♦ Preoperative
Operative Planning
- Physical examination
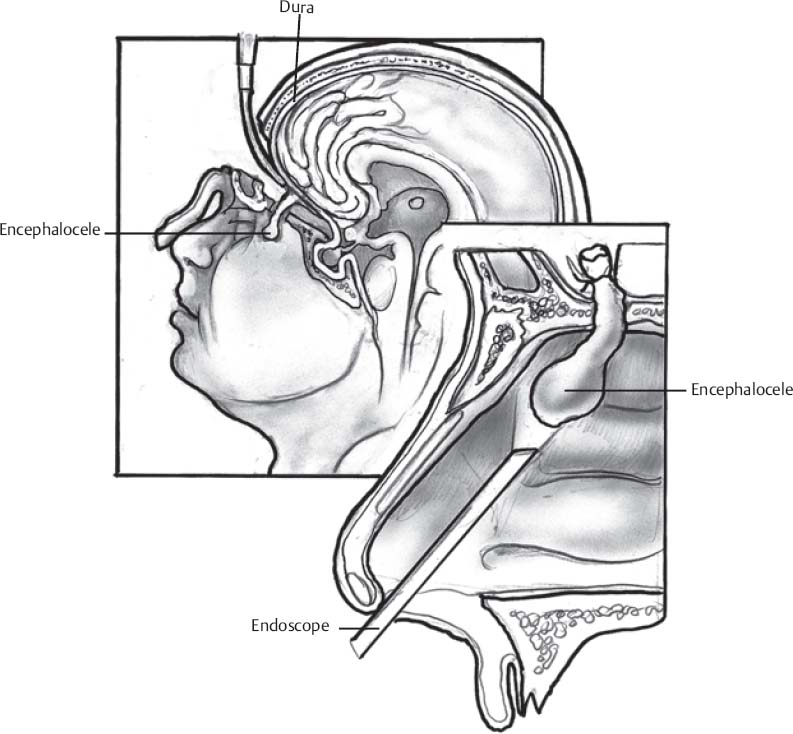
- Basal: Examine nose and mouth to reveal pulsatile mass in epipharynx or nasal cavity between septum and middle turbinate
- Sincipital: Forehead midline (interfrontal, splitting metopic suture), nasion (nasofrontal, through foramen cecum), parasagittal forehead and orbit (na-soethmoidal, through foramen cecum and nasal bone)
- Convexity: Frontal, parietal, or occipital midline (with possible neurovascu-lar elements of the posterior fossa)
- Basal: Examine nose and mouth to reveal pulsatile mass in epipharynx or nasal cavity between septum and middle turbinate
- Counsel family: Review developmental, natural history, and prognosis, and discuss major comorbidity, hydrocephalus
- Obtain consultations from plastic surgery/otolaryngologist for basal/sincipital encephaloceles
Imaging
- Radiologic studies
- In utero ultrasound can allow for diagnosis and preoperative, prenatal counseling
- Magnetic resonance imaging/magnetic resonance angiography
- Delineates intracranial anatomy and neurovascular structures within encephalocele
- Assess extent of hydrocephalus
- Delineates intracranial anatomy and neurovascular structures within encephalocele
- Three-dimensional computed tomography: defines extent of bony defect
- In utero ultrasound can allow for diagnosis and preoperative, prenatal counseling
Special Equipment
- Endoscope: useful in select basal encephaloceles
- Lumbar drain, external ventricular drain
Anesthetic Issues
- As for any pediatric craniotomy
< div class='tao-gold-member'>Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree