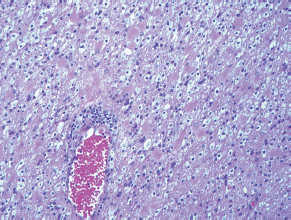
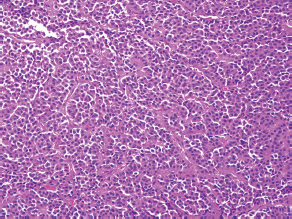
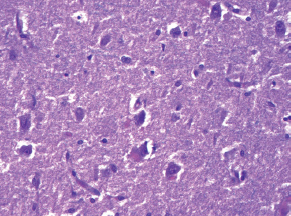
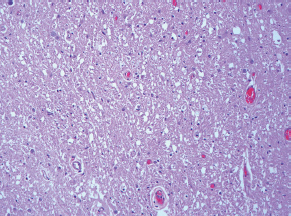
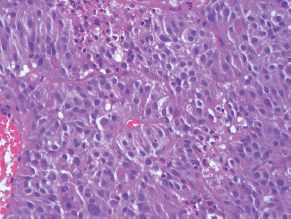
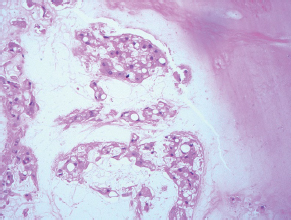
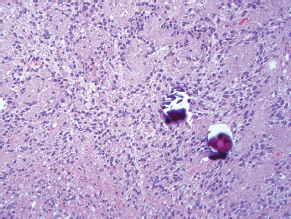
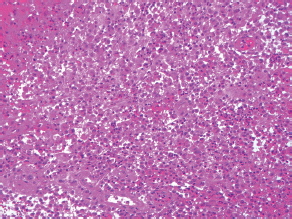
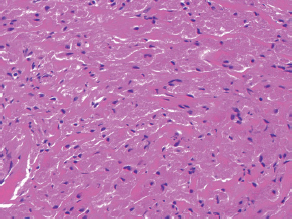
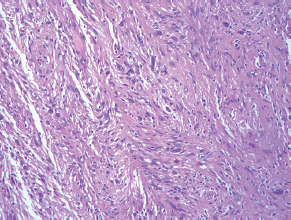
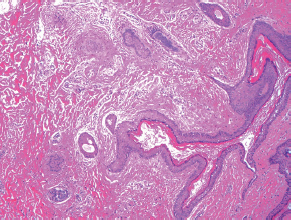
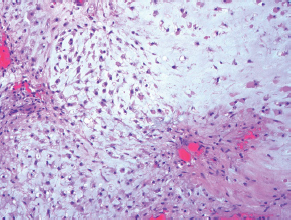
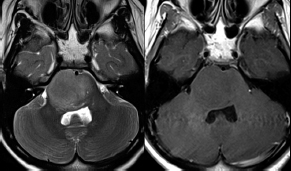
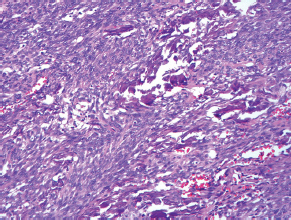
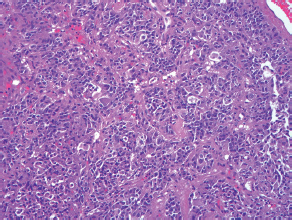
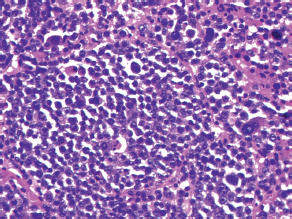
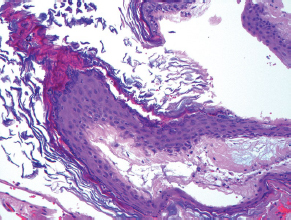
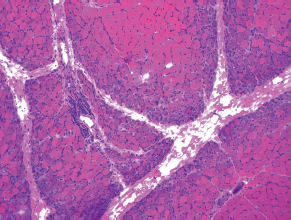
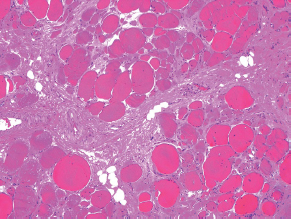
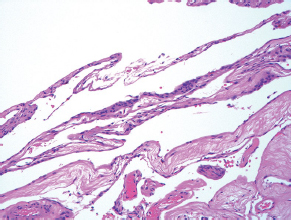
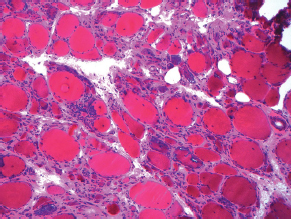
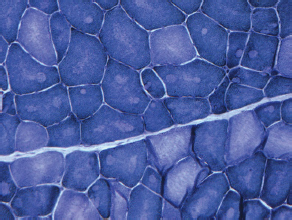
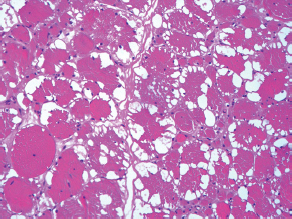
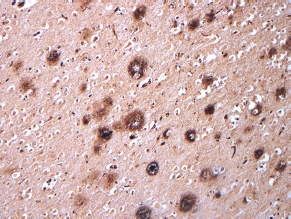
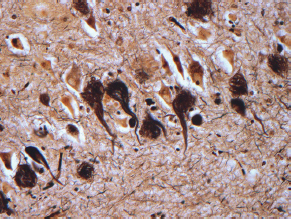
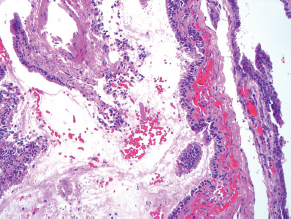
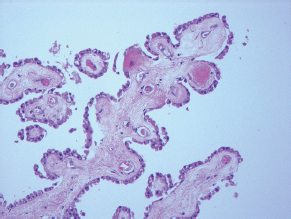
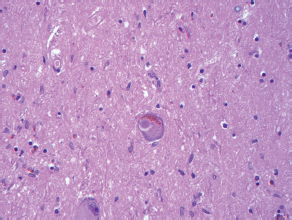
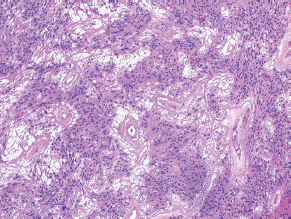
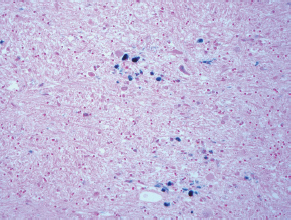
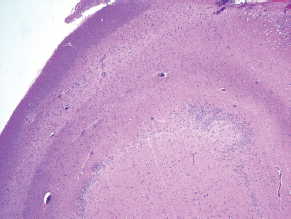
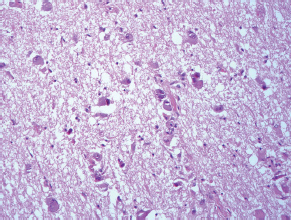
7Pathology/Histology In cerebral amyloid angiopathy, what typically occurs with respect to the basal membrane and the internal elastic lamina of the affected vessels? A. The basal membrane thins, and the internal elastic lamina thickens. B. The basal membrane thickens, and the internal elastic lamina fragments. C. The basal membrane fragments, and the internal elastic lamina thickens. D. The basal membrane is unaffected, and the internal elastic lamina fragments. E. The basal membrane thickens, and the internal elastic lamina is unaffected. This image shows a specimen from cerebral white matter. What is the underlying pathology? A. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease B. Multiple sclerosis C. Subacute infarction D. Sarcoidosis Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors commonly have what set of immunohistochemical features? A. Alterations in chromosome 17, S-100, and nestin B. Alteration in chromosome 22, GFAP, and CD10 C. Alterations in chromosome 6, vimentin, MIB-1 D. Alterations in chromosome 4, AFP, and CD20 E. Alterations in chromosome 18, HCG, and desmin A pathologist reports that a resected mass displays basophilic psammoma bodies with mesenchymal and epithelial cells that stain for vimentin and epithelial membrane antigen. Dural feeders in a sunburst pattern were noted in the lesion on preoperative angiogram. What is the likely pathology? A. Dural arteriovenous fistula B. Arteriovenous malformation C. Meningioma D. High-grade glioma E. Hemangioblastoma What type of craniopharyngioma occurs in children, and with what type of keratin is it typically associated? A. Adamantinomatous; dry B. Adamantinomatous; wet C. Papillary; dry D. Papillary; wet E. Both adamantinomatous and papillary; dry The most common neurologic manifestation of HIV infestation is: A. Toxoplasmosis B. Primary central nervous system lymphoma C. AIDS dementia complex D. Encephalitis E. Vacuolar myelopathy What neurotoxic agent is responsible for causing primarily a myelinopathy? A. Amiodarone B. Bismuth C. Lead D. Mercury E. Methanol What type of hematoma occurs in the loose connective tissues of the scalp that may cross sutures, may require blood transfusions, and does not calcify? A. Subgaleal hematoma B. Subperiosteal hematoma C. Subdural hematoma D. Temporalis contusion A 43-year-old patient presents with a large, enhancing mass with a necrotic center with mass effect and significant vasogenic edema. Following resection, histology demonstrated neovascularization with endothelial proliferation and pseudopalisading around areas of necrosis. Histopathology was significant for a TP53 mutation. What is the most likely diagnosis? A. Primary glioblastoma B. Secondary glioblastoma C. Rhabdoid meningioma D. Medulloblastoma E. Chordoma What syndrome is associated with tumors in the optic/visual pathways with histology demonstrating Rosenthal fibers? A. Von Hippel-Lindau B. Neurofibromatosis type 1 C. Neurofibromatosis type 2 D. Tuberous sclerosis E. Sturge-Weber The sellar mass shown in this image, if hormonally active, most likely secretes: A. Adrenocorticotrophic hormone B. Follicle-stimulating hormone C. Growth hormone D. Prolactin E. Vasopressin The eosinophilic cytoplasmic inclusion shown in this image of a patient with Alzheimer disease represents what histological entity? A. Amyloid body B. Granulovacuolar degeneration C. Hirano body D. Lewy body E. Neurofibrillary tangle A 65-year-old man has diffuse muscle wasting with spasticity, slowed movements, and muscle cramping. The section shown in this image was taken from the anterior horn cell region of the lumbar spinal cord. The most likely diagnosis is: A. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis B. Multiple system atrophy C. Spinal muscular atrophy type 1 D. Spinal muscular atrophy type 2 E. Syphilis A germinal matrix hemorrhage with intraventricular hemorrhage and ventricular enlargement represents what grade of lesion? A. Grade 1 B. Grade 2 C. Grade 3 D. Grade 4 E. Grade 5 Small, round, eosinophilic neuronal cell inclusions known as Bunina bodies are associated with what disease? A. Alzheimer disease B. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis C. Huntington chorea D. Machado-Joseph disease E. Olivopontocerebellar atrophy of Menzel A bruise of the skin and underlying tissue on the scalp with hemorrhage defines a(n): A. Abrasion B. Avulsion C. Contusion D. Laceration E. Scrape What immunohistochemical profile is most consistent with metastatic melanoma, shown in this image? A. Epithelial membrane antigen and cytokeratin AE1/3 positivity B. Glial fibrillary acidic protein and S-100 protein positivity C. Melan-A and HMB-45 positivity D. S-100 protein and progesterone receptor positivity E. TTF-1 and synaptophysin positivity The neoplasm shown in this image arises from what cellular origin? A. Chondrocytes B. Ependymal cells C. Epithelial cells D. Nevoid cells E. Notochord remnants A biopsy is taken targeting a midline mass. The frozen section appearance of the biopsy is shown in this image. The best diagnosis for the frozen section is: A. Normal hypothalamus B. Normal neurohypophysis C. Normal pineal gland D. Optic chiasm E. Pilocytic astrocytoma This fontal convexity mass shown in this image is thought to represent an eosinophilic granuloma. The best stain to prove that the macrophage cells are Langerhans histiocytes is one staining: A. CD1a B. CD15 C. CD45RB D. CD68 E. HAM56 The paraspinal soft tissue mass shown in this image was diagnosed as a granular cell tumor. The granular quality of the cytoplasm is due to an increased number or amount of: A. Endoplasmic reticulum B. Lysosomes C. Mitochondria D. Neurofilaments E. Ribosomes The cerebellopontine angle mass shown in this image is associated with alterations in what gene? A. NF2 B. TP53 C. PTEN D. SOD1 E. TSC2 What type of metastatic brain tumor generally is considered radiosensitive to whole brain radiation therapy? A. Thyroid B. Renal C. Melanoma D. Breast E. Sarcoma A 32-year-old man with mental retardation and a history of seizures presents for resection of a tumor associated with hydrocephalus. Histology shows fibrillary areas alternating with large cells containing generous amounts of eosinophilic cytoplasm. On what chromosome(s) can abnormalities associated with this disease be found? A. Chromosome 17p B. Chromosomes 9q and 16p C. Chromosomes 1p and 19q D. Chromosomes 3q, 7q, and 7p E. Chromosome 15 The lesion shown in this image is best classified as a(n): A. Craniopharyngioma B. Colloid cyst C. Dermoid cyst D. Endodermal cyst E. Epidermoid cyst The tumor shown in this image represents what pathology? A. Chondroma B. Chondrosarcoma C. Chordoid meningioma D. Chordoma E. Teratoma A 7-year-old previously healthy girl presented with progressive ataxia and palsy of cranial nerves VI and VII. Representative scans from an MRI study are shown in these images. What is a characteristic of this entity? A. There is a high incidence of distal metastases. B. Hydrocephalus is an early complication. C. Most pontine tumors have high-grade histology. D. Calcifications frequently are identified. The dural-based, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) negative mass shown in this image represents a(n): A. Chondrosarcoma B. Gliosarcoma C. Hemangiopericytoma D. Metaplastic meningioma E. Osteosarcoma On the histological level, the morphological changes of hypoxic ischemia typically are first observed how soon after the precipitating event? A. 3 hours B. 6 hours C. 12 hours D. 36 hours E. 48 hours The chromogranin positive staining mass shown in this image is most likely to arise in what location? A. Cerebellum B. Filum terminale C. Frontal lobe D. Lateral ventricle E. Pons The lytic skull lesion shown in this image was biopsied in a 72-year-old man who also has a history of recently developing renal failure. The lesion most likely will stain with what antibody? A. CD3 B. CD5 C. CD45 D. CD79 E. CD138 What is the most common site of origin of the cystic mass shown in this image? A. Cerebellopontine angle B. Foramen of Monro C. Lumbar cord D. Temporal lobe E. Sella A tear in the middle meningeal artery is most likely responsible for a hemorrhage in what space or location? A. Epidural space B. Intraventricular space C. Subarachnoid space D. Subdural space E. Thalamus How long after a diffuse axonal injury can dystrophic axons be visualized with β-amyloid precursor protein staining? A. 2 hours B. 4 hours C. 8 hours D. 12 hours E. 24 hours The pathological findings seen in the vastus lateralis muscle shown in this image from a 32-year-old woman are consistent with what pathology? A. Dermatomyositis B. Inclusion body myositis C. Polyarteritis nodosum D. Polymyositis E. Sarcoidosis The muscle shown in this image is from a 4-year-old boy who has proximal muscle weakness, a positive Gower sign, and calf muscle hypertrophy. Abnormal staining with what antibody is anticipated? A. Dysferlin B. Dystrophin C. Merosin D. Sarcoglycan alpha E. Spectrin This right temporal lobe cyst shown in this image is classified best as a(n): A. Arachnoid cyst B. Choroid plexus cyst C. Cystic meningioma D. Ependymal cyst E. Epidermoid cyst A 72-year-old man presents with muscle weakness, atrophy, and a biopsy shown in this image. The pathological process is likely to respond to what therapy? A. Statins B. Intravenous IgG C. Methotrexate D. Steroids E. No available therapies The findings in the NADH-stained section of skeletal muscle shown in this image are associated with what underlying pathological process? A. CCTG repeats B. Loss of myosin filaments C. Mitochondrial myopathy D. Nemaline rod myopathy E. Ryanodine receptor gene mutation A 2-year-old boy presents with vacuolar changes on muscle biopsy. The vacuoles are filled with glycogen and stain with acid phosphatase, as shown in this image. The patient’s most likely diagnosis is: A. Acid maltase deficiency B. Debrancher enzyme deficiency C. Hypokalemic periodic paralysis D. Myophosphorylase deficiency E. Phosphofructokinase deficiency What protein is unlikely to form cerebral amyloid? A. Cystatin C B. Gelsolin C. Kappa light chain protein D. Prion protein A CAG trinucleotide repeat in what gene is associated with Huntington disease? A. Ataxin-2 gene B. CACNAIA gene C. Chorein gene D. HTT gene E. Myotonin gene The pathology illustrated with the Bielschowsky stain shown in this image is encountered most commonly in what disease process? A. Alzheimer disease B. Diffuse Lewy body disease C. Ganglioglioma D. Mitochondrial encephalopathy E. Pick disease An antibody for what protein best highlights the structures shown in this Bielschowsky stain image? A. α-synuclein B. Congo red C. Glial fibrillary acidic protein D. Tau E. Thioflavin S What tumor pathology consists of tumor cells forming cuffs around blood vessels? A. Germinoma B. Ependymoma C. Chordoma D. Lymphoma E. Hemangioblastoma The presence of xanthochromia, high protein, and clotting of the cerebrospinal fluid is referred to as: A. Queckenstedt syndrome B. Coup de poignard of Michon C. Froment sign D. Froin syndrome E. Foix-Alajouanine The cyst shown in this image is situated near the foramen of Monro. What is an unlikely presenting symptom for the most likely lesion? A. Headache B. Incontinence C. Personality change D. Seizure E. Sudden death The eosinophilic deposits shown in this image represent amyloid accumulation in a