♦ Preoperative
Operative Planning
- Magnetic resonance imaging: with and without contrast images essential; recommend asking for acquisition of postcontrast images in all planes for operative planning
- Image guidance: often helps in localizing the tumor to plan the incision, bony opening, and dural incision
- Angiogram: some surgeons will embolize large meningiomas preoperatively to reduce intraoperative bleeding
- Blood: if the lesion is large or next to the sinus, type and cross the patient for at least 2 units of blood
- Steroids: consider preoperative administration if there is significant edema
Anesthetic Issues
- Central line is important for the parasagittal meningioma cases so that the anesthesiologist can address the potential for air embolism
- Peripheral intravenous needles should be large bore to allow rapid blood transfusions, if needed
- Antibiotics
- Mannitol (0.5 to 1.0 g/kg) for large cases
♦ Intraoperative
Equipment
- Craniotomy tray
- Mayfield head holder
- High-speed drill
- Ultrasonic aspirator
- Micro scope
Surgical Approach
Convexity
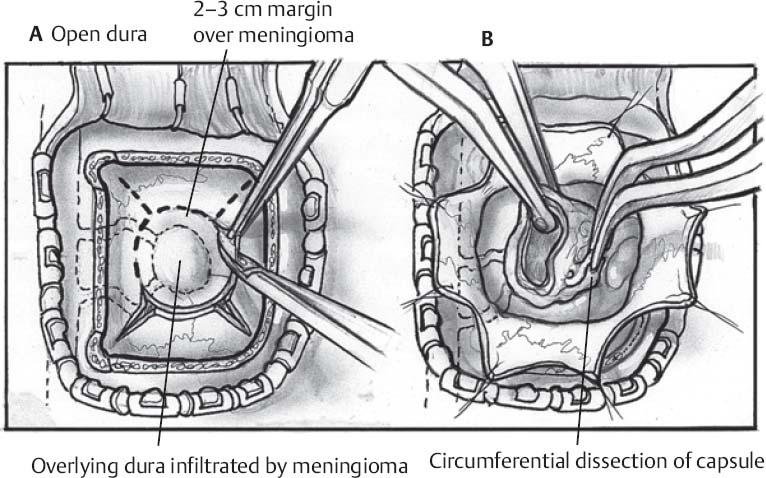
- Incision and bony opening are tailored to the location of the lesion (Fig. 38.1A)
- Position the patient accordingly to allow for the operative field to be at the highest point
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue








