlated with clinical state. The anatomy varies among patients, and in some cases, there is no uncal herniation or it is the contralateral pupil that dilates first, so that the mechanism of the third nerve palsy is likely to be central (i.e., intrinsic to the midbrain) in these cases. Horizontal displacement of the central supratentorial structures may also contribute to or cause the depressed conscious state (see Investigation of Coma).17
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree