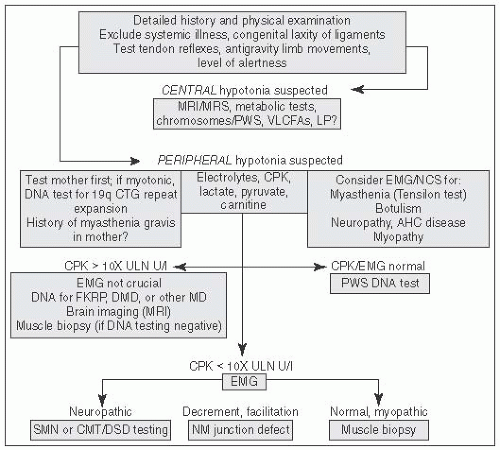
 FIGURE 6.1 Approach to Hypotonia. MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; MRS, magnetic resonance spectroscopy; PWS, prader willi syndrome; VLCFA, very long chain fatty acids; LP, lumbar puncture; AHC, anterior horn cell; CPK, creatine phosphokinase; CMT, Charcot Marie Tooth; DMD, Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy; DSD, Dejerine Sottas Disease; EMG, electromyography; NCS, nerve conduction studies; NM, Neuromuscular (From Perlman J, ed. Neonatology: Questions and Controversies. London, UK: Elsevier; 2012, with permission.) |
TABLE 6.1 Classification of Spinal Muscular Atrophies (SMA) | |
|---|---|
|
first 2 wk); (AMSAN) mildly reduced nerve conduction velocities combined with a marked reduction in motor and sensory action potential amplitudes; (3) serum: (AMAN) IgG reactivity to GM1, GD1a, and GD1b positive, GQ1b negative.
and external rotation at the shoulder, elbow flexion, supination at the wrist, and extension at the fingers (aka “waiter’s tip”). Klumpke palsy is less common (related to disruption at the C7, C8, and T1 nerve roots) and involves weakness of the intrinsic muscles of the hand and flexors of the wrist and fingers (aka “claw hand”). A supinated forearm with absent grasp reflex may be noted on exam. Involvement of the 1st thoracic root can result in an ipsilateral Horner syndrome. The phrenic nerve (arising from C3, C4, and C5) may also be affected and lead to ipsilateral diaphragmatic paralysis.