Other cranial nerves
Face, motor and sensory
Trigeminal nerve (5th)
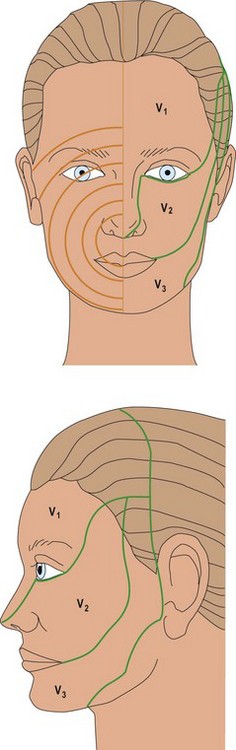
Facial sensation is supplied by the trigeminal nerve (Fig. 1), which has three branches:
2. The maxillary, supplying the cheek to the angle of the jaw and the inner aspect of the mouth and upper palate.
Facial nerve (7th)
Look at the patient’s face for asymmetries. Compare the blink rate.
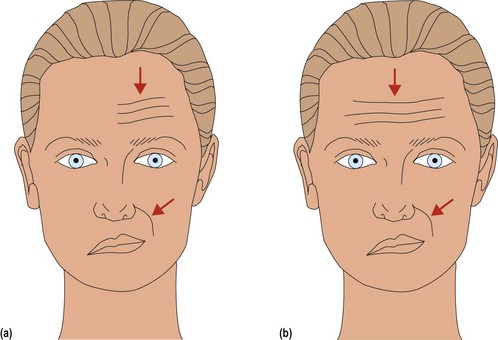
To test facial nerve function, ask the patient to look up at the ceiling (look at the frontalis), screw up the eyes (look at the orbicularis oculi), to whistle and show the teeth. Three patterns of abnormality are seen (Fig. 2):
1. Lower motor neurone (LMN) 7th: all facial muscles are affected. If severe, the patient is unable to close the eye and the eye is seen to roll up on attempted closure (Bell’s phenomenon) (common cause is Bell’s palsy; see Box 1). Reduced blink rate.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree