♦ Preoperative
Imaging
- Magnetic resonance imaging (level of nerve root involvement)
- Computed tomography
- Bone scan
- Metastatic work-up
Biopsy
- For diagnosis
- Plan extent of resection
- Plan biopsy tract to be included and excised in definitive surgery
- Patient counseling
- Postoperative deficits: bowel/bladder incontinence, sexual dysfunction, neurologic deficits
Bowel Preparation
- Neomycin/erythromycin and polyethylene glycol electrolyte solution by mouth
Equipment
- Basic spine tray
- High-speed drill
- Osteotomes
- Cell saver
- Andrews table
Operating Room Set-up
- Headlight
- Loupes
- Bipolar and Bovie cautery
- Fluoroscopy (if instrumentation needed)
Anesthetic Issues
- Prepare for large blood loss (3 to 10 liters)
- Large bore intravenous access
- Central line or Swan-Ganz monitoring if necessary
- Foley cather
- Consider steroids if neural manipulation is likely
♦ Intraoperative (Fig. 140.1)
Positioning
- Patient prone with face and eyes padded; Andrews frame is helpful
- Lateral position for combined abdominosacral approach
Sterile Scrub and Prep
- Include large volume intraoperative enema
Incision
- Midline for small, distal tumors in nonirradiated tissue
- Omega flap is needed for larger, proximal resection
< div class='tao-gold-member'>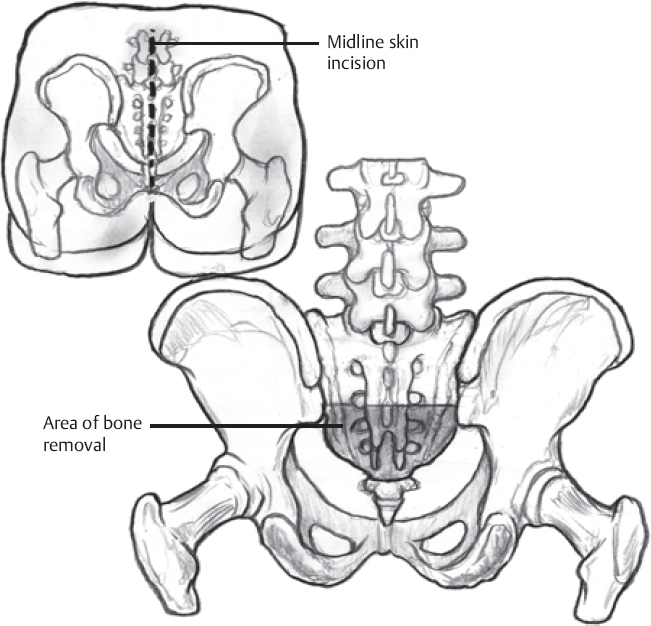 Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







