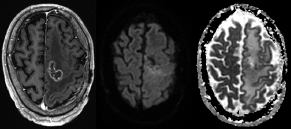
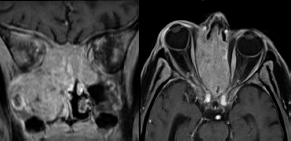
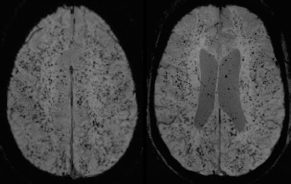
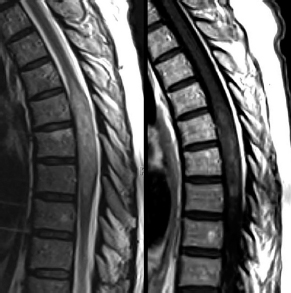
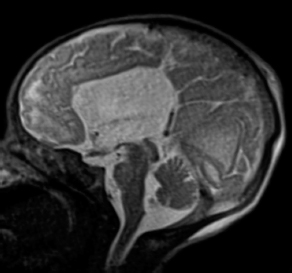
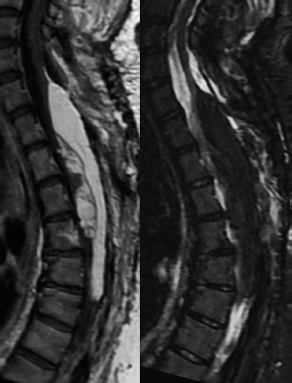
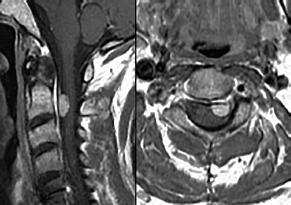
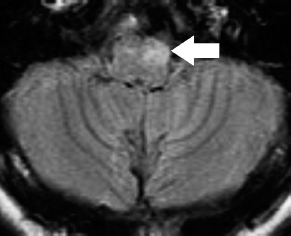
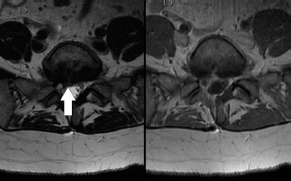
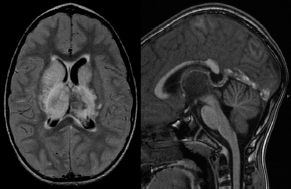
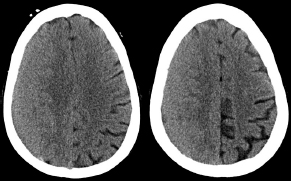
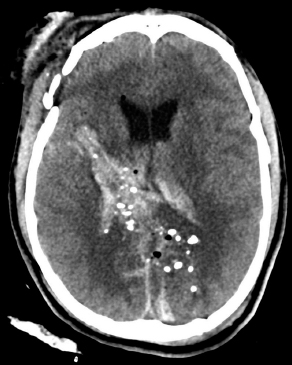
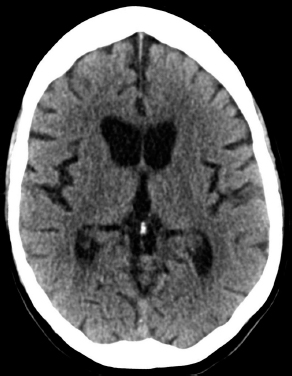
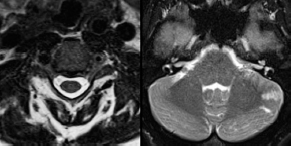
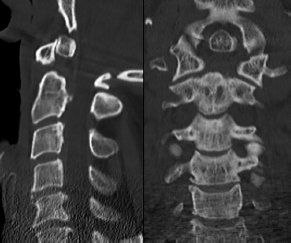
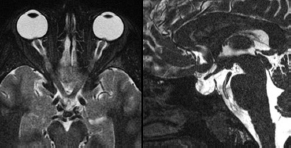
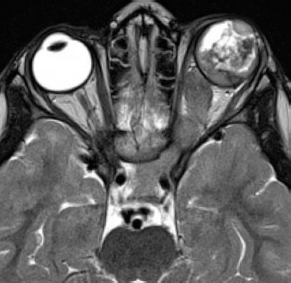
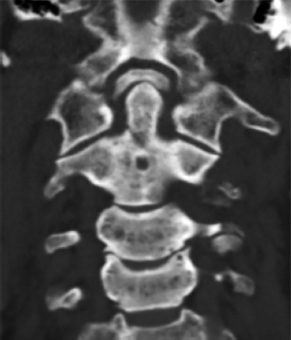
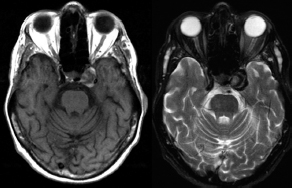
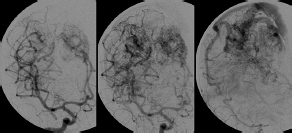
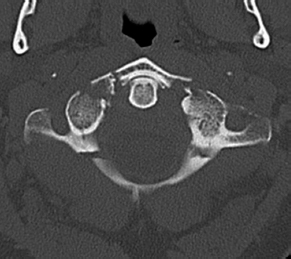
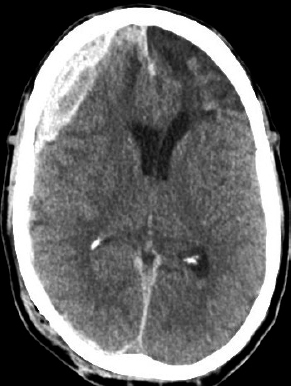
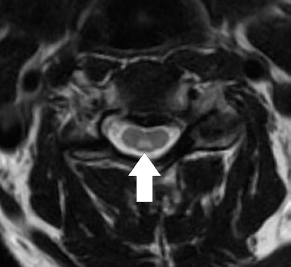
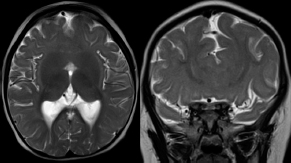
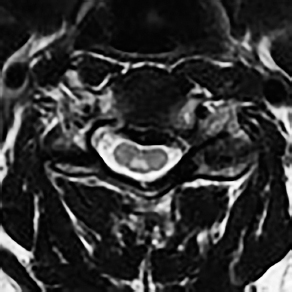
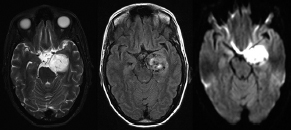
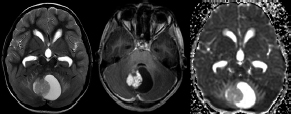
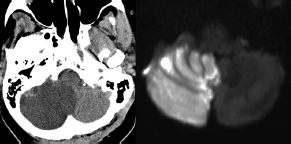
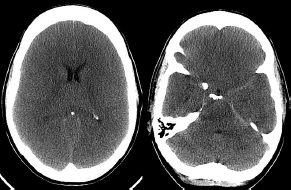
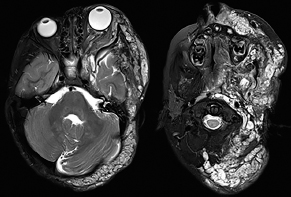
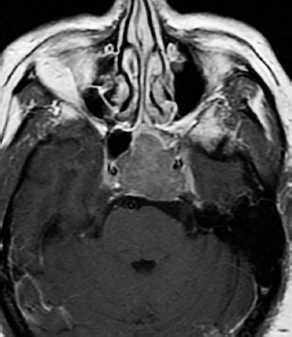
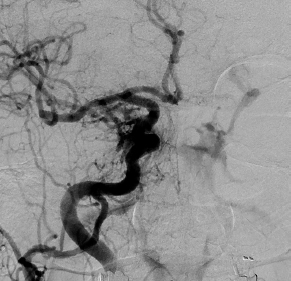
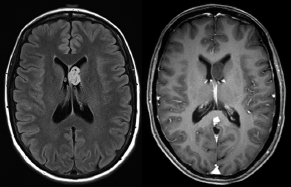
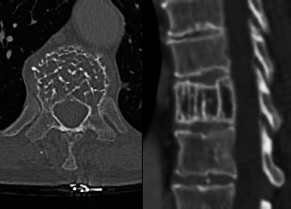
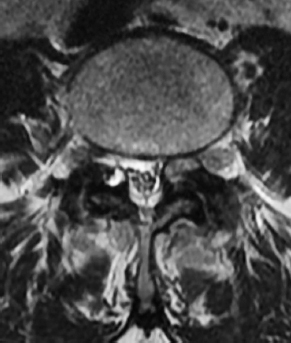
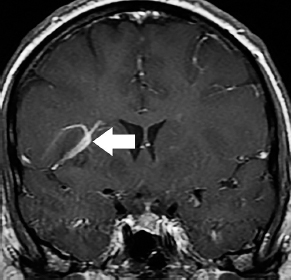
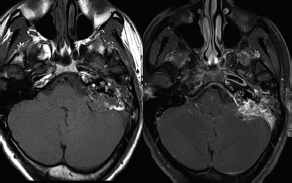
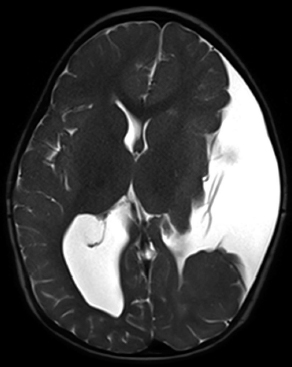
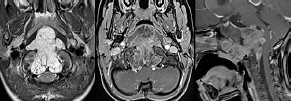
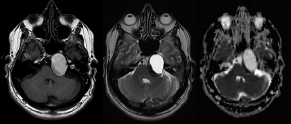
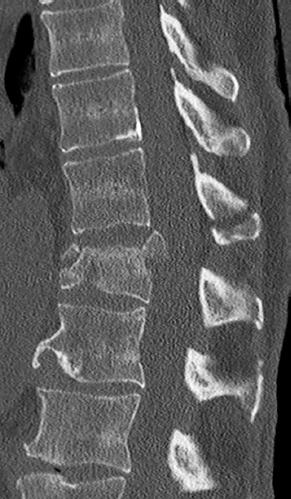
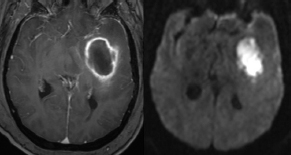
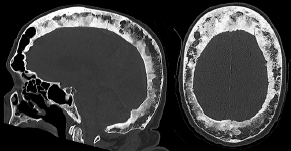
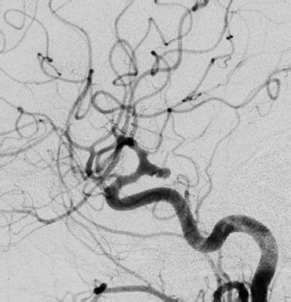
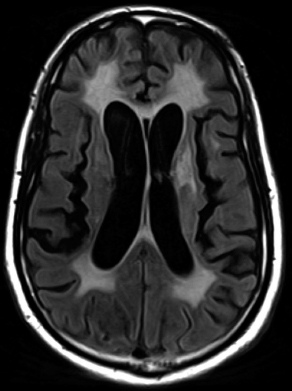
6Radiology A 56-year-old man presents to the emergency room with 1 week of altered mental status. His medical history is significant for a glioblastoma treated with resection followed by temozolomide therapy and whole brain radiation 1 year ago. An MRI is performed, and contrast-enhanced, diffusion-weighted, and apparent diffusion coefficient sequences are shown in these images. Perfusion maps (not shown) demonstrate decreased relative cerebral blood volume. What is the likely cause of his new symptoms? A. Radiation necrosis B. Recurrent glioblastoma C. Secondary tumor caused by chemotherapy regimen D. Encephalomalacia from tumor resection The lesion shown in these images depicts a(n): A. Optic nerve glioma B. Meningioma C. Chordoma D. Esthesioneuroblastoma What likely is associated with the imaging findings on the MR susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) sequence shown in these images? A. Shearing injury from rotational acceleration B. β-amyloid peptide deposits C. Mutations in the CCM1 gene D. Long bone fractures A 22-year-old man without a significant medical history presents with progressive midthoracic pain. An MRI examination of the spine is shown in these images. What is the most likely diagnosis? A. Astrocytoma B. Ependymoma C. Metastasis D. Tumefactive demyelination A neonate underwent an MRI of his brain, shown in this image. What may be an associated finding? A. Interhemispheric cysts B. Collapse of ventricular atria and occipital horns C. Low-riding third ventricle D. Curvilinear pericallosal lipomas What is a characteristic of the lesion depicted in the MRI study shown in these images? A. Results from premature disjunction of the cutaneous ectoderm from the neuroectoderm during neurulation B. Infiltrative hypercellular lesion with variable degrees of mitosis/atypia C. Results from clonal transformation of cells of B-cell origin D. May be associated with endolymphatic sac tumors, renal cell carcinomas, and retinal angiomas A 30-year-old woman with a history of recurrent genital and oral aphthae and erythema nodosum underwent an MRI of the brain. What is a likely imaging finding in this patient? A. Enhancing lesion involving the brainstem B. Fluid-attentuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) hyperintense lesion sparing red nuclei and substantia nigra C. Lesions with a leading edge of restricted diffusion D. Lesions involving the pulvinar and dorsomedial thalamic nuclei E. Lesions with an incomplete rim of enhancement A 54-year-old man underwent an MRI of the spine. Sagittal and axial postcontrast T1-weighted images are shown in these images. What is the patient’s likely diagnosis? A. Leptomeningeal metastasis B. Neurofibroma C. Schwannoma D. Meningioma The lesion shown in this image (arrow) can result from injury to what structure? A. Central tegmental tract B. Lateral lemniscus C. Spinothalamic tract D. Reticulospinal tract Axial T2 and postcontrast T1-weighted imaging of the lumbar spine are shown in these images. To what does the abnormality indicated by the arrow correspond? A. Disk protrusion B. Epidural scar C. Disk extrusion D. Epidural abscess E. Sequestered disk A 12-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department in an obtunded state following an episode of seizures. Based on these images, what is the diagnosis? A. Cortical venous thrombosis B. Deep venous thrombosis C. Mitochondrial encephalopathy D. Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy E. Arterial infarction A woman underwent a head CT, shown in these images. What is the likely diagnosis? A. Infiltrative tumor B. Acute infarct C. Intracranial hemorrhage D. Meningitis A boy with truncal ataxia and abnormal eye movements undergoes an MRI of the brain, which shows continuation of the cerebellar hemispheres and dentate nuclei and absence of the vermis. What is the most likely diagnosis? A. Pontine tegmental cap dysplasia B. Rhombencephalosynapsis C. Joubert syndrome D. Dandy-Walker malformation A 38-year-old man who sustained a gunshot wound to the head underwent an emergent CT scan, shown in this image. What finding portends the worst prognosis? A. Presence of both entry and exit wounds B. Involvement of the inner and outer tables of the calvaria C. Bullet tract crossing the deep midline structures D. Presence of metallic fragments along the bullet trajectory E. Presence of an open comminuted fracture The axial CT scan in this image shows the level of termination of bilateral cerebral deep brain stimulation leads. What is the anatomic location of these leads? A. Globus pallidus interna B. Subthalamic nuclei C. Ventral intermediate nuclei D. Red nuclei A man is reported to have a “string of pearls” appearance on his angiogram. What is the likely diagnosis? A. Severe carotid artery stenosis B. Dural arteriovenous fistula C. Fibromuscular dysplasia D. Arteriovenous malformation E. Carotid artery dissection A sagittal T2-weighted image of a patient with a tethered cord is shown in this image. What is a characteristic of the pathology represented here? A. Reduced risk following folic acid supplementation B. Associated with Chiari 2 malformations C. Secondary to premature disjunction of the neural ectoderm D. Most cases are familial What is the origin of the lesion on the contrast-enhanced T1 image shown here? A. Facial nerve B. Vestibular nerve C. Aberrant carotid artery D. Inferior petrosal sinus A falcotentorial arteriovenous malformation is noted to have its primary vascular supply from an enlarged tentorial artery. What is the usual origin of this vessel? A. Meningohypophyseal trunk B. Inferolateral trunk C. Neuromeningeal trunk D. Posterior cerebral artery Sagittal CT and MRI STIR sequences of the cervical spine are shown in these images. What is the injury type demonstrated? A. Hangman fracture B. Clay-shoveler fracture C. Jefferson fracture D. Flexion-distraction injury E. Locked facets What MRI features would favor a metastatic (pathological) compression fracture over a benign osteoporotic fracture? A. Horizontal low signal intensity bands B. Convex posterior vertebral margins C. Areas of spared vertebral marrow D. Retropulsion of a bone fragment E. Enhancement of the involved vertebra A man with a history of depression presents with rapid and involuntary movements involving his face and limbs. The clinical exam is notable for hypotonia, hyperreflexia, and mild bradykinesia. A noncontrast CT of the head is shown in this image. What mutation is the likely cause of the patient’s presentation? A. Trinucleotide repeat expansion B. Point mutation C. Frameshift mutation D. Deletion Gradient echo MRI sequences are particularly useful for the detection or evaluation of what process or pathology? A. Myelin injury B. Purulence C. Acute ischemia D. Glucose metabolism E. Blood products A man without a history of trauma is brought to the emergency department with nausea, vomiting, and ataxia. Axial T2-weighted images of the neck and posterior fossa are shown here. What is a characteristic of the lesion in the neck? A. It may be related to connective tissue disorders. B. The majority occur in patients older than 60 years of age. C. Intradural lesions are more common. D. Rupture is more common in extradural than intradural lesions. A 56-year-old patient involved in a motor vehicle collision underwent a cervical spine CT scan, shown in these images. What is true of the osseous abnormality demonstrated? A. It is consistent with an acute type 2 odontoid fracture. B. It results from failure of fusion of the ossiculum terminale. C. It is associated with Morquio syndrome and multiple epiphyseal dysplasia. D. Orthotopic lesions are more likely to be unstable than dystopic lesions. A 52-year-old obese woman with a history of headaches presents to clinic. An MRI of the brain was obtained, and is shown in these images. What additional radiographic finding may be seen? A. Dural venous sinus stenosis B. Venous sinus engorgement C. Brainstem sagging D. Decreased mammillopontine distance A woman who was involved in a motor vehicle collision underwent a CT of the cervical spine, which shows a fracture involving an occipital condyle. What structure is likely to be affected? A. Cranial nerve IX B. Cranial nerve X C. Cranial nerve XI D. Cranial nerve XII The lesion shown in this image is associated with a chromosome 13q deletion. What is a characteristic of this lesion? A. Has a tendency for leptomeningeal spread B. Anterior eye segment enhancement indicates disease infiltration C. Likely has high apparent diffusion coefficient values D. Likely has high signal intensity on susceptibility-weighted imaging What is true regarding the lesion shown in this CT image? A. Usually heals well with traction and immobilization B. Usually considered stable C. Constitutes the most common type of fracture at this site D. Fracture occurs above the transverse band of the cruciform ligament E. Most likely fracture type to progress to nonunion A patient with left-sided cranial neuropathies underwent a brain MRI study, shown in these images. What is a likely complication of this lesion? A. Malignant transformation B. Carotid-cavernous fistula C. Subarachnoid hemorrhage D. Posterior circulation infarcts What is a characteristic of the entity depicted on the digital subtraction angiographic images shown here? A. Cortical venous reflux denotes increased bleeding risk. B. Multiple lesions may be seen in Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome. C. Deep venous drainage connotes increased surgical risk. D. Most have a primarily dural vascular supply. What is a characteristic of the injury shown on this CT scan? A. Combined offset of the lateral C1 masses relative to C2 greater than 6 mm, which suggests disruption of the alar ligaments B. Frequently associated with diving head first into shallow water C. High frequency of neurologic injury D. Most commonly occurs in infants and young children E. Usually warrants emergent surgical fixation The abnormality in the left frontal lobe on the CT of the head shown in this image is consistent with what process? A. Acute infarction B. Cortical contusion C. Remote injury D. Neoplasm E. Abscess What entity is compatible with the abnormality indicated by the arrow on the MRI shown in this image? A. Ependymoma B. Neuromyelitis optica C. Subacute combined degeneration D. Infectious myelitis A patient with extensive T2 hyperintensity and enhancement of the skull base shows a “black turbinate” sign on postcontrast T1 MRI sequences. What is the likely etiology of these findings? A. Bacterial infection B. Invasive fungal infection C. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma D. Osseous infarction What explains the development of the abnormality demonstrated on the brain MRI shown in these images? A. Failure of closure of the rostral neuropore B. Failure of diverticulation C. Nondisjunction of the neural ectoderm D. Premature disjunction of the neural ectoderm What tumor type would be expected to show the lowest apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values on an MRI of the brain? A. Atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor B. Juvenile pilocytic astrocytoma C. Ependymoma D. Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor E. Diffuse astrocytoma What is a characteristic of acute demyelinating encephalomyelitis? A. Most cases occur following vaccination. B. Deep gray nuclei usually are spared. C. Most lesions show contrast enhancement. D. It is typically a monophasic process. A 5-year-old boy with visual and hearing deficits and loss of developmental milestones presents for evaluation. MRI of the brain shows occipitoparietal periventricular demyelination with a leading edge of enhancement. What is the patient’s likely diagnosis? A. Adrenoleukodystrophy B. Canavan disease C. Alexander disease D. Krabbe disease E. Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease The spinal cord lesion in the T2-weighted MRI shown in this image is consistent with what disease process? A. Poliomyelitis B. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis C. Guillain-Barré syndrome D. Subacute combined degeneration A brain MRI shows a small lesion in the pons that is slightly hyperintense on T2-weighted imaging and shows “brush-like” enhancement and signal dropout on gradient echo sequences. There is no surrounding edema. This lesion is consistent with what disease process? A. Demyelinating plaque B. Metastasis C. Cavernous malformation D. Capillary telangiectasia Where is a type C carotid-cavernous fistula located according to the Barrow classification? A. Between meningeal branches of the external carotid artery and cavernous sinus B. Between meningeal branches of the internal carotid artery and cavernous sinus C. Directly between the cavernous internal carotid artery and cavernous sinus D. Between meningeal branches of both the external and internal carotid arteries and cavernous sinus What is a characteristic of the lesion depicted in the MRI shown in these images? A. Lined by arachnoid cells resulting in accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid B. Most are intraventricular C. Show complete signal suppression on MR FLAIR sequences D. Usually show areas of patchy enhancement E. Associated with a risk of malignant transformation A 12-year-old boy presented to the emergency department with progressive headaches, nausea, and vomiting. Axial T2 and contrast-enhanced T1- weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient maps are shown in these images. What is the patient’s likely diagnosis? A. Medulloblastoma B. Ependymoma C. Pilocytic astrocytoma D. Hemangioblastoma E. Metastasis A 74-year-old woman presents to the emergency room complaining of vertigo and nausea increasing in severity over the past several hours. CT and MRI studies were performed, and representative images are shown here. This lesion likely represents a(n): A. Primary neoplasm B. Acute infarction C. Metastatic disease D. Arachnoid cyst E. Epidermoid cyst A man who was found lying on the ground underwent an emergent CT of the head, shown in these images. What is the likely diagnosis? A. Ruptured cerebral aneurysm B. Acute arterial infarction C. Global anoxic injury D. Venous thrombosis A young woman underwent an MRI study, shown in these images. What tumor is she at risk of developing? A. Glioma B. Meningioma C. Ependymoma D. Endolymphatic sac tumor E. Subependymal giant cell tumor What factor favors an epidural versus a subdural empyema? A. Restricted diffusion B. Crescentic shape C. Crosses sutures D. Less common cerebral edema E. Peripheral enhancement A mass, shown in this image, was discovered in a 29-year-old woman presenting with progressive bitemporal hemianopsia and hyperprolactinemia. Immunohistochemistry and electron microscopy following resection demonstrated chromophobic tumor cells and “misplaced exocytosis” with extrusion of secretory granules. What neuroimaging feature is highly suggestive of cavernous sinus invasion? A. Extension beyond the lateral intercarotid line B. Carotid encasement greater than 180 degrees C. Obliteration of the superior venous compartment D. Obliteration of the inferolateral venous compartment What is a characteristic of the lesion depicted in this angiogram? A. Fibromuscular dysplasia predisposes to an increased risk of direct-type lesions. B. Spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage is the most common presentation. C. Dural-type lesions commonly present with a subjective bruit. D. A majority of direct-type lesions result from venous thrombosis. E. Dural-type lesions most commonly present in young males. The tumor depicted in the MRI shown in these images demonstrated microcysts and mild pleomorphism on histological examination and stained positive for glial fibrillary acidic protein, neuron-specific enolase, and neuronal cell adhesion molecule. What is true about this lesion? A. Associated with a high recurrence rate B. Presents most commonly in young adults C. Frequently complicated by hemorrhage D. Associated with TSC-1 and TSC-2 gene mutations E. Usually shows minimal to no contrast enhancement What is a feature of the focal areas of signal intensity (FASI) or unidentified bright objects (UBOs) in neurofibromatosis type 1? A. They are most common in basal ganglia and dentate nuclei. B. They are premalignant lesions. C. A small proportion show contrast enhancement. D. The presence of mass effect is characteristic. What MRI sequence specifically should be included to evaluate a patient with suspected cerebral abscess? A. Susceptibility weighted B. Diffusion weighted C. Time of flight D. Constructive interference in steady state (CISS) E. FLAIR A 74-year-old man underwent a CT study of the chest, which demonstrated the lesion shown in these images. This lesion is compatible with what diagnosis? A. Metastasis B. Paget disease C. Hemangioma D. Plasmacytoma A 67-year-old man with left L5 radiculopathy underwent MRI of the lumbar spine, shown in this image. This lesion likely represents a(n): A. Extruded disk B. Synovial cyst C. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy D. Uncovertebral joint hypertrophy What is true regarding the lesion indicated by the arrow in the contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MRI shown in this image? A. It is usually angiographically occult. B. It is composed of radially arranged medullary veins emptying into a dilated draining vein. C. High flow from shunting may result in flow-related aneurysms. D. A larger nidus is associated with an increased surgical risk. A patient presents to clinic for follow-up after suffering from a nontraumatic retinal detachment. The lesion shown in these images is found on a subsequent MRI. The patient should be screened for: A. Lisch nodules B. Bilateral vestibular schwannomas C. Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma D. Renal cell carcinoma E. Low levels of serum ceruloplasmin What is a characteristic of the condition depicted in the T2-weighted MRI shown in this image? A. Lined by dysplastic white matter B. Frequently accompanied by microcephaly and other cerebral anomalies C. Lined by endodermal endothelium D. May show variable signal intensities depending on its contents E. Results from a bilateral vascular insult to the anterior cerebral circulation in utero A 12-year-old boy with progressive headaches and lower cranial nerve palsies underwent an MRI scan, shown in these images. Which is the likely diagnosis? A. Chondrosarcoma B. Chordoma C. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma D. Meningioma E. Lymphoma A man presented with dysfunction of the left cranial nerves V and VI. T1- and T2-weighted MRI and the corresponding apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map are shown in these images. What is the patient’s likely diagnosis? A. Cholesterol granuloma B. Cholesteatoma C. Trapped secretions within pneumatized petrous cells D. Trigeminal schwannoma What is the likely mechanism that caused the injury shown in this image? A. Lateral bending and compression B. Axial rotation C. Abrupt extension D. Axial loading E. Flexion and distraction A 37-year-old man who is an intravenous drug user presented with headaches. An MRI of the brain was performed, shown in these images. What is an additional expected imaging finding? A. Presence of lactate and amino acids on MR spectroscopy B. Hyperintense capsule on T2 sequence C. Increased apparent diffusion coefficient values in the center of the lesion D. High relative cerebral blood volume ratio in the capsule relative to white matter A 75-year-old man underwent a CT scan of the head. Representative images are shown here. What is the patient’s likely diagnosis? A. Multiple myeloma B. β-thalassemia C. Prostate cancer metastases D. Paget disease The digital subtraction angiogram shown here depicts a(n): A. Middle cerebral artery/anterior cerebral artery bifurcation aneurysm B. Posterior communicating artery aneurysm C. Basilar tip aneurysm D. Ophthalmic artery aneurysm A 53-year-old man is status post–glioblastoma resection and radiation therapy with concomitant temozolomide. A brain MRI shows an increasing enhancing lesion. What neuroimaging finding would favor the presence of recurrent tumor over radiation necrosis/pseudoprogression? A. Increased apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values B. Increased relative cerebral blood volumes C. “Cut green pepper” appearance D. Decreased FDG uptake on PET A 48-year-old woman with a history of HIV underwent a brain MRI, shown in this image. The MRI findings are consistent with:
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree