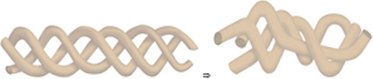Chapter 17 Intradiscal Therapies
Intradiscal decompression for chronic intractable discogenic pain can be achieved by means of various methods, such as intradiscal electrothermal therapy (IDET), nucleoplasty, and percutaneous discectomy. Tables 17.1 and 17.2 summarize these three techniques.
Table 17.2 The Evidence for Efficacy Intradiscal Electrothermal Therapy (IDET) and Nucleoplasty in Management of Chronic Discogenic Low Back Pain
| Therapy | Evidence of Short-Term Relief | Evidence of Long-Term Relief |
|---|---|---|
| IDET | Strong | Moderate |
| Nucleoplasty | Limited | Limited |
Data from Boswell MV, Shah RV, Everett CR, et al. Interventional techniques in the management of chronic spinal pain: Evidence-based practice guidelines. Pain Physician 2005;8:1-47.
Intradiscal electrothermal therapy
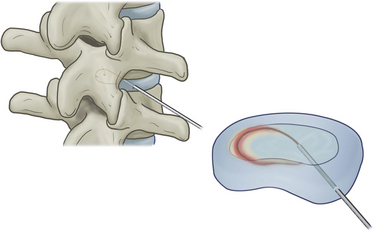
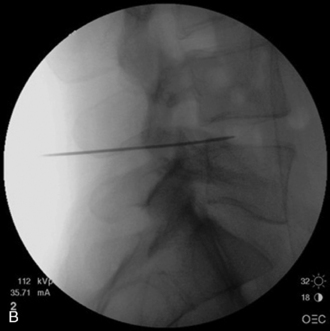
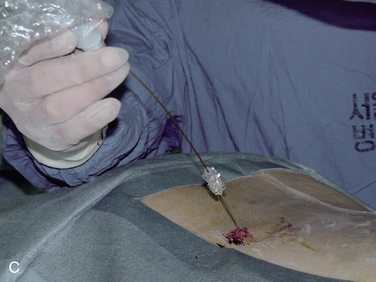
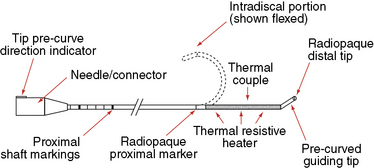
In IDET, the collagen fibers of the disc are modified and the nociceptors causing axial back pain are destroyed by thermal energy delivered through the percutaneous threading of a flexible catheter, composed of a thermal resistive coil, into the disc from the side contralateral to the lesion under fluoroscopic guidance (Fig. 17-1).
Mechanisms of Action
Thermal modification of collagen fibers acts as follows:
 With disc temperatures reaching 65° C, collagen may contract as much as 35% from its original size (Fig. 17-2).
With disc temperatures reaching 65° C, collagen may contract as much as 35% from its original size (Fig. 17-2). The tightening of anular tissue may enhance the structural integrity of the degenerated disc and may repair the anular fissures.
The tightening of anular tissue may enhance the structural integrity of the degenerated disc and may repair the anular fissures.Indications and Contraindications
Ideal candidates for IDET have the following features:
Indications
The indications for IDET are as follows:
 Failure of a minimum of 6 weeks of conservative treatment (including pain medication and physical therapy) to improve the symptoms
Failure of a minimum of 6 weeks of conservative treatment (including pain medication and physical therapy) to improve the symptoms The presence of degenerative disc disease on magnetic resonance imaging with global disc degeneration or posterior or posterolateral anular tear evident
The presence of degenerative disc disease on magnetic resonance imaging with global disc degeneration or posterior or posterolateral anular tear evident The presence of one- or two-level symptomatic disc degeneration as determined by provocative lumbar discography at L3-L4, L4-L5, L5-S1 and with an adjacent asymptomatic “control” disc
The presence of one- or two-level symptomatic disc degeneration as determined by provocative lumbar discography at L3-L4, L4-L5, L5-S1 and with an adjacent asymptomatic “control” disc At the target level, the discogram and subsequent computed tomography scanning demonstrate spread of the contrast agent to the outer anulus or beyond the confines of the disc (Fig. 17-3)
At the target level, the discogram and subsequent computed tomography scanning demonstrate spread of the contrast agent to the outer anulus or beyond the confines of the disc (Fig. 17-3)Related Anatomy and Pathophysiology
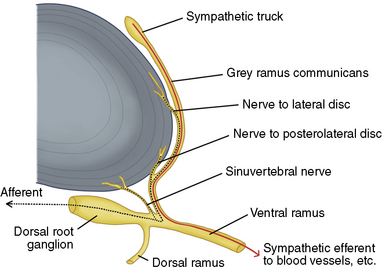
Figure 17-3 illustrates innervations of an intervertebral disc related to IDET.
Procedure
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree