6 Cranial Nerve V
Trigeminal
Anatomy
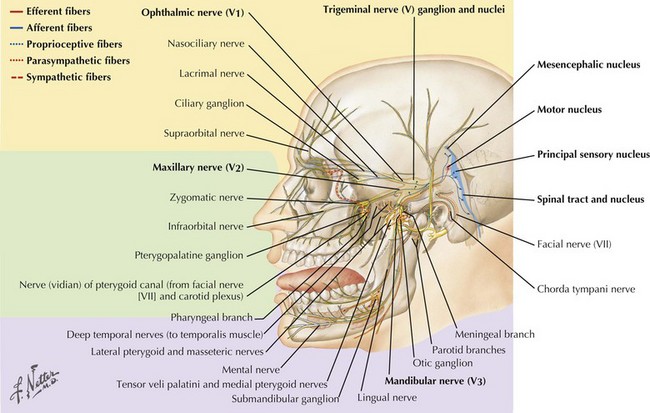
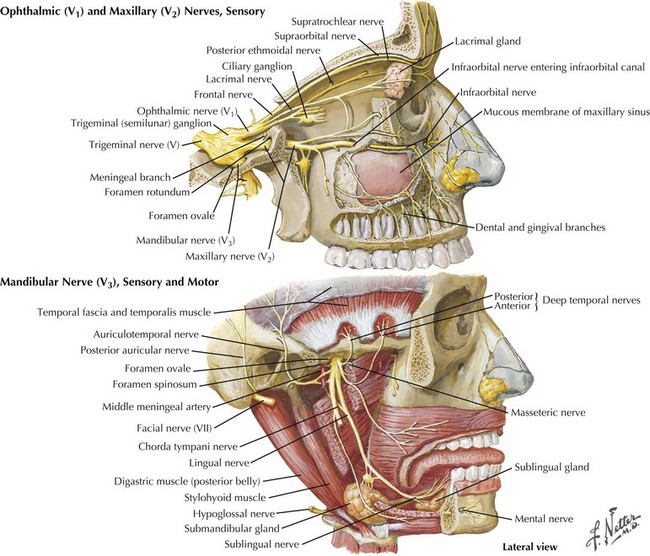
The trigeminal cranial nerve (CN-V) has three major divisions: ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular (Figs. 6-1 and 6-2). CN-V is the major sensory nerve of the face, mouth, and nasal cavity. It also supplies motor and proprioceptive fibers to the muscles of mastication. The trigeminal nerve sensory and motor roots are derived from a large sensory and smaller motor nucleus within the pons. These roots converge to emerge at the midlateral pons, then continue toward the trigeminal (Gasserian) ganglion at the base of the middle cranial fossa. General sensory fibers are derived from their cell bodies of origin within this ganglion. Distal to the trigeminal ganglion, three sensory divisions respectively exit the skull through the superior orbital fissure, foramen rotundum, and foramen ovale. The motor component passes through the trigeminal ganglion into the mandibular division.
CN-V Nuclei
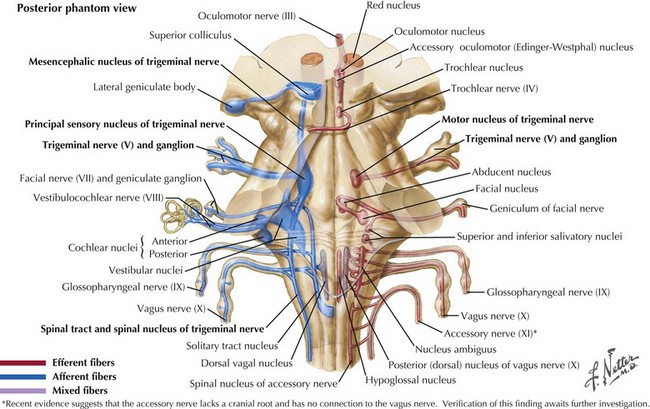
The sensory nucleus is the largest of the trigeminal pontine complex. This begins rostrally within the midbrain, and extends caudally through the pons and medulla into the second segment of the cervical spinal cord (Fig. 6-3). It is subdivided into three portions: (1) the spinal tract nucleus primarily dedicated to pain and temperature fibers; (2) the principal sensory nucleus, the pontine trigeminal portion, which primarily receives tactile stimuli and, therefore, principally subserves light touch; (3) the mesencephalic sensory nucleus, which contains cell bodies of sensory fibers carrying proprioceptive information from the masticatory muscles. Lastly, there is a motor nucleus located within the pons medial to the large sensory nucleus.
Principal Sensory Component
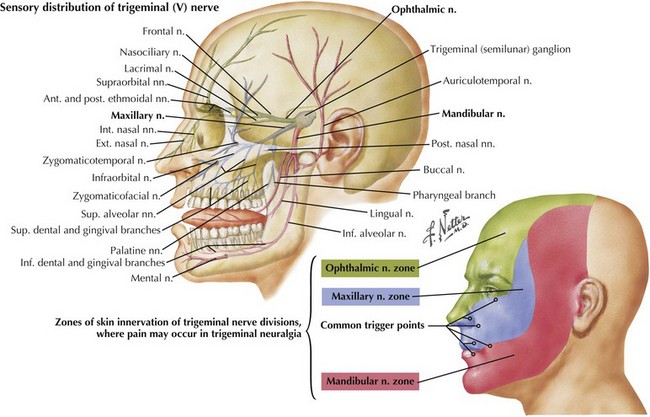
This component of CN-V conveys general sensation from the facial skin and scalp to the top of the head, tragus of the ear, and anterior wall of the external auditory meatus (Fig. 6-4). Also, it provides general sensation from the mouth, including the tongue and teeth, nasal and paranasal sinuses, and meninges lining the anterior and middle cranial fossae.
Trigeminal (Gasserian, Semilunar) Ganglion
The cell bodies of almost all sensory CN-V fibers are located within the trigeminal ganglion (Fig. 6-5). This is contained within a skull-based depression, the Meckel cave, that is located in the floor of the middle cranial fossa. Central processes of neuronal cell bodies constitute the large sensory root that enters the pons and projects into the pontine trigeminal main sensory nucleus and spinal tract nucleus. The peripheral processes of this nerve divide into the three sensory divisions that exit the skull through the superior orbital fissure, the foramen rotundum, and the foramen ovale.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree