Fig. 38.1
Bone marrow necrosis related to HiDAC. Sagittal T2-weighted (a), T1-weighted (b), and post-contrast T1-weighted (c) images show diffuse, extensive geographic signal abnormality and peripheral enhancement within the vertebral bone marrow without vertebral body height loss or expansion
38.4 Differential Diagnosis
A variety of other chemotherapy agents have been implicated in the development of bone marrow necrosis, including imatinib mesylate and G-CSF. Otherwise, a variety of bone marrow alterations can be encountered on MRI in patients being treated for malignancies. For example, on MRI leukemia can manifest as heterogeneous areas of enhancement (Fig. 38.2), anemia appears as diffuse low T1 and T2 signal due to red marrow conversion (Fig. 38.3), while spinal irradiation produces diffuse high T1 and T2 signal due to fatty marrow conversion (Fig. 38.4).
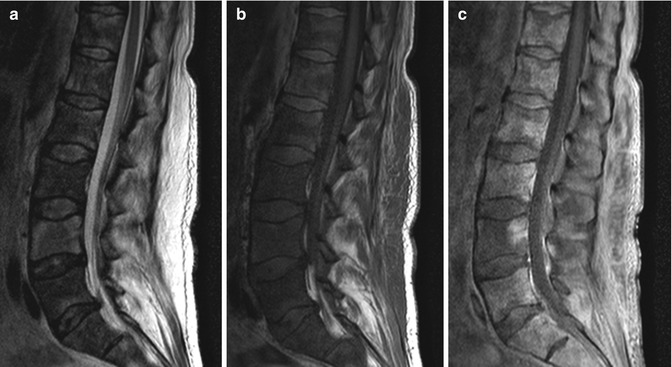

Fig. 38.2




Acute myelogenous leukemia. Sagittal T2-weighted (a), T1-weighted (b), and post-contrast T1-weighted (c) MR images show diffusely heterogeneous bone marrow signal and enhancement
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








