Fig. 1
Orexin and orexin receptors. a Structures of various species of orexin A and orexin B. The topology of the two intrachain disulfide bonds of orexin A is indicated above the sequence. Shadows indicate amino acid identity. Mammalian orexin A sequences thus far identified (human, rat, mouse, pig, dog, sheep, cow) are all identical. b Orexin A and orexin B are derived from a common precursor peptide, prepro-orexin. The actions of orexins are mediated via two G protein-coupled receptors named orexin-1 (OX1R) and orexin-2 (OX2R) receptors. OX1R is relatively selective for orexin A, whereas OX2R shows similar affinities for both orexin A and orexin B. OX1R is coupled to the Gq subclass of heterotrimeric G proteins, whereas OX2R couples to Gi/o and/or Gq in neuronal cell lines
Our structural analysis of purified peptides showed that orexin A is a 33-amino-acid peptide with an N-terminal pyroglutamyl residue, two intra-chain disulfide bonds, and C-terminal amidation. This structure is completely conserved among several mammalian species identified so far (human, rat, mouse, cow, sheep, dog and pig). Orexin B is a 28-amino-acid, C-terminally amidated linear peptide. There are several species differences in the structure of orexin B, although also highly conserved. The C-terminal half of orexin B is very similar to that of orexin A, whereas the N-terminal half is more variable.
An mRNA encoding the same precursor peptide was independently identified by de Lecea et al. as a hypothalamus-specific transcript (de Lecea et al. 1998), as described in detail in the separate chapter (de Lecea). They predicted that the transcript encoded a polypeptide precursor that is cleaved to form two neuropeptides, termed hypocretin-1 and hypocretin-2 (corresponding to orexin A and orexin B, respectively).
1.2 Orexin Receptors
Because an in vitro study suggested that orexin B has a much lower affinity to HFGAN72 than orexin A did, we had searched several EST data bases, and identified another subtype of orexin receptor, which we term orexin-2 receptor (OX2R), which appeared to have similar affinities to both orexin A and orexin B, and we re-named HFGAN72 as orexn-1 receptor (OX1R) (Fig. 1a). The actions of orexins are mediated via these two G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). OX1R has one-order-of-magnitude greater affinity for orexin A over orexin B. In contrast, OX2R binds both ligands with similar affinities (Sakurai et al. 1998) (Fig. 1b). OX1R and OX2R mRNAs exhibit a markedly different and basically complementary distributions, suggesting that these receptors have distinct physiological roles through different neuronal pathways (Marcus et al. 2001; Mieda et al. 2011). Recently, the structure of the human OX2R bound to suvorexant was solved using lipid-mediated crystallization (Yin et al. 2014). The structure revealed that suvorexant adopts a π-stacked horseshoe-like conformation and binds to the receptor deep in the orthosteric pocket, stabilizing extracellular salt bridges and blocking transmembrane helix motions necessary for activation. Signal transduction system and physiological roles of these receptors are discussed in a separate chapter by Mieda et al.
2 Orexin-Producing Neurons
2.1 Anatomical Feature of Orexin-Producing Neurons
We and others raised antisera for orexin, and examined histological characteristics of orexin-producing neurons. Numbers of orexin neurons are estimated to be around 3,000 in rat or mouse brains, or 70,000 in human brains (Peyron et al. 1998; Nambu et al. 1999). These neurons are found exclusively in the hypothalamic regions, including the lateral hypothalamic area (LHA), perifornical area, and posterior hypothalamus (PH) (Peyron et al. 1998; Nambu et al. 1999; Date et al. 1999) (Fig. 2). However, orexin-imunoreactive fibers were observed in the almost entire neuroaxis excluding the cerebellum (Peyron et al. 1998; Nambu et al. 1999; Date et al. 1999). Especially dens staining of fibers were found in the paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus, several regions of the hypothalamus, including arcuate nucleus, ventromedial hypothalamus, and posterior hypothalamus, and most notably, monoaminergic nuclei in the hypothalamic/brain stem regions, such as the locus coeruleus (LC) (containing noradrenergic neurons), raphe nuclei (containing serotonergic neurons), tuberomammillary nucleus (TMN) (containing histaminergic neurons), and laterodorsal and pedunculopontine tegmental nuclei (LDT/PPT) (containing cholinergic neurons) (Nambu et al. 1999; Date et al. 1999; Peyron et al. 2000). The distribution of the orexin receptor mRNA was consistent with these projection sites, with differential expression of each subtype; within the brain, OX1R is most abundantly expressed in the LC, while OX2R is highly expressed in the TMN (Marcus et al. 2001). Both regions are important for the maintenance of arousal (Marcus et al. 2001). The raphe nuclei, LDT/PPT, and ventral tegmental area (VTA) contain both OX1R and OX2R (Marcus et al. 2001), although they are expressed in distinct neuronal populations in each region (Mieda et al. 2011). These observations suggest that these monoaminergic regions, implicated in the regulation of wakefulness, are major effector sites of orexins.
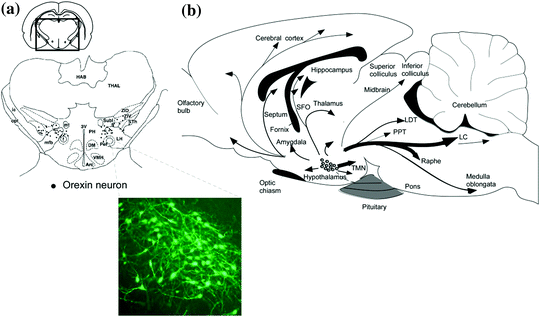

Fig. 2
Schematic drawing of coronal section and sagittal section of rat brain, summarizing the orexin neuronal system. a Prepro–orexin mRNA-containing neurons are shown in black superimposed upon anatomical structures of the hypo- and subthalamic areas. The rectangle designates the area schematized in the figure. Abbreviations: lateral hypothalamic area (LH), perifornical nucleus (PeF), posterior hypothalamic area (PH), subthalamic nucleus (Sth), subincertal nucleus (SubI), ventral zona incerta (ZIV). Additional landmarks include: thalamus (THAL), habenular complex (HAB), internal capsule (ic), optic tract (opt), mammillothalamic tract (mt), fornix (f), medial forebrain bundle (mfb), third ventricle (3V), arcuate hypothalamic nucleus (Arc), dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus (DM), and ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus (VMH). Inset shows immunostaining image of orexin neurons. b Orexin neurons are found only in the lateral hypothalamic area and project to the entire central nervous system. The thickness of arrows represents relative abundance of projections. Abbreviations: third ventricle (3V), fourth ventricular (4V), tuberomammillary nucleus (TMN), locus coeruleus (LC), laterodorsal tegmental nucleus (LDT), pedunculopontine nucleus (PPT)
In vivo recording studies revealed changes of orexin neuronal activity across the sleep-wake cycle in rats or mice (Mileykovskiy et al. 2005; Lee et al. 2005; Takahashi et al. 2008). Basically, orexin neurons fire during active waking, decrease discharge during quiet waking, and virtually cease firing during both rapid eye movement (REM) and non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. This firing pattern was consistent with earlier studies showing that Fos expression (a marker of neuronal activity) in orexin neurons in rats or mice is increased during the dark, active period in which the awake state is dominant (Estabrooke et al. 2001), and orexin levels in CSF peak during the dark period and decrease during the light period in which the sleep state is dominant (Yoshida et al. 2001).
2.2 Regulation of Orexin Neurons
2.2.1 Input and Output of Orexin Neurons
Orexin system is involved in the diverse functions. Knowledge about the regulatory mechanisms of orexin neurons is important for understanding the roles of orexin neurons in these functions (Fig. 3). Studies using anterograde and retrograde tracers suggest that orexin neurons receive abundant projections from the lateral septum, preoptic area, amygdala, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST), posterior/dorsomedial hypothalamus, and the raphe nuclei (Sakurai et al. 2005; Yoshida et al. 2006). Input and output of orexin neurons are described in detail in a chapter by Mochizuki.
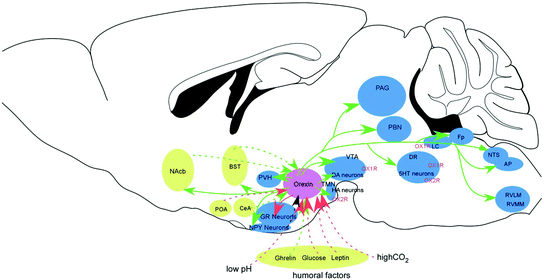

Fig. 3
Connections of orexin neurons with other regions. Orexin neurons in the lateral hypothalamic area (LHA) provide a link between the limbic system, energy homeostasis and the brain stem nuclei. Modified from Sakurai (2007). Circles show major target sites for orexins. Included in these are the locus coeruleus (LC, containing noradrenaline, NA), tuberomammillary nucleus (TMN, containing histamine, HA), raphe nuclei (Raphe, containing 5-HT), ventral tegmental area (VTA, containing dopamine, DA), and laterodorsal/pedunclopontine tegmental nuclei (PPT/LDT, containing acetylcholine, Ach). Orexin neurons promote wakefulness through the monoaminergic/cholinergic nuclei that are wake-active. Connection between dopaminergic centers and orexin neurons plays to modulate the reward systems. Input from the limbic system might be important to regulate the activity of orexin neurons upon emotional stimuli to evoke emotional arousal or fear-related responses. Sleep-active neurons in the POA send inhibitory influences to monoaminergic/cholinergic neurons and orexin neurons. Orexin neurons send both direct excitatory input to cholinergic neurons in the LDT/PPT and indirect inhibitory input to these cells through GABAergic local interneurons and GABAergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars reticulata (Takakusaki et al. 2005). Noradrenergic neurons in the LC and serotonergic neurons in the RN also send inhibitory influences to these cholinergic neurons. Blood glucose levels also affect the activity of orexin neurons through fluctuations of glucose levels in the CSF and vagal afferent. NAc nucleus accumbens; PVH paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus; TMN tuberomammilary nucleus; LHA lateral hypothalamic area; DMH dorsomedial hypothalamus; ARC arcuate nucleus; VTA ventral tegmental area; SN substantia nigra; SCN suprachiasmatic nucleus; RN raphe nucleus; LC locus coeruleus; PPT pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus; LDT laterodorsal tegmental nucleus
Abundant input from the limbic system suggests it plays a part in the regulation of the firing rate of orexin neurons by conveying emotive factors to maintain arousal. The limbic input to orexin neurons might also be involved in the regulation of feeding behavior, because some of the affective content of the perception of food is thought to be processed in the amygdala and limbic system (Berthoud 2004). Interestingly, it is well known that food perception often evokes cataplexy in narcoleptic dogs (Reid et al. 1998), suggesting that orexin signaling is activated upon perception of food, and that this system is necessary to evoke normal feeding behavior.
Orexin neurons also receive abundant input from the preoptic area (POA), which is thought to play an important role in initiation and maintenance of sleep. This connection seems to be important for silencing orexin neurons during sleep (Saito et al. 2013).
2.2.2 Factors that Influence Firing of Orexin Neurons
In vitro electrophysilogical studies identified a number of factors that affect activity of orexin neurons (Table 1). In addition to the classical aminoacid neurotransmitters, glutamate and GABA, several factors were shown to influence the activity of orexin neurons. Both noradrenaline and serotonin inhibited orexin neurons through the activation of G protein-regulated inwardly rectifying K+ (GIRK or Kir3) channels via α2-adrenoceptors and 5HT1A-receptors, respectively (Li et al. 2002; Yamanaka et al. 2003b, 2006). The cholinergic agonist carbachol activated 27 % and inhibits 6 % of orexin neurons (Sakurai et al. 2005; Yamanaka et al. 2003b), whereas histamine had little effect on orexin neurons. Although orexin neurons do not express functional dopamine receptors, dopamine inhibited orexin neurons by acting through α2-adrenoceptors (Yamanaka et al. 2003b, 2006). Several neuropeptides, including cholecystokinin (CCK-8S), neurotensin, oxytocin, and vasopressin, induced depolarization and excitation of orexin neurons (Tsujino et al. 2005). A synthetic surrogate ligand for an orphan receptor, BRS-3, also directly activated these neurons, although it also inhibits orexin neurons through activation of GABAergic interneurons (Furutani et al. 2010). Orexin itself was also shown to activate orexin neurons through OX2R, suggesting a positive feedback mechanism that maintain orexin neuronal activity (Yamanaka et al. 2010). Similarly, neurotensin was shown to co-localize with orexin neurons and excites orexin neurons (Furutani et al. 2013).
Table 1
Factors that influence activity of orexin neurons
Excitation | Receptor involved |
|---|---|
Glutamate | AMPAR, NMDAR mGluRs |
Acetylcholine (muscarinic) (27 %) | M3 |
Orexin | OX2R |
Ghrelin | GHSR |
Cholecystokinin | CCKA |
Neurotensin | NTSR2 (unpublished data) |
Vasopressin | V1a |
Oxytocin | V1a |
Glucagon-like peptide 1 | ND |
Corticotropin-releasing factor | CRFR1 |
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone | TRH1 |
BRS3 agonist | BRS3 |
ATP | P2X |
H+ | ASIC1a |
CO2 | ND |
Mixture of amino acids | System-A amino acid transporters |
Inhibition | |
Glucose | Unknown |
GABA | GABAA, GABAB |
Glycine | Glycine receptor |
Serotonin | 5HT1A |
Noradrenaline | α2 |
Dopamine | α2 |
Acetylcholine (muscarinic) (6 %) | ND |
Neuropeptide Y | Y1 |
Enkephalin | μ opioid-R |
Nociceptin | NOPR |
Leptin | Ob-R |
Adenosine | A1 |
BRS3 agonist | BRS3 |
Interestingly, metabolic signals also seem to contribute to the regulation of orexin neurons. Decreasing the extracellular glucose concentration produced depolarization and increased the frequency of firing of orexin neurons, whereas increasing glucose concentration induced hyperpolarization and cessation of firing (Yamanaka et al. 2003a; Burdakov et al. 2005). Importantly, this mechanism is sensitive enough to monitor variations in glucose levels in cerebrospinal fluid reflecting those occurring physiologically between normal meals (Burdakov et al. 2005). These responses were shown to be mediated by tandem-pore K+ (K2P) channels (Burdakov et al. 2006).
In addition, a gut/stomach-derived hormone, ghrelin activated 60 % of dispersed orexin neurons with depolarization and an increase in firing frequency (Yamanaka et al. 2003a). By contrast, bath-application of leptin, an anorexigenic protein hormone secreted by adipocytes, was found to robustly inhibit most of the orexin neurons examined, causing hyperpolarization and a decrease in firing rate (Yamanaka et al. 2003a). These findings show that peripheral humoral factors that are related to energy metabolism influence the activity of orexin neurons (Sakurai et al. 1998; Yamanaka et al. 2003a; Willie et al. 2001). The ability of orexin neurons of sensing metabolic signals might play an important physiological role in the regulation of feeding behavior. This suggests that negative energy balance activates orexin neurons to increase arousal, thereby reinforcing food-seeking/feeding pathways. Consistently, orexin neurons-ablated mice failed to exhibit this fasting-induced arousal (Yamanaka et al. 2003a), suggesting that orexin neurons are necessary for evoking adaptive behavioral arousal during fasting. The mechanism that helps to ensure survival in nature clearly involves orexins. As discussed later, motivation toward food might also activate orexin neurons when animals are fasted.
3 Physiological Functions of Orexins
3.1 Orexin and Feeding
We initially reported orexins as factors that is involved in the regulation of feeding behavior (Sakurai et al. 1998). Orexin neurons are bilaterally and synmetorically distributed within the LHA and adjacent regions (Sakurai et al. 1998). The LHA has been thought to be the “feeding center”, because lesions in this region caused anorexia, whereas electrical stimulation resulted in overeating and obesity in rats (Anand and Brobeck 1951). Indeed, we found an orexigenic effect of intracerebroventricular (icv) administration of orexin A and orexin B in rats (Sakurai et al. 1998), and this effect was subsequently confirmed in several species (Sakurai 2007b). Furthermore, central administration of an orexin antibody or an OX1R antagonist have been shown to decrease food intake (Yamada et al. 2000; Haynes et al. 2000a).
Intraperitoneal administration of the selective OX1R antagonist (1-SORA) SB-334867 or RNAi-mediated knockdown of the orexin gene reduced food intake in mice exposed to mild food restriction (Sharf et al. 2010a), and orexin-deficient mice showed decreased food intake (Willie et al. 2001; Hara et al. 2005). However, importantly, orexin signaling increases not only food intake but also energy expenditure, and a decrease in the overall orexin tone generally results in obesity (Funato et al. 2009; Hara et al. 2001). This is consistent with the findings that human narcolepsy patients show increased incidence of obesity (Hara et al. 2001). The role of orexins in body weight regulation is discussed in a separate chapter of this volume (Funato).
The orexin system may contribute to the regulation of energy homeostasis by integrating information regarding metabolic state and regulating wakefulness to support feeding behavior (Yamanaka et al. 2003a; Mieda and Sakurai 2012; Sakurai and Mieda 2011). Indeed, mice lacking orexin neurons do not show an increase in wakefulness or locomotor activity in response to starvation, unlike wild-type mice (Yamanaka et al. 2003a). Moreover, prepro–orexin mRNA is upregulated in fasted animals (Sakurai et al. 1998) and several studies reported that the firing rates of orexin neurons are influenced by glucose, triglycerides and amino acids (Yamanaka et al. 2003a; Burdakov et al. 2005b; Venner et al. 2011; Chang et al. 2004; Karnani et al. 2011). Orexin neurons were also shown to be innervated by neurons in the arcuate nucleus (which are primary sensors for plasma leptin levels) (Elias et al. 1998), and they are directly inhibited by leptin and excited by ghrelin (Yamanaka et al. 2003a). Together, these observations suggest that orexin neurons sense the animal’s metabolic and nutritional status through both direct and indirect pathways, and integrate it in order to evoke a level of arousal necessary to promote food-seeking behavior in response to negative energy balance. In addition, motivation toward food might also contribute to activate orexin neurons.
As already mentioned, one of the possible mechanisms by which orexins promote feeding is that these factors increase arousal to secure feeding behavior. However, although the OX2R is thought to be a major player in the regulation of wakefulness, the studies using 1-SORA SB-334867 pointed to the importance of OX1R in the regulation of food seeking (Sharf et al. 2010a; Haynes et al. 2000b). This suggests that the orexin system influences food intake and wakefulness through at least partially different receptors and pathways.
Orexins might also directly affect the neuronal circuits in the hypothalamus that are implicated in the regulation of feeding behavior. They inhibit glucoreceptor neurons in the ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH), and excite neuropeptide Y (NPY) neurons in the arcuate nucleus and melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) neurons in the LHA (van den Pol et al. 2004; Shiraishi et al. 2000; Yamanaka et al. 2000). Local injection of orexin in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN), DMH or LHA increased food intake in rats (Dube et al. 1999; Thorpe et al. 2003; Sweet et al. 1999). The area postrema and nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) were also shown to be involved in orexin-mediated feeding (Baird et al. 2009; Thorpe and Kotz 2005). Together, orexin is likely to promote feeding by influencing multiple elements of the feeding circuitry.
Orexin-mediated feeding seems to be closely related with the reward system, in which OX1R has been also shown to be involved (Sharf et al. 2010a; Harris et al. 2005b; Choi et al. 2010). In rats, orexin increased the motivation to food-seeking when administered icv, especially for palatable food (Borgland et al. 2009, 2010; Thorpe et al. 2005). Furthermore, feeding behavior induced by administration of the mu-opioid receptor agonist DAMGO (D-Ala(2)-N-MePhe(4)-Gly-ol(5)-enkephalin) into the shell of the nucleus accumbens (NAc) was dependent on OX1R activation (Zheng et al. 2007), and intraperitoneal injection of the 1-SORA SB-334867 reduced high-fat food intake in food-restricted rats (Choi et al. 2010; Borgland et al. 2009; Nair et al. 2008).
A recent study showed that the number of Fos-immunoreactive orexin neurons in the hypothalamus increased in response to a chow-predictive (that is, conditioned) cue in rats (Petrovich et al. 2012). Similarly, the expectation of receiving a palatable food like chocolate increased numbers of Fos-positive hypothalamic orexin neurons (Choi et al. 2010). Numbers of Fos-positive orexin neurons in the LHA were increased after conditioned place preference training for a sweet cereal reward in rats (Harris et al. 2005a). Together, these findings indicate that orexin plays a role in food pursuit, especially when motivation towards food is high (e.g., when an animal is food-deprived or when foods are palatable), or when reward-conditioned cues are present. Input from the limbic system and NAc, which are thought to process the affective content of the perception of food (Berthoud 2004), might be involved in this function. Notably, food-related cues often evoke cataplexy in narcoleptic dogs (which are defective in orexin signaling) (Reid et al. 1998), suggesting that the perception of food normally induces orexin signaling, and that this signaling is necessary to elicit feeding behavior, including the maintenance of motor activity and wakefulness. Collectively, orexin neurons are likely to be excited by food-related cues and/or a low energy balance through neuronal connections with the limbic system and by factors that indicate a low energy balance to ensure feeding behavior.
3.2 Orexin and Wakefulness
The importance of orexins in the maintenance of wakefulness was highlighted by the findings that showed the involvement of the dysfunction of orexin signaling in a sleep disorder, narcolepsy. Clues that revealed the dysfunction of orexins are involved in narcolepsy initially came from animal models (Chemelli et al. 1999; Lin et al. 1999) (see other chapters). The link between orexin signaling and narcolepsy was subsequently supported by studies with human patients (Peyron et al. 2000; Thannickal et al. 2000).
Narcolepsy is a debilitating neurological disorder that affects approximately 1 in 2,000 individuals in the United States (Mignot 1998). A cardinal symptom of the disorder is excessive daytime sleepiness (an insurmountable urge to sleep), which often results in falling asleep at inappropriate times and situations (‘sleep attack’). The latency for rapid eye movement (REM) sleep is notably reduced in narcolepsy patients, and the existence of ‘sleep-onset REM periods’ (i.e. REM-sleep is directly preceded by an awake period) is one of the diagnostic criteria for narcolepsy. Nocturnal sleep is also often disturbed by nocturnal wakening combined with the occurrence of hypnagogic hallucinations, vivid dreaming, and sleep paralysis. Narcolepsy patients often suffer from a condition called “cataplexy”, which is a sudden weakening of muscle tone, ranging from jaw dropping and speech slurring to complete bilateral collapse of the postural muscles. Cataplexy is usually triggered by emotional stimuli. Unlike the sleep attack, consciousness is preserved during cataplexy.
A postmortem study of human narcoleptic brains showed no detectable levels of orexin peptides in the cortex and pons, in which normally orexinergic projections are found. In the hypothalamus, an 80–100 % reduction in the number of neurons containing detectable prepro–orexin mRNA or orexin-like immunoreactivity were found (Peyron et al. 2000; Thannickal et al. 2000). More than 90 % of patients with narcolepsy are shown to have decreased orexin A levels in the cerebrospinal fluid (Mignot et al. 2002). Relationship between orexin deficiency and narcolepsy is described in detail in other chapters (Nishino, Kanbayashi).
As already discussed, the projection pattern of orexin neurons and distributions of orexin receptor mRNAs suggested that main effector sites for orexin are monoaminergic/cholinergic neurons in the brainstem, and electrophysiological experiments also showed that firing rates of monoaminergic cells in these nuclei are increased by orexins. For instance, noradrenergic cells of the LC (Hagan et al. 1999; Horvath et al. 1999), dopaminergic cells of the VTA (Nakamura et al. 2000), serotonergic cells of the dirsal raphe (DR) (Liu et al. 2002; Brown et al. 2002), and histaminergic cells in the TMN (Yamanaka et al. 2002) were all shown to increase their firing rates by orexins. The firing rates of these monoaminergic neurons are well known to be associated with sleep/wakefulness states. They fire tonically during awake period, less during NREM sleep, and cease firing during REM sleep (Vanni-Mercier et al. 1984), displaying similar firing patterns with orexin neurons. These observations suggest that firing of these wake-active monoaminergic neurons mediates arousal are supported by orexins. Orexin neurons also project directly to the LDT/PPT, which contain cholinergic neurons. Some populations of these cholinergic neurons are implicated in the maintenance of wakefulness and REM sleep (W/REM-on neurons) (Shouse and Siegel 1992), whereas other populations are implicated in desynchronization of cerebral cortex and muscle atonia during REM sleep (REM-on neurons) (Shouse and Siegel 1992). Pharmacologically, a direct injection of orexin A into the LDT of cats results in an increased awake time and a decreased REM sleep time (Xi et al. 2001). In addition, several reports have shown that orexin induces long-lasting excitation of cholinergic neurons in the LDT (Takahashi et al. 2002). However, recent work also showed that orexin A inhibits cholinergic neurons in the PPT via activation of GABAergic local interneurons and GABAergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars reticulate (SNr), which send inhibitory projections to the PPT (Takakusaki et al. 2005). Since orexins show strong inhibitory effects on REM sleep, the indirect inhibition of cholinergic neurons of orexin might play an important role during REM sleep. In fact, we found robust expression of OX1R in the cholinergic neurons, and both receptor expressions in GABAergic neurons in these regions (Mieda et al. 2011). Collectively, these results indicate that in the LDT/PPT, orexin may directly activate W/REM-on cholinergic neurons through OX1R to facilitate wakefulness. Simultaneously, orexin is likely to activate GABAergic interneurons through both receptors to inhibit REM-on cholinergic neurons. Additionally, orexinergic activations of wake-active noradrenergic and serotonergic neurons in the LC and raphe nuclei, respectively, are likely to counteract activation of REM-on cholinergic neurons in the LDT/PPT during wakefulness (Sakurai 2007a; Pace-Schott and Hobson 2002). This is consistent with the fact that tricyclic antidepressants and serotonin-specific reuptake inhibitors are effective for treating cataplexy in narcoleptic patients.
Recent optogenetic studies revealed that orexin neurons are also glutamatergic (Schone et al. 2014). Glutamate-mediated fast and orexin-mediated slow neurotorasmission make it possible for orexin neurons to convert signals into transient and sustained signals in the same postsynaptic target neurons. The downstream pathways of orexin receptor-expressing neurons are described in more detail in a separate chapter (Mieda).
3.3 Orexin and Reward/Addiction
Besides feeding and arousal, orexin system also plays an important role in the reward system. The reward system is closely related to both feeding and wakefulness. Cues and contexts associated with rewards, including food, sex and drugs, increase the number of Fos-positive orexin neurons and prepro–orexin mRNA levels (Sakurai et al. 1998; Harris et al. 2005a; Di Sebastiano et al. 2011; Cason et al. 2010). Orexin neurons send dense projections to the ventral tegmental area (VTA), in which dopaminergic neurons that send innervations to the NAc are localized (Yoshida et al. 2006) (Fig. 2). The NAc in turn sends projections to orexin neurons, constituting a reciprocal link. Intracerebroventricular injection of orexins or local administration into the VTA can reinstate previously-extinguished drug-seeking or food-seeking behaviour in rodents (Boutrel et al. 2005; Harris et al. 2005a), and orexin neurons are activated during the behavioural expression of preferences for cues associated with reward (Harris et al. 2005a). The VTA expresses both OX1R and OX2R (Marcus et al. 2001), with dopaminergic neurons predominantly expressing OX1R, and orexin signaling in the VTA has been implicated in reinforcement and reward-related processes via actions on VTA dopamine neurons (Balcita-Pedicino and Sesack 2007) (Fig. 3).
An increasing body of work shows that orexin neurons also play a part in the behavioural presentation of addiction to drugs including cocaine, amphetamine, morphine, heroin, nicotine, ethanol and cannabinoids (Espana et al. 2011; Mahler et al. 2012; Martin-Fardon and Boutrel 2012). Generally, orexin seems to be involved in the modulation of highly-motivated reward seeking, especially when this seeking is triggered by external cues that are conditioned with the rewards. Although the 1-SORA SB-334867 did not affect the expression of cocaine and amphetamine-sensitization in animals tested immediately after training (Borgland et al. 2006), it blocked the expression of sensitization after a period of abstinence following amphetamine sensitization training, as did the DORA almorexant (Quarta et al. 2010; Winrow et al. 2010). This suggests that the OX1R is involved in the acquisition of sensitization. In another example, the 1-SORAs SB-334867 and GSK-1059865 attenuated the expression of cocaine and amphetamine-induced conditioned place preference in rats (Gozzi et al. 2011; Hutcheson et al. 2011; Sartor and Aston-Jones 2012).
Importantly, neither orexins nor their receptor antagonists affect self-adminstration of addictive drugs such as cocaine in rodents (Espana et al. 2010, 2011; Hutcheson et al. 2011), suggesting that orexins have no major role in the reinforcing or the priming effects of cocaine. However, orexin A has been shown to promote motivation in a study using rats in which high levels of effort were required for seeking addictive drugs in self-administration paradigms (Borgland et al. 2009). These results suggested that orexins plays an essential role in reward-seeking not by influencing the primary reinforcing or priming effects of rewards, but by supporting motivated behavior. Intraperitoneal injections or intra-VTA administration of the 1-SORA SB-334867 blocked reinstatement of cocaine seeking elicited by either discrete cues or contextual stimuli in rats (Smith et al. 2009, 2010; James et al. 2011), whereas intraperitoneal injection of the 2-SORA 4-PT did not affect cue-induced reinstatement (Smith et al. 2009). These observations suggest that orexin neurons might be activated by external reward-related stimuli and then send information to the VTA to induce reinstatement through the activation of OX1R.
Orexins also seem to play a role in addiction to drugs other than cocaine and amphetamine. For example, Fos expression was increased in orexin neurons in rats following acute nicotine administration or nicotine withdrawal (Pasumarthi et al. 2006; Plaza-Zabala et al. 2013), and nicotine withdrawal was decreased in orexin knockout mice (Plaza-Zabala et al. 2013). Prior intraperitoneal administrations of the 1-SORA SB-334867, but not the 2-SORA TCSOX229, attenuated nicotine withdrawal (Plaza-Zabala et al. 2013), as did intra-PVN infusion of the 1-SORA SB-334867 (Plaza-Zabala et al. 2013). Moreover, systemic administration of the DORA almorexant or the 1-SORA SB-334867 reduced nicotine self-administration (Hollander et al. 2008; LeSage et al. 2010).
Orexin knockout mice and wild-type mice that received the 1-SORA SB-334867 show reduced morphine withdrawal responses (Sharf et al. 2010a, b; Georgescu et al. 2003), suggesting that orexin may also be involved in opiate addiction. Furthermore, intraperitoneal injection of the 1-SORA SB-334867 reduced the expression of morphine-induced conditioned place preference in rats and mice (Harris et al. 2005a; Sharf et al. 2010b). Similarly, a report showed that orexin-deficient mice did not show morphine-induced conditioned-place preference and hyperlocomotion (Narita et al. 2006), although this finding is argued in another study (Sharf et al. 2010b). Action of orexin in the VTA is important for the expression of morphine-induced conditioned place preference (Richardson and Aston-Jones 2012). Moreover, in contrast with the lack of effect of the 1-SORA SB-334867 on cocaine self-administration, intraperitoneal delivery of the 1-SORA SB-334867 reduced heroin self-administration (Smith and Aston-Jones 2012).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