patient with suspected Alzheimer disease. What is the single best stain to prove the diagnosis? A. β-amyloid B. Luxol fast blue C. Mucicarmine D. Prussian blue E. Trichrome A lesion with a vascular nature is resected, and the pathology lab reports that the lesion is consistent with a vascular hamartoma with irregular thick-and thin-walled sinusoidal vascular channels without intervening brain tissue. What is the diagnosis for this lesion? A. Capillary telangiectasia B. Cavernous malformation C. Venous angioma D. Arteriovenous malformation E. Dural arteriovenous fistula Sturge-Weber disease is inherited in what fashion? A. Autosomal dominantly B. Autosomal recessively C. X-linked recessively D. Sporadically with no obvious genetic transmission The cytoplasmic inclusion shown in this image is most likely associated with a mutation in what gene? A. SNCA B. PARK1 C. PARK2 D. PARK5 E. PARK8 A man presents for genetic counseling with deafness, skeletal abnormalities, mental retardation, and coarse facial features. He is found to have an autosomal recessive mucopolysaccharidosis. What is the patient’s enzyme deficiency? A. L-iduronidase B. Iduronate sulfatase C. Galactose 6-sulfatase and β-galactosidase D. Sulfatase B E. β-glucuronidase Klippel-Feil syndrome is associated with what common findings? A. Low posterior hairline, brevicollis, and decreased neck motion B. Sebaceous adenomas, mental retardation, and seizures C. Anorectal malformation, anterior sacral defects, and presacral masses D. Dementia, urinary incontinence, and gait instability Axonal spheroids are seen with what neurologic pathology? A. Friedreich ataxia B. Huntington disease C. Cerebral infarction D. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis The best diagnosis for the mucin and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-positive spinal cord mass shown in this image, presenting in a 33-year-old man with a 4-year history of lower back pain, is: A. Meningioma B. Metastatic adenocarcinoma C. Myxopapillary ependymoma D. Paraganglioma E. Schwannoma The Prussian blue stain shown in this image highlights increased iron accumulation in a patient with a PANK2 gene mutation. The iron accumulation most commonly is seen in what location in the central nervous system? A. Basal ganglia B. Cerebellum C. Cervical and lumbar spinal cord D. Hippocampus E. Pons A 22-year-old woman with seizures for 12 years has hippocampal sclerosis pathology, as shown in this image. What two regions of the hippocampus usually are affected most severely? A. CA1 and CA2 B. CA1 and CA3 C. CA1 and CA4 D. CA2 and CA4 E. CA3 and CA4 Multisystem atrophy (cerebellar predominant type) is characterized by what pathological or clinical finding? A. Atrophy of the putamen B. Dysautonomia C. Neuronal loss in the striatonigral system D. Rigidity and dystonia E. Ubiquitin positive tangles A mutation in what gene is associated with 20% of familial cases of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis? A. PTEN B. SMN1 C. SMN2 D. SOD1 E. TARDBP The optic nerve shown in this image was sampled at autopsy. The most likely pathology observed is:
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree