♦ Preoperative
Operative Planning
- Review imaging (magnetic resonance imaging [MRI], selective spinal angiography)
Embolization
- Preoperative embolization with polyvinyl alcohol, coils, or balloons 1 day before surgery may facilitate resection by reducing blood flow
- Dexamethasone is given to reduce swelling after embolization
Routine Equipment
- Laminectomy instruments
- High-speed drill
- Microsurgical instruments
Special Equipment
- Consider neurophysiological monitoring for somatosensory evoked potentials and motor evoked potentials
Operating Room Set-up
- Open-frame spinal table or electric table with bolsters or Wilson frame
- Ensure ability to obtain anteroposterior and lateral radiographs to confirm operative levels
- Headlight
- Loupes (optional)
- Bipolar (irrigating and nonirrigating) and Bovie cautery
- Microscope with bridge
- General anesthesia
- Arterial line for blood pressure monitoring
- Intravenous antibiotics (cefazolin 2 g or vancomycin 1 g for adults) should be given 30 minutes prior to incision
- Minimize halogenated inhalational agents and nitrous oxide to optimize responses if performing neurophysiological monitoring
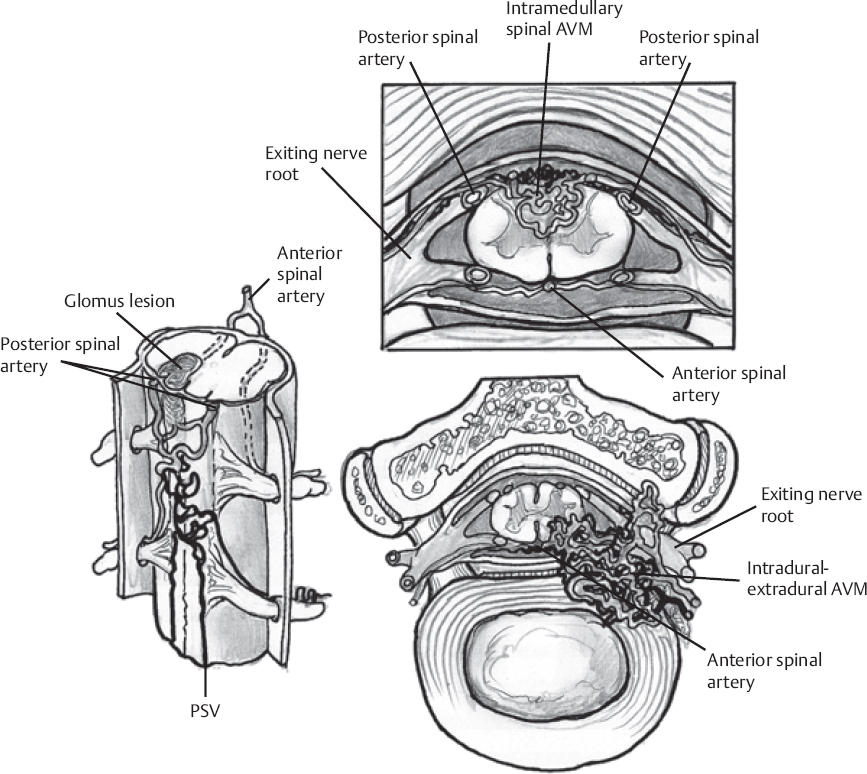
♦ Intraoperative (Fig. 137.1)
Positioning
- Head secured with foam mask, Gardner-Wells tongs with 15 lb of traction, or Mayfield head holder
- If using foam mask, ensure no ocular pressure
- For lesions at T6 or above, arms well padded and tucked along sides; for more distal lesions, shoulders abducted and elbows flexed 90 degrees
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue








