SEXUAL RESPONCE
Normal anatomy
The normal anatomy of the female genitalia is shown in Figure 9.1 and that of the male genitalia in Figure 9.2. Patients with sexual dysfunction may not be aware of the structures shown and it is therefore often helpful to show them such diagrams (or models).
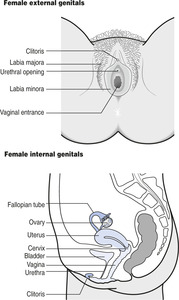 |
| Figure 9.1 (With permission from Puri BK, Laking PJ, Treasaden IH 2002 Textbook of psychiatry. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh.) |
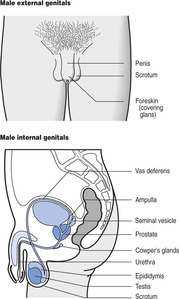 |
| Figure 9.2 (With permission from Puri BK, Laking PJ, Treasaden IH 2002 Textbook of psychiatry. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh.) |
Normal sexual response
In Masters and Johnson’s model of the sexual response there are four phases (Fig. 9.3).
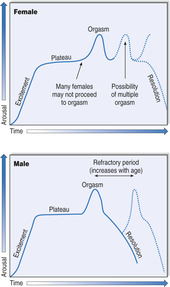 |
| Figure 9.3 (With permission from Puri BK, Laking PJ, Treasaden IH 2002 Textbook of psychiatry. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh.) |
Excitement phase
Arousal occurs in response to sexual stimulation (which may be fantasy as well as reality) and there is a desire to engage in sexual activity.
In females the following occur during the excitement phase:
• A subjective sense of sexual pleasure
• Rapid vaginal lubrication
• Expansion and distension of the inner vagina
• Swelling and elongation of the clitoris
• Elevation of the uterus
• Nipple erection (in some women)
• Increased pulse.
In males the following occur:
• Erection of the penis
• Thickening of the scrotal skin
• Elevation of the testes
• Increased pulse.
Plateau phase
There is an intensification of the sexual excitement to a level from which orgasm can occur.
In males the following occur:
• Some change in colour in the head of the penis
• Enlargement of the testes
• Further elevation of the testes
• Increased muscle tension
• Increased blood pressure
• Increased pulse
• Occasionally a flush across the front of the trunk and head.
Orgasm phase
During this phase the sexual pleasure reaches a maximum, with an involuntary release of sexual tension and rhythmic contractions of the perineal muscles and reproductive organs.
In females the following occur during orgasm:
• Rhythmic contractions of the outer third of the vagina – these are not always subjectively experienced by the woman
• Uterine contractions
• Rhythmic contractions of the anal sphincter
• Maximal pulse
• Maximal blood pressure
• Maximal respiratory rate.
In males the following occur during orgasm:
• The sensation of ejaculatory inevitability (during which ejaculation from the prostate and seminal vesicles and other glands contributes to the creation of seminal fluid), followed by rhythmic contractions of the urethra to cause ejaculation of the seminal fluid
• Rhythmic contractions of the anal sphincter
• Maximal pulse
• Maximal blood pressure
• Maximal respiratory rate.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







