♦ Preoperative
Operative Planning
- Review imaging (magnetic resonance imaging ± contrast with magnetic resonance venogram to evaluate draining vein pattern and sinus patency; computed tomography to evaluate bone changes, calcium)
- Angiography may be useful for large tumors for consideration of preoperative embolization and evaluation of venous drainage and sinus involvement
- Intraoperative frameless stereotaxy as necessary
- Preoperative steroids for significant edema
- In patients with symptomatic mass effect, preoperative embolizing can precipitate worsening of clinical condition; embolization timing must be coordinated with surgery soon thereafter
Equipment
- Craniotomy tray
- High-speed drill
- Frameless stereo axy
- Mayfield head holder
- Yasargil bar and Greenberg retractor
Operating Room Set-up
- Headlight
- Loupes
- Bipolar cautery and Bovie cautery
- Microscope (prepare if necessary)
- Ultrasonic aspirator for large, soft tumor
Anesthetic Issues
- Arterial line blood pressure monitoring
- Intravenous (IV) antibiotics (oxacillin 2 g or vancomycin 1 g for adults) should be given 30 minutes prior to incision
- Dexamethasone 10 mg IV preoperatively
- Anticonvulsant medication
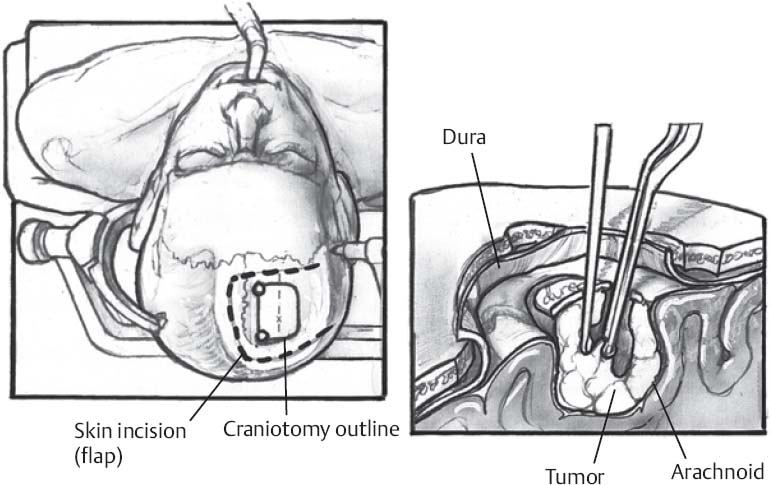
♦ Intraoperative (Fig. 9.1)
Positioning
- Depends on location, size of lesion
- Patient’s head should be positioned so that the bone flap overlying the lesion is parallel to the floor and at the highest point in the room
- Most frontal, temporal, and parietal convexity lesions can be removed with patient in supine position using skull pins and head holder
- Occipital and large parietal lesions may require patient to be in prone or lateral position, or semisitting position
♦ Sterile Scrub and Prep
Incision
- Incision based on location, size of lesion (centered on the lesion)
- Imaging landmarks used to assist (e.g., external auditory meatus)
- Correlate with scalp landmarks (e.g., coronal suture)
- Frame-based or frameless stereotaxy useful in some cases, especially for small lesions
- For large lesions, especially dural-based lesions, ensure that there is sufficient exposure circumferentially around the entire lesion to resect a 1- to 2-cm dural margin
- U-shaped incision useful for lesions near sinus; midline is crossed with both incision and bone flap for sinus control
< div class='tao-gold-member'>Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree