♦ Preoperative
Operative Planning
- Review imaging and determine the portion of the cavernous sinus requiring exposure and how it relates to cranial nerve anatomy of the cavernous sinus
Equipment
- Major set-up
- High-speed drill with a small cutting burr
- Cranial fixation plates and screws
- Osteotome/mallet
- Mayfield head holder
Operating Room Set-up
- Headlight
- Bipolar cautery
- Loupes
- Bovie cautery
- Anticonvulsants
- Perioperative antibiotic coverage
- Dexamethasone
♦ Intraoperative
Positioning
- Mayfield headholder placed in anteroposterior position with single pin set to the contralateral side
- Head is turned 30 to 60 degrees to the contralateral side with the zygoma as the most superior point of the operative field
- Shoulder roll is placed under ipsilateral shoulder to ensure jugular venous return
- The ipsilateral thigh or abdomen is prepped and draped (should there be a need for fat graft)
Planning
- Mark skin incision as a gentle curve 1 cm anterior to the tragus and at the inferior border of the zygoma to a point just lateral to the midline on the contralateral side
- Prep and drape
Craniotomy Incision/Exposure
- Infiltrate with 0.5% lidocaine and epinephrine
- Incise the skin and begin reflecting the scalp flap
- Dissect along the temporalis fascial plane until the subgaleal fat pad is identified
- To avoid damage to the frontalis and zygomatic branches of the facial nerve, the superficial fascial layer of the temporalis is incised and reflected anteriorly with the fat pad
- The fascia becomes continuous with the periosteum of the lateral orbit and zygoma at this point and is therefore bluntly dissected from the bone with the aid of a small periosteal elevator or Adson dissector
- Proceed with craniotomy of the pterional region (Fig. 7.1A) with or without orbitozygomatic or transzygomatic modification as described in prior chapters
- Place dural tacking sutures and obtain epidural hemostasis
- Bone edges are waxed for hemostasis
♦ Extradural Osteotomy (Fig. 7.1B)
- Flatten the sphenoid wing with a drill or a Kerrison rongeur
- The region of the meningo-orbital artery near the apex of the superior orbital fissure is identified and the artery is cauterized and cut
< div class='tao-gold-member'>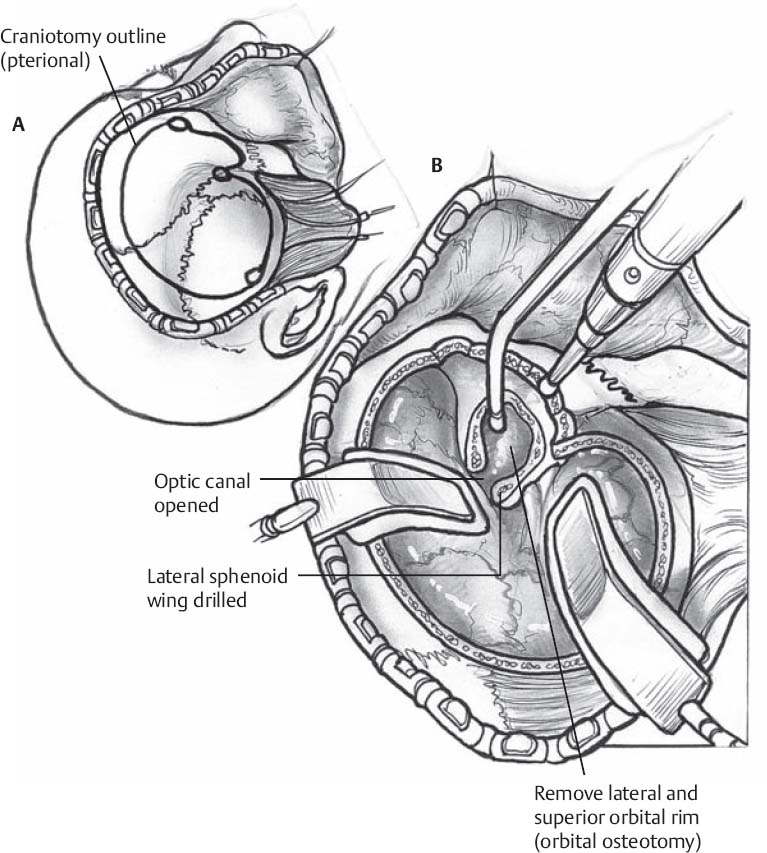
Fig. 7.1(A) The Dolenc approach begins with a pterional craniotomy. (B) Extradural drilling of the optic strut and anterior clinoid process.
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







