Fig. 12.1
Normal iodinated contrast material distribution. Axial non-contrast CT (a) and corresponding post-contrast CT (b) show expected enhancement of the dural sinuses (black arrow), internal cerebral veins (white arrow), choroid plexus (blue arrow), and cortical arteries (red arrow)
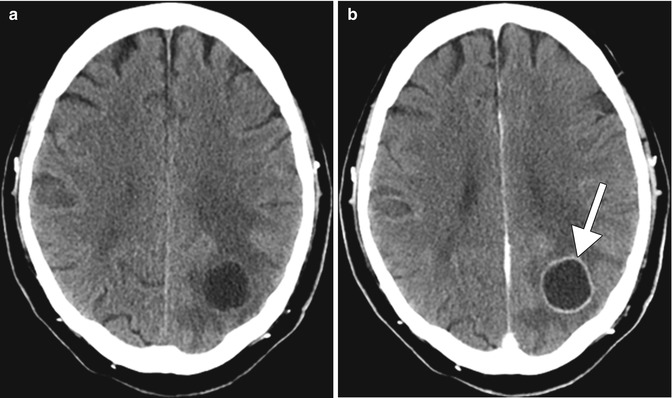
Fig. 12.2
Pre- and post-contrast CT showing a cerebral abscess. Axial pre- (a) and post-contrast CT (b) images show a thin rim-enhancing fluid collection with surrounding vasogenic edema in the left parietal lobe (arrow)
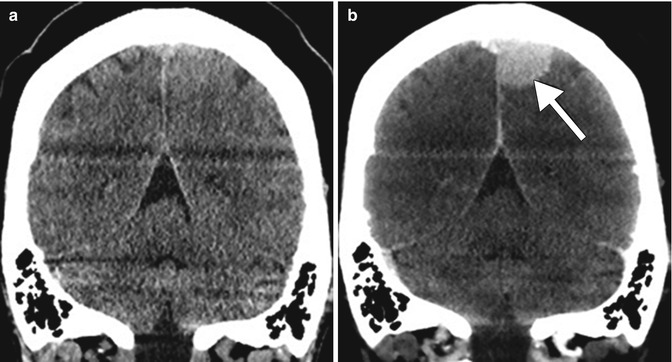
Fig. 12.3
Pre- and post-contrast CT showing a meningioma. Coronal pre- (a) and post-contrast (b) CT images show a homogeneously enhancing mass in the left parafalcine parietal convexity (arrow)
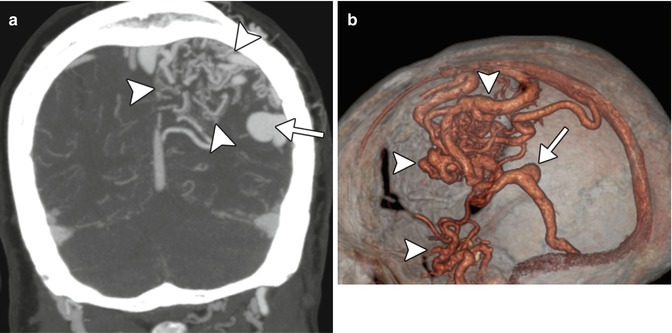
Fig. 12.4
CTA showing an arteriovenous malformation. Coronal CTA MIP (a) and 3D CTA volume rendered (b) images show a large nidus in the left cerebral hemisphere with associated high-glow aneurysm (arrow)
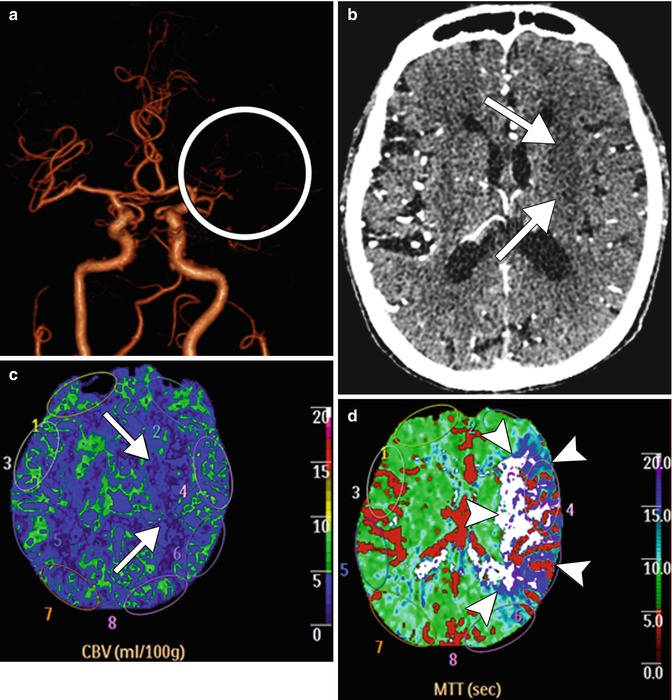
Fig. 12.5
CT perfusion showing acute ischemia. Frontal projection 3D volume rendered CTA image (a) shows absent opacification of the left MCA (circle). Axial CTA image (b) shows hypoattenuation within the left basal ganglia, which corresponds to an acute infarct (arrows). The corresponding CBV map (c) shows a perfusion defect in the left basal ganglia (arrows). However, the MTT map (d) shows a much larger area of prolonged transit time, indicating tissue at risk, but potentially salvageable (arrowheads)
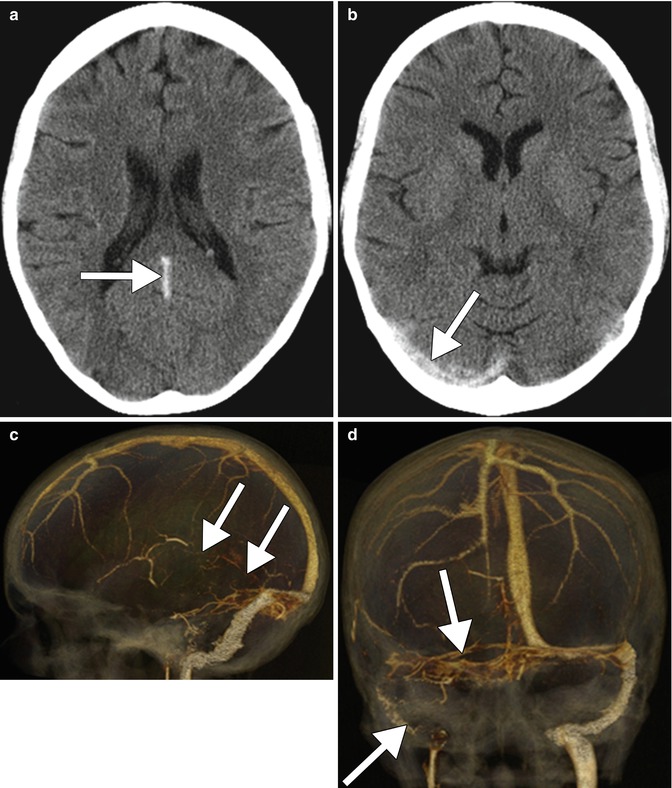
Fig. 12.6
CTV showing venous sinus thrombosis. Axial non-contrast CT images (a, b) show hyperattenuation within the straight and right transverse venous sinuses (arrows). Lateral (c) and frontal (d) projection 3D CTV volume rendered images show lack of opacification in the corresponding venous sinuses (arrows)
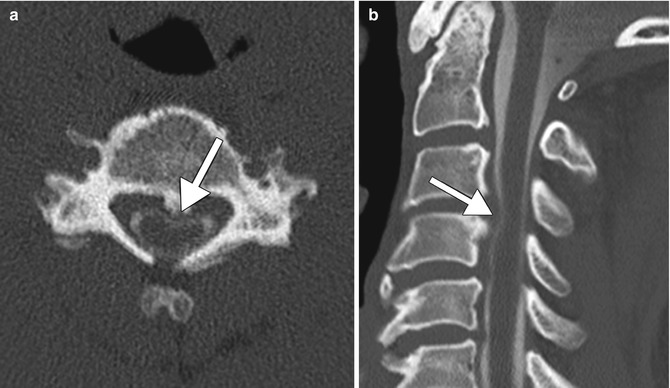
Fig. 12.7




CT myelogram. Axial (a) and sagittal (b) CT images show contrast material outlining a posterior disc-osteophyte complex (arrows) that impinges upon the cervical spinal cord
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








