♦ Intraoperative
Positioning
- Use radiolucent Mayfield skull clamp if intraoperative angiography is planned
- Patient is supine with head fixation using double Mayfield skull pin sites positioned low at ipsilateral retromastoid region and single pin in sagittal plane of contralateral midpupillary line just behind the hairline if possible
- Turn head away from side of craniotomy and extend neck so that malar eminence is at highest point of operative field to allow gravity to facilitate brain retraction
- Neck should be positioned to avoid excessive compression of jugular veins and the endotracheal tube
- Elevation of the head of bed and ipsilateral shoulder elevation with a shoulder roll are used to ensure adequate jugular venous return
Planning of Incision and Shave
- Strip shave of 1 cm width located 2 cm behind the hairline to leave a cuff of hair; or, alternatively, shave extending for 3 cm behind the hairline, from the most anterior portion of the hairline at the midline (widow’s peak) inferolaterally to the sideburn
- Curvilinear incision from the midline widow’s peak and extending laterally to 1 cm anterior to the tragus, terminating within a skin crease (Fig. 5.1A)
- Preserve superficial temporal artery if possible
Temporalis Muscle Dissection
- Temporalis fascia is divided sharply in line with the skin incision
- Temporalis muscle is divided with Bovie electrocautery in line with the fascial incision
- Myocutaneous flap is reflected anteriorly and inferiorly by subperiosteal dissection of temporalis muscle with periosteal elevator and minimal Bovie electrocautery, until the root of the zygoma, keyhole (located over the frontosphenoidal suture ~1 cm behind the frontozygomatic suture), and supraorbital ridge are identified
< div class='tao-gold-member'>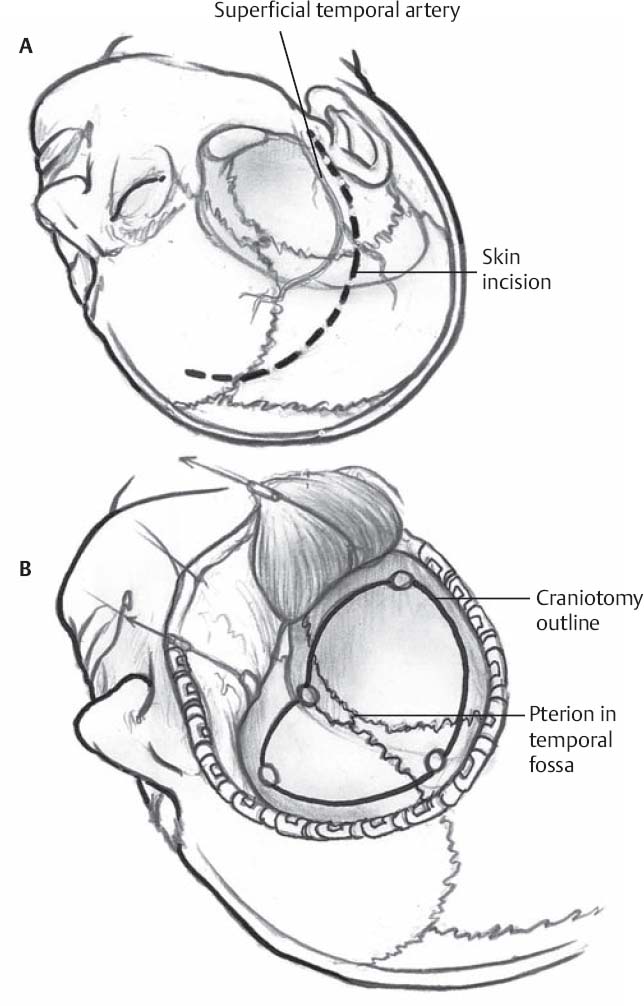
Fig. 5.1 (A) Curvilinear incision from the midline (or just medial to superior temporal line) extending laterally to 1 cm anterior to the tragus allows a frontotemporal craniotomy centered at the frontosphenoid suture. (B) Burr hole locations and craniotomy.
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







