Chapter 9 Radiographic Evaluation of Lesions within the Vertebrae
IMAGING MODALITIES
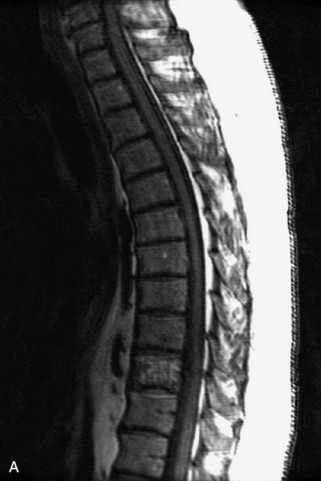
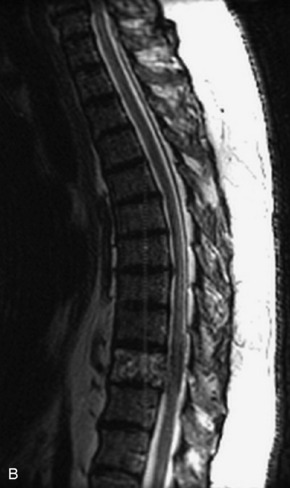
Radiographs, radionuclide scintigraphy (most often bone scan), positron-emission tomography (PET), computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are the imaging modalities available for evaluating lesions of the vertebrae. Of these, CT and MRI are relied on the most heavily. CT provides useful diagnostic information, characterizing cortical destruction, lesion margins, and tumor matrix, and may demonstrate pathognomonic features for specific lesions. MRI is the most sensitive tool for detecting infiltration of bone marrow and for assessment of extension into the spinal canal and compression of the spinal cord and nerve roots.1–5 Patients should be cleared for MRI contraindications before undergoing imaging. A discussion of contraindications is beyond the scope of this chapter, but a useful reference is Shellock’s Reference Manual for Magnetic Resonance Safety, Implants, and Devices.6 Of note, metallic implants for spinal fusion are not a contraindication, but may create magnetic susceptibility artifacts, which are greatest on fat saturated images and gradient echo (GRE) sequences and are minimized with the fast spin echo (FSE) technique.7 When assessing the spine, sagittal spin echo T1-weight images (T1WI) and T2-weighted images (T2WI) with axial GRE or FSE T2WI images are part of our routine protocol. In the evaluation of neoplastic processes, post-gadolinium images and STIR (short tau inversion recovery, a fat saturated T2-weighted sequence) have been shown to increase sensitivity for detection of disease.8–10 Although some proponents advocate use of STIR instead of gadolinium-enhanced images for screening of vertebral body pathology,11,12 post-gadolinium fat saturated images may add clinically important information in cases of abnormal STIR images.13 Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) has shown promise for differentiating benign from pathological fractures.14–17 However, there are some reservations about DWI’s specificity in this setting,18 and DWI has shown to be no better than conventional imaging in the absence of a fracture.19 For now, DWI remains unproven and technically challenging in the spine (Tables 9-1 and 9-2 and Figs. 9-1 and 9-2).
Table 9-1 Common MRI Sequences for Evaluation of Spinal Tumors
| T1-weighted SE | Marrow in adults has high signal because of fat Marrow signal lower than intervertebral disc indicates infiltrative process20 |
| T2-weighted FSE | High signal lesions may be inconspicuous on background of high signal marrow using FSE technique without fat saturation |
| T1-weighted + gadolinium | Without fat saturation, enhancing vertebral lesions may become less conspicuous8 Sequence useful for characterizing epidural, intradural, and paraspinal disease |
| STIR | Fat saturated T2-weighted sequence Shown to have better homogeneity of fat saturation than FSE T2 with fat saturation10 Lesions usually hyperintense on background of dark normal marrow |
SE, spin echo; FSE, fast spin echo; STIR, short tau inversion recovery.
Table 9-2 Classification of Vertebral Body Lesions
| Multiple Lesions | Solitary Lesions | Tumor Mimics |
|---|---|---|
| Hemangiomas | Chordoma | Infection |
| Metastases | Plasmacytoma | Heterogeneous marrow |
| Multiple myeloma | Giant cell tumor | Paget disease |
| Lymphoma | Aneurysmal bone cyst | Fibrous dysplasia |
| Leukemia | Osteoid osteoma | Renal osteodystrophy |
| Langerhans’ cell histiocytosis | Osteoblastoma | Anemia |
| Osteochondroma | Avascular necrosis | |
| (These lesions also may present as solitary lesions within the spine) | Osteogenic sarcoma | Kümmell’s disease |
| Chondrosarcoma | ||
| Ewing sarcoma | ||
| Neuroblastic tumors |
MULTIPLE LESIONS
Hemangiomas
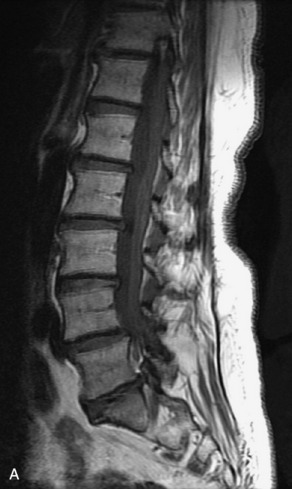
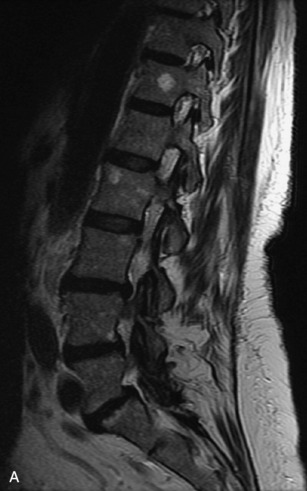
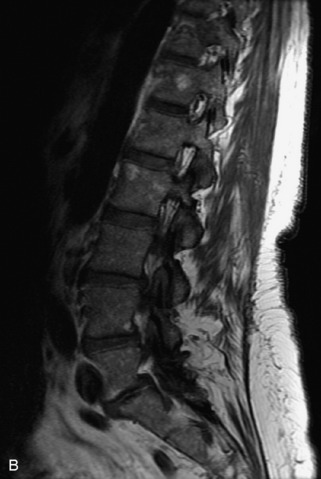
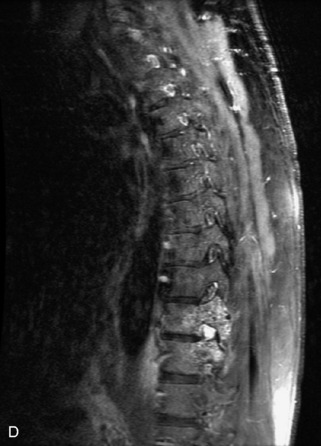
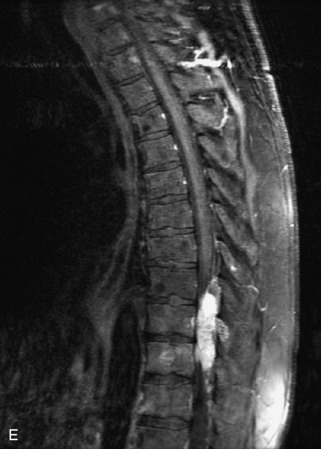
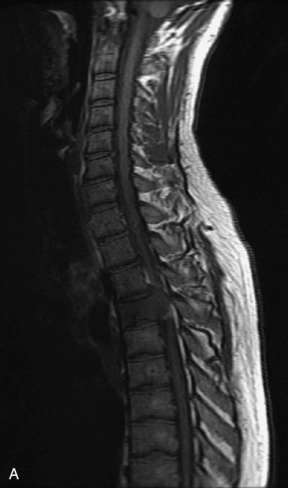
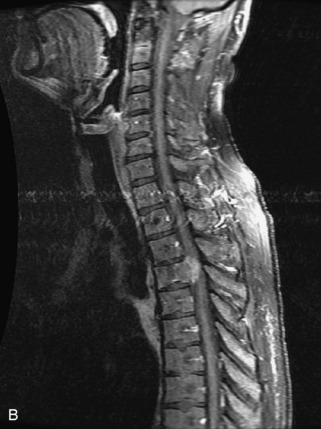
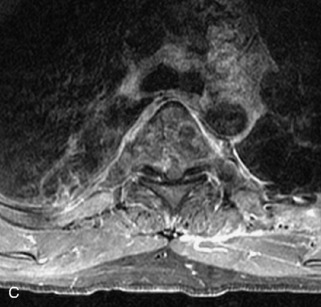
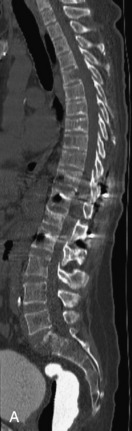
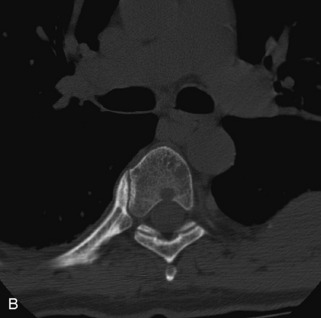
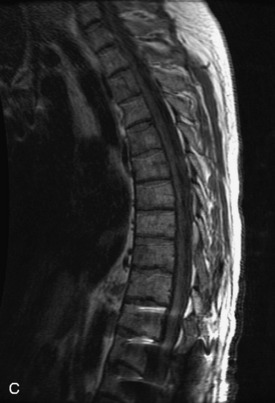
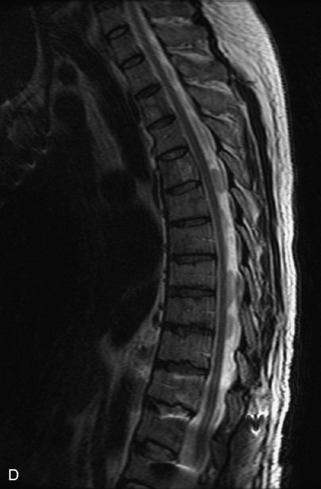
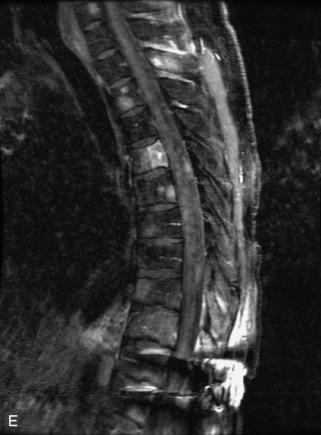
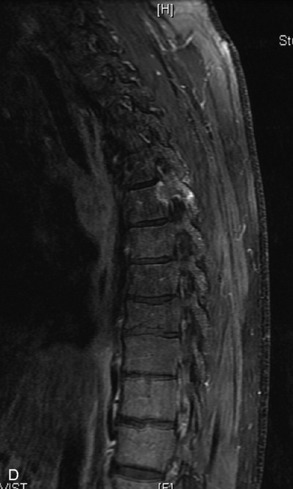
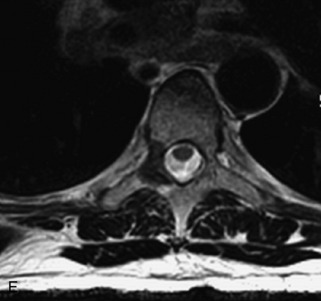
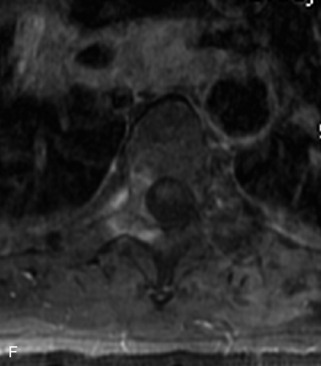
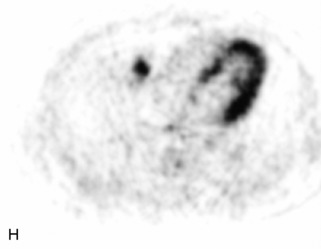
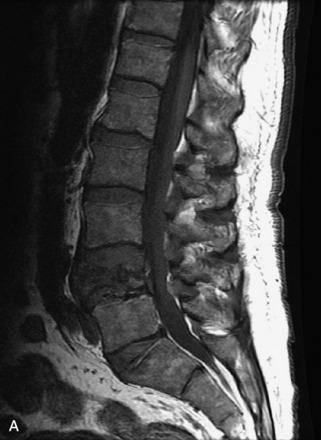
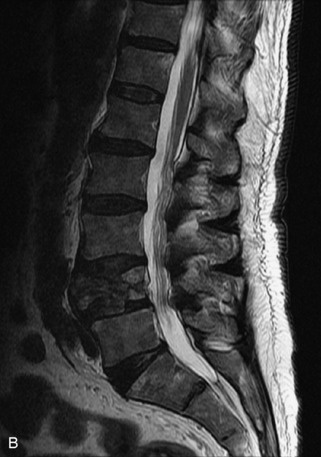
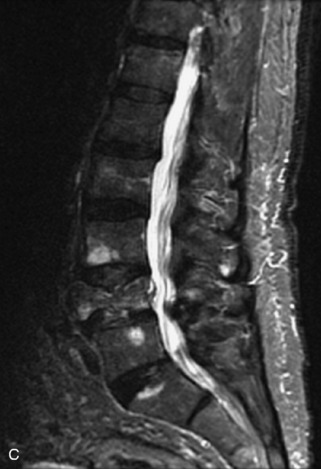
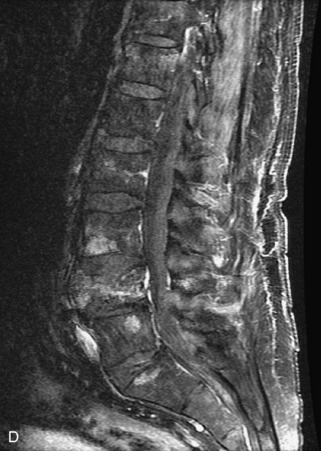
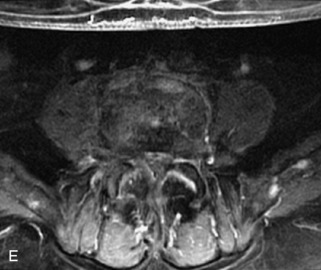
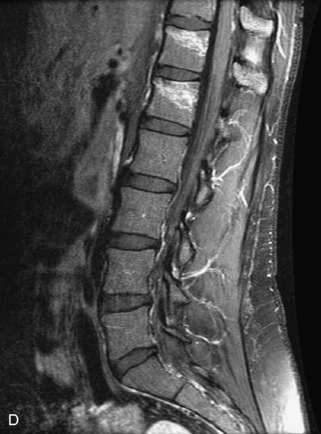
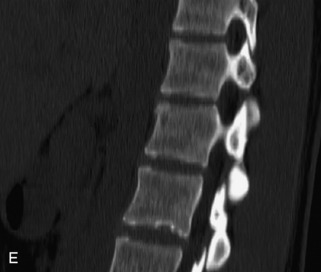
Hemangiomas are benign vascular tumors that occur in more than 10% of adults and are commonly detected as an incidental finding on imaging studies performed for unrelated indications. They are the most common primary bone tumor in adults, occur most commonly in the thoracic spine, and are usually solitary but can be multiple in approximately 30% of cases.1,2,21 They typically arise in the vertebral body but may involve the posterior elements. The CT appearance of a low attenuation lesion with coarse trabeculae throughout (giving a “polka-dot” appearance in cross-section) is diagnostic.22 MRI demonstrates the fatty stroma, which is bright on T1WI and iso-intense to hyperintense to marrow on T2WI, with avid enhancement after administration of gadolinium.23 Bone scan is typically normal.24 An aggressive subtype of hemangioma is recognized that tends to be associated more commonly with epidural extension and pathological fracture. These lesions are often iso-intense to hypointense to marrow on T1WI and can be impossible to distinguish from a malignant lesion, such as a metastasis, on imaging (Table 9-3 and Figs. 9-3 to 9-6).25,26
Table 9-3 Features of Hemangiomas
STIR, Short tau inversion recovery.
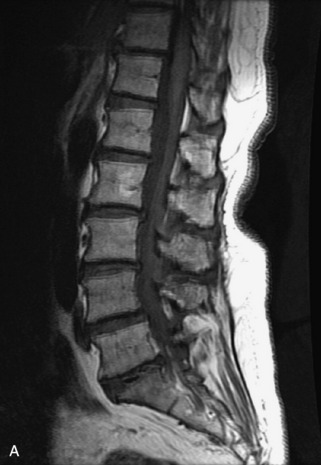
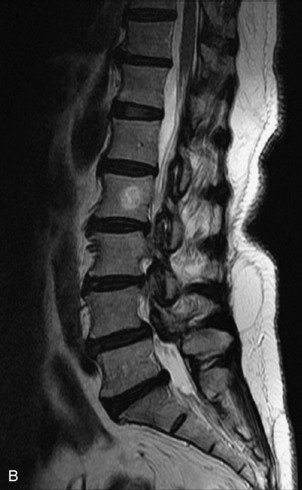
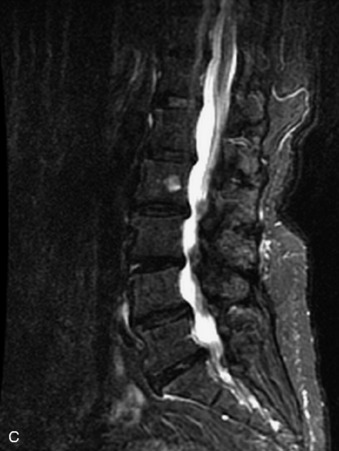
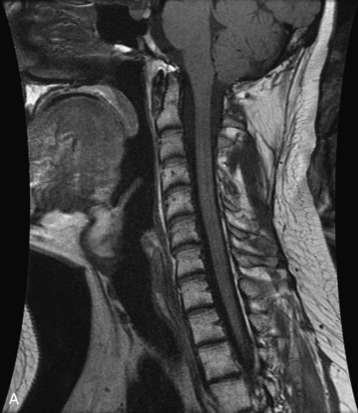
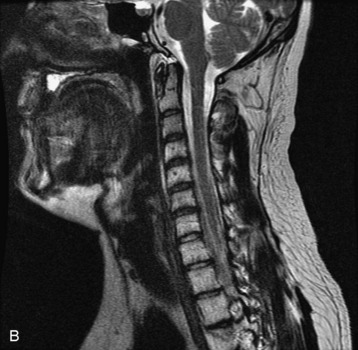
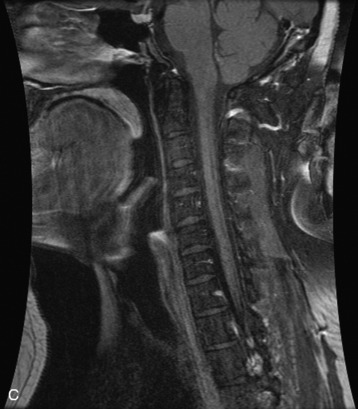
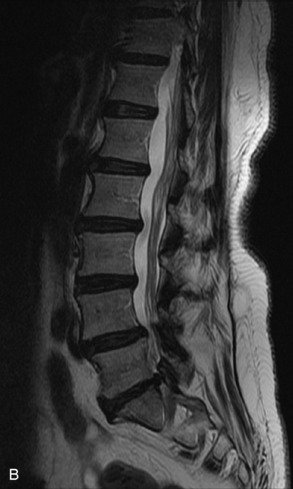
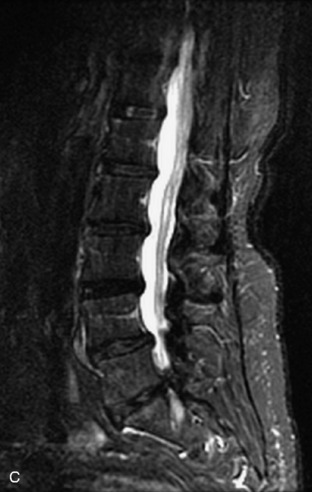
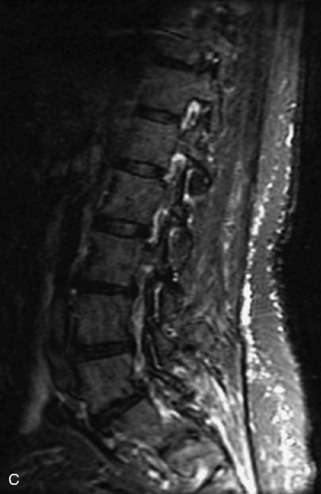
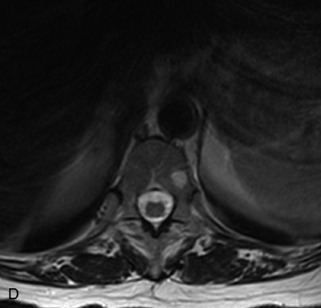
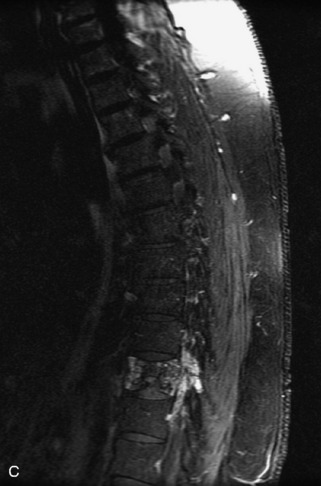
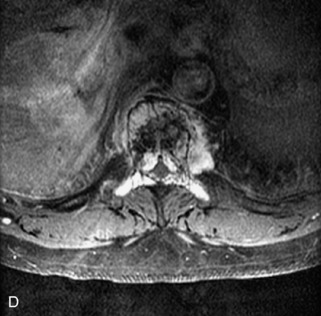
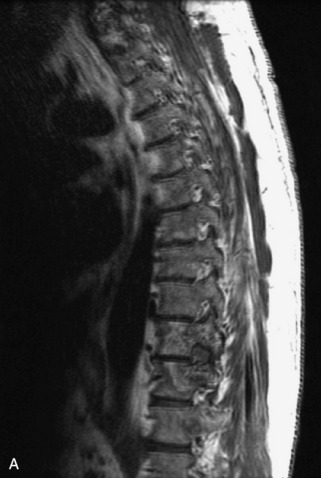
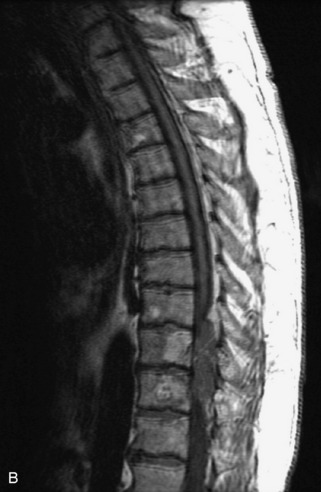
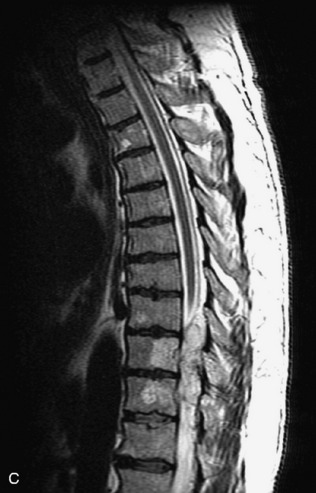
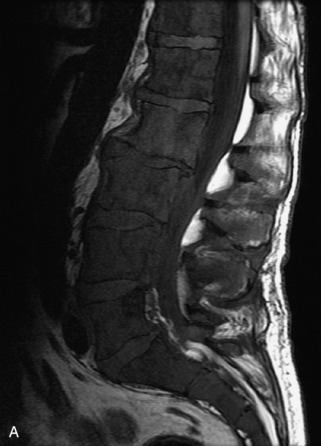
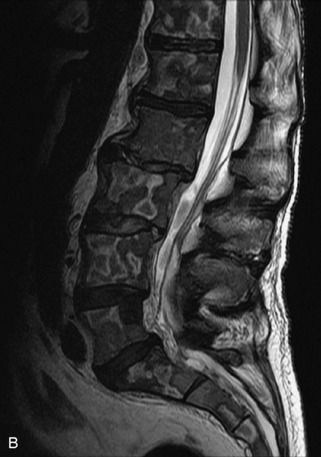
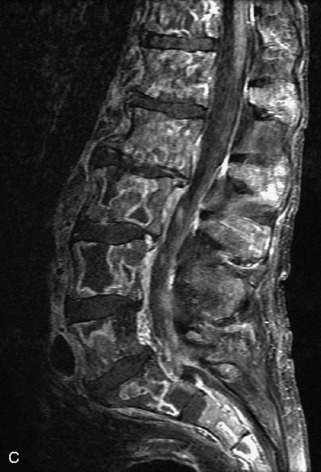
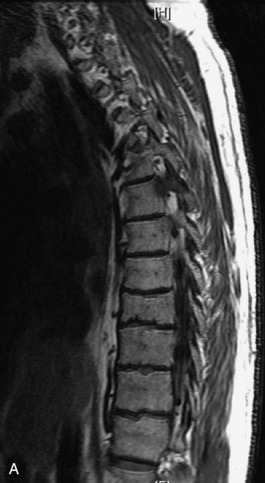
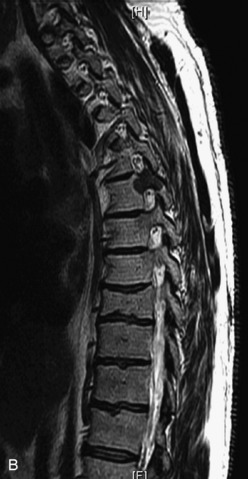
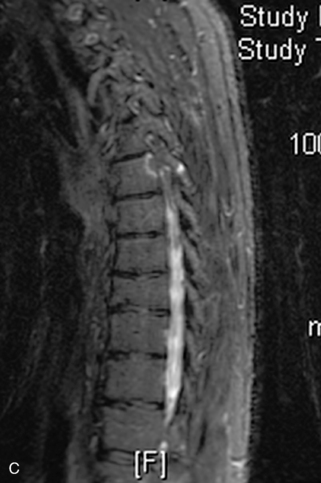
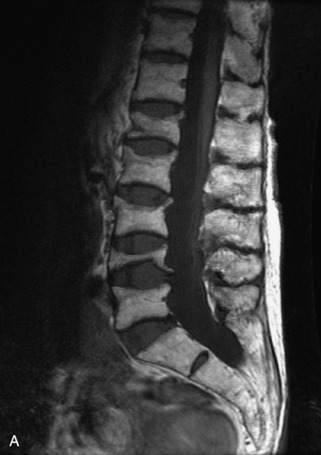
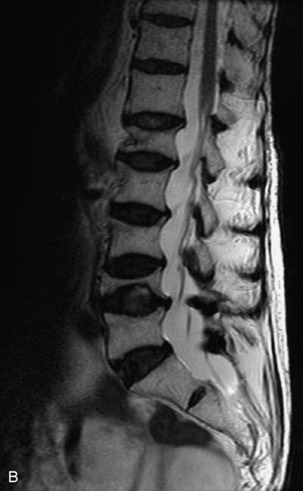
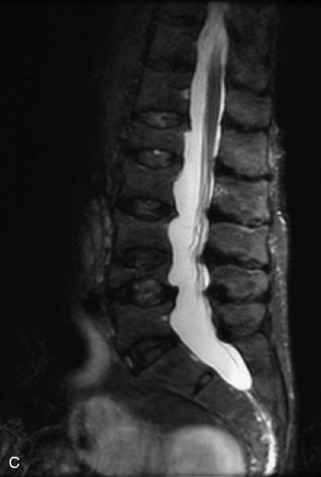
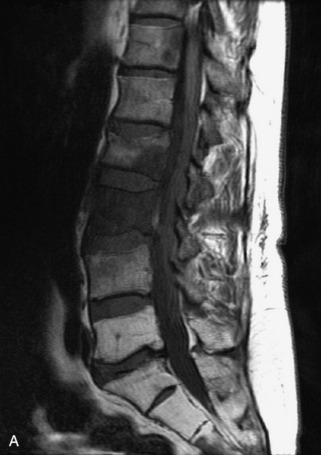
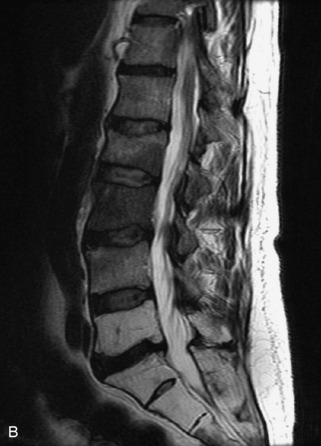
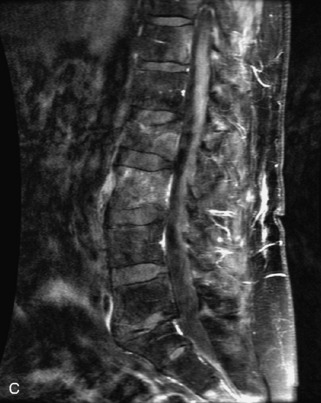
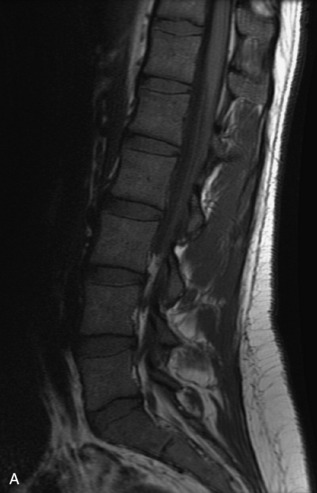
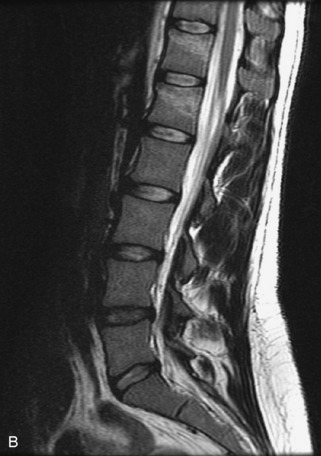
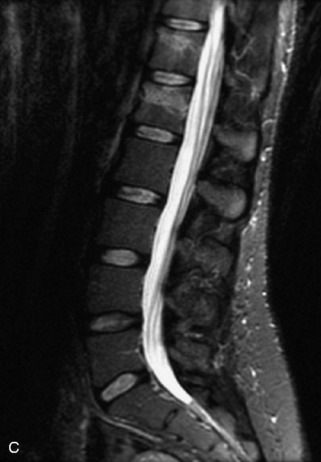
Fig. 9-4 Typical benign hemangiomas may sometimes have high signal on STIR images. A, Sagittal T1WI demonstrates a well-circumscribed hyperintense lesion within the L2 vertebral body consistent with a hemangioma. B, Sagittal T2WI demonstrates high signal within this lesion confirming the diagnosis of hemangioma. C, Sagittal STIR image. Unlike the previous example in Figure 9-3, high signal is seen within the L2 hemangioma on STIR. This does not change the diagnosis of hemangioma.
Metastases
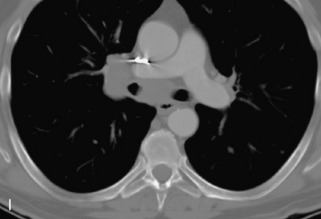
Metastatic disease is defined as dissemination or extension of tumor by direct, hematogenous, or lymphatic routes. Metastases are the most common malignancy to affect the spinal column. Bone metastases occur in 50% of all cancer patients, and 40–70% of these lesions are located within the vertebrae.27 In adults, breast, lung, prostate, lymphoma, sarcoma, and kidney account for the majority of primary sites. In children, neuroblastoma and Ewing sarcoma are the most common primary malignancies to metastasize to the spine.21,28 Metastases typically involve the vertebral body and posterior elements, and compression fractures as well as extension into the epidural space are common features. Most lesions have a lytic appearance on radiographs and CT, but blastic or sclerotic metastases can occur, especially in the setting of prostate carcinoma.1,2 Bone scan traditionally has been used to screen for metastatic disease to the spine. It has a sensitivity of approximately 95%, but can have false negatives if there is only marrow infiltration without cortical involvement, and is often non-specific. MRI has been shown to be both more sensitive and specific than scintigraphy.3 Radiographs are insensitive to assess for metastatic disease, requiring at least 50–70% bone destruction for detection of lesions.27,29,30 Classic radiographic signs include an absent or sclerotic pedicle, cortical destruction, and paraspinal soft tissue mass.29–31 CT is more sensitive than radiographs to detect bony destruction, sclerosis, and paraspinal masses but is less sensitive than MRI and is poor for assessment of cord compression. On MRI, lesions are typically hypointense to normal marrow and intervertebral discs on T1WI, usually hyperintense on T2WI, and demonstrate heterogeneous enhancement.1,2 In the case of epidural extension, the “draped curtain” sign has been described, whereby there is sparing of the midline because of an intact midline septum that attaches the dura anteriorly to the posterior longitudinal ligament, in contrast to infection, which does not spare the midline.32 When pathologic fracture occurs as a result of an underlying metastasis, restricted diffusion may be helpful to distinguish the metastatic lesion from a benign osteoporotic fracture14–17 (Table 9-4 and Figs. 9-7 to 9-10).
Table 9-4 Features of Spinal Metastases
Pathological vs. Benign Compression Fractures
Vertebral compression fractures in the absence of trauma are a common clinical problem in the elderly population. Although clinical history is helpful, up to one-third of fractures in patients with known primary malignancy are benign, and approximately one-quarter of fractures in apparently osteopenic patients are caused by metastases.31 Diagnosis of an underlying lesion is important because it influences clinical staging, treatment planning, and prognosis for the patient. In the chronic setting, the differentiation between pathologic fracture as a result of underlying malignancy and benign osteoporotic fracture is fairly simple and can be made with a high level of certainty.33,34 Marrow signal of chronic benign fractures is iso-intense to normal bone marrow on all sequences, whereas fractures associated with metastases demonstrate low signal intensity on T1-weighted sequences and high signal intensity on T2-weighted sequences.33,35 STIR images provide the greatest contrast between normal and abnormal bone marrow.33 Acute compression fractures, however, may share many of the imaging findings of metastatic lesions, and differentiation is more challenging.35,36 Features that favor acute benign osteoporotic fractures include retropulsion of a bony fragment, preservation of normal marrow signal intensity, a horizontal band-like pattern of low signal intensity on T1WI and T2WI, and the presence of other compression fractures.37,38 Features more likely to be seen in metastatic compression fractures include pedicle involvement, an associated focal paraspinal soft tissue mass or epidural mass (particularly one encasing the dural sac), convex posterior cortex, diffuse low signal intensity within the vertebral body on T1WI, and the presence of other metastases.35,37–30 Some studies have suggested that a pattern of intense or heterogeneous contrast enhancement supports diagnosis of metastatic compression fracture, but this finding is inconsistent in the literature and may not be reliable.34,35,37,39 There has been increasing interest in the use of diffusion weighted imaging for differentiating benign vertebral fractures from those associated with metastases, with early results showing that reduced diffusion is highly specific for diagnosing an underlying metastatic lesion.14–17 However, even this technique is not foolproof18 and either bone biopsy or follow-up imaging is often required (Table 9-5 and Figs. 9-11 to 9-14).
Table 9-5 Imaging Features to Differentiate Benign Fracture from Malignancy
| Benign Osteoporotic Fracture | Malignant Lesion with Fracture |
|---|---|
| Acute Preservation of normal bone marrow signal Retropulsed bone fragment Horizontal band-like low signal intensity Presence of other compression fractures | Acute Diffuse low signal intensity on T1WI Pedicle involvement Convex posterior cortex Epidural soft tissue mass Focal paraspinal soft tissue mass Presence of other metastases |
| Chronic Preservation of normal bone marrow signal | Chronic Bone marrow replacement with abnormal signal—low signal on T1WI, high on T2WI |
Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a multifocal malignant proliferation of monoclonal plasma cells that occurs most commonly in men older than 60 years. Diagnosis is confirmed by bone biopsy or by demonstrating Bence Jones proteins (free light chains) in urine or monoclonal gammopathy in serum. Although it is the most common primary bone malignancy, multiple myeloma accounts for only 1% of all cancers.31 The axial skeleton is more commonly involved than long bones. Vertebral body destruction and fractures are common with spine involvement.40 Punched out lytic bone lesions, diffuse osteopenia, fractures, and, rarely, sclerotic lesions are the hallmarks of disease on CT and radiographs.1 MRI findings reflect a number of different patterns of bone marrow involvement. These patterns include microscopic infiltration with normal MRI appearance in up to 20%, focal lesions, homogeneous diffuse infiltration of the bone marrow (best seen as low signal on T1WI), combined diffuse and focal disease, and a heterogeneous/variegated pattern with interposition of fat islands giving a “salt and pepper” appearance.41 Marrow involvement or lesions are typically hypointense on T1WI, hyperintense on T2WI and STIR images, and enhance avidly with gadolinium. MRI is helpful for following treatment response, with decreased T2 signal abnormality and decreased enhancement representing good prognostic signs.42,43 Bone scan has limited sensitivity, detecting bone involvement in 75% of myeloma patients and only demonstrating 10% of lesions. However, technetium (Tc)-99m-sestamibi scintigraphy is both sensitive and specific for diagnosing myeloma lesions and is complementary to bone scan. Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET is gradually assuming an increasingly important role in following response to treatment44 (Table 9-6 and Figs. 9-15 and 9-16).
Table 9-6 Features of Multiple Myeloma
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|