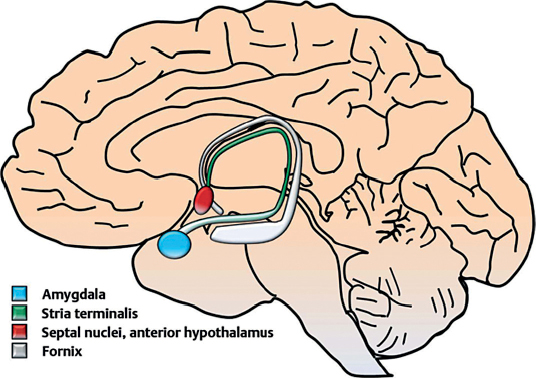
19 What is a unique feature of the circumventricular organ’s blood–brain barrier (BBB) capillaries? They are fenestrated (the BBB is essentially absent).1 What are the functions of the seven circumventricular organs? 1. Subfornical organ: role in regulation of bodily fluid1 2. Vascular organ of the lamina terminalis: may detect proteins and amino acids in the blood 3. Median eminence: hypothalamic-releasing hormones are produced and released here 4. Posterior lobe of pituitary (neurohypophysis): release of oxytocin and ADH 5. Subcommissural organ: function unknown2 6. Pineal gland: regulates circadian rhythms, releases melatonin 7. Area postrema: induces vomiting3 Which is the only paired circumventricular organ? The area postrema4 Above which structure does the anterior hypothalamus lie? Optic chiasm (known as the chiasmatic region of the hypothalamus) Which nuclei are contained within the anterior hypothalamus? Medial and lateral preoptic nuclei, supraoptic nucleus, lateral nucleus, paraventricular nucleus, anterior nucleus, suprachiasmatic nucleus Which nucleus is responsible for bodily temperature regulation? Anterior nucleus5 Which nuclei contain the magnocellular neurosecretory cells? Paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei contain large cells (magnocellular), which are responsible for the production and release of oxytocin and vasopressin, respectively. To which portion of the pituitary (hypophysis) do the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei project? Posterior pituitary Which anterior-region hypothalamic nucleus mediates circadian rhythms? Suprachiasmatic nucleus6 Which nuclei are contained within the posterior hypothalamus? Mammillary bodies, posterior nucleus, and lateral nucleus The posterior hypothalamic nucleus is continuous posteriorly with what midbrain structure? Periaqueductal gray matter Which nuclei are contained within the lateral tuberal hypothalamus? Lateral nucleus, lateral tuberal nuclei, and tuberomammillary nucleus Which nucleus is responsible for the sensation of hunger? Lateral nuclei Which nuclei are contained within the medial tuberal hypothalamus? Dorsomedial and ventromedial nuclei, arcuate (infundibular) nucleus Which nucleus is involved with the sensation of satiety? Ventromedial nucleus7 Which nucleus is involved with the rage response? Dorsomedial nucleus Which medial tuberal hypothalamic nucleus secretes small peptides known as hypothalamic-releasing and -inhibiting hormones? Arcuate nucleus and other median eminence nuclei Which vessel carries the hypothalamic-releasing and -inhibiting hormones from the median eminence to the anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)? The portal vein Which fibers are present in the stria terminalis? Efferent fibers from the amygdala to the septal nuclei and anterior hypothalamus and reciprocal projections from the hypothalamus to the amygdala Fig. 19.1 Sagittal view of stria terminalis.
Neuroendocrinology
19.1 Circumventricular Organs
19.2 Hypothalamus
19.2.1 Anterior
19.2.2 Posterior
19.2.3 Lateral
19.2.4 Medial
19.2.5 Hypothalamic Input/Output Pathways
Neuroendocrinology
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue

Full access? Get Clinical Tree






