♦ Preoperative
Subcortical Arteriovenous Malformations
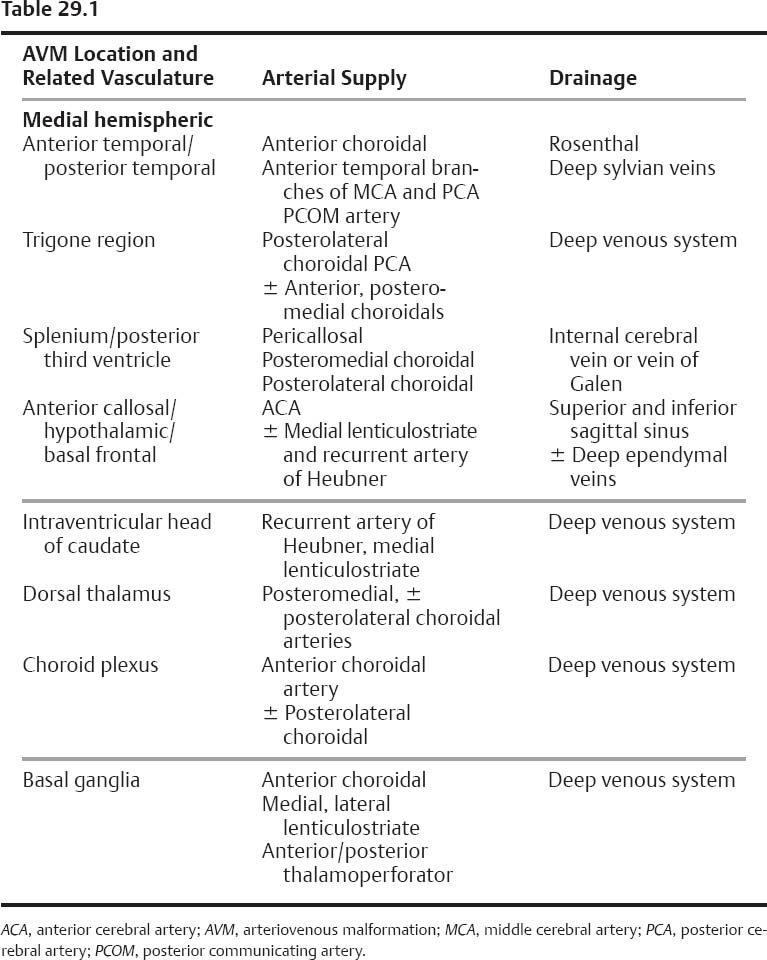
- Medial hemisphere AVMs
- Anterior (amygdalo-uncal): anterior mediobasal temporal lobe
- Posterior (parahippocampal-fusiform): middle and posterior mediobasal temporal lobe, commonly involve walls of temporal horn, posterior inferior thalamus, and lateral geniculate body
- Trigone region: may involve the superior, medial, or inferior atrial walls; pulvinar, deep temporal, parietal, or occipital lobes
- Splenium/posterior third ventricle
- Anterior callosal/cingulate gyrus: may extend laterally into head of caudate or basal ganglia acquiring medial lenticulostriate or Heubner artery feeders. Lateral lenticulostriate feeders indicate internal capsule involvement and relative unresectability.
- Hypothalamic/basal frontal: small and related closely to anterior communicating (ACOM) artery complex, optic chiasm, hypothalamus, septal area
- Anterior (amygdalo-uncal): anterior mediobasal temporal lobe
Intraventricular
- Head of caudate: medial lenticulostriate and Heubner artery supply
- Dorsal thalamus: AVM of medial posterior dorsal thalamus, medial to fornix, involving velum interpositum and roof of third ventricle
- Choroid plexus: usually involve trigone and temporal horn
- Basal ganglia: in basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, lateral to body of lateral ventricle, and medial to insula; thalamoperforator supply commonly present not seen on angiogram
Operative Planning
Surgical resectability is dependent on representation of AVM on ventricular or brain surface, involvement of internal capsule, etc. This can sometimes be determined by the blood supply (i.e., lateral lenticulostriate supply suggests involvement of internal capsule and thus high surgical risk).
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Assess size and location of AVM
- Assess hematoma cavity in relation to AVM for surgical planning
- Relationship of AVM to eloquent structures (ventricular system, thalamus, internal capsule, basal ganglia, etc.)
- Functional MRI
- Diffusion tensor imaging
- Angiography
- Early phase feeding/draining vessels (see Table 29.1)
- Nidus characteristics
- Associated aneurysms
- Venous characteristics: stenosis, etc.
- Assess size and location of AVM
- ± Frameless neuronavigation for craniotomy and trajectory planning
- Irrigating bipolar cautery
- Graduated ball tipped suction tips
- Micro aneurysm clips for temporary occlusion of vessels to determine feeder versus en passage arteries
- Aneurysm/vascular clips for permanent occlusion of larger feeding arteries
- Microdissection instruments: Rhoton dissectors, microscissors
- High-resolution portable digital fluoroscope for angiography
Anesthetic Issues
- Hyperventilation (pCO2 28 to 30 mm Hg)
- Intravenous (IV) mannitol (1 g/kg) at time of incision for brain relaxation
- IV antibiotics 30 minutes prior to skin incision
- IV anticonvulsants loading and maintenance as necessary during case
- Strict blood pressure control maintained at 120 to 130 systolic blood pressure, or ~80% of baseline if systolic blood pressure is higher
♦ Intraoperative
Special
- Lumbar drain as needed (i.e., interhemispheric, subtemporal approaches)
- ± Somatosensory evoked potential
Positioning
- Head position should not impede jugular venous flow
- Use gravity to aid in brain retraction: for subtemporal approach use lateral flexion to allow dependent temporal lobe retraction; for interhemispheric approach place lateral and ipsilateral side down, etc.
- Prepare groin for intraoperative angiogram
Craniotomy/ Dissection
Dependent on Location and Approach
- Mediobasal temporal
- Anterior (amygdalo-uncal): pterional craniotomy, wide sylvian fissure split, retracting AVM with temporal lobe laterally, stretches feeders to be taken from middle cerebral artery, anterior choroidal artery (AChA), posterior communicating artery, and posterior cerebral artery (PCA). Care to preserve peduncle perforators from AChA.
- Posterior (parahippocampal-fusiform): standard temporal craniotomy with horseshoe incision and subtemporal dissection; if larger involving floor of temporal horn, use inferior temporal gyrus corticectomy and enter temporal horn and follow AChA to AVM; superior or middle temporal gyrus approach may be more direct but with increasing risk of visual field defect and language in dominant hemisphere. Safe to resect if inferior to basal ganglia, lateral to internal capsule, and anterior to posterolateral thalamus.
- Trigone region: for AVM inferior/lateral to trigone, use temporal craniotomy and subtemporal or inferior temporal gyrus corticectomy anterior or posterior to Labbé’s vein; for AVM medial or superior to trigone, use a parietooccipital craniotomy with a high parasagittal parietal corticotomy 9 cm above inion and 2 cm ipsilaterally in prone position. In atrium, find posterolateral choroidal and PCA feeders coursing anteroinferiorly to AVM.
- Splenium/posterior third ventricle: use parietooccipital craniotomy and use posterior parietal interhemispheric approach with ipsilateral side down in the lateral position, wide anteroposterior dimension craniotomy for choice to traverse cortical draining veins anteriorly or posteriorly; early access to pericallosal feeders. Enter cingulate gyrus defining anterior and posterior surfaces of AVM, open falx, and identify medial border in splenium; posteromedial choroidal supply then stretched and taken. Deep venous drainage taken last; other option is the contralateral interhemispheric parafalcine approach.
- Anterior callosal/cingulate: frontal craniotomy with interhemispheric approach for simple AVMs; either staged pterional and frontal craniotomies for more complex AVMs with ACOM artery and proximal A2 feeders; other option is a single setting frontal-pterional craniotomy allowing both subfrontal and interhemispheric approaches. Initial control of ACOM artery and A2 feeders followed by pericallosal/callosomarginal feeders, then deep medial and intraventricular dissection and control of medial lenticulostriate supply.
- Hypothalamic/basal frontal: small and closely related to ACOM complex, optic chiasm, hypothalamus, septal area
- Splenium/posterior third ventricle: use parietooccipital craniotomy and use posterior parietal interhemispheric approach with ipsilateral side down in the lateral position, wide anteroposterior dimension craniotomy for choice to traverse cortical draining veins anteriorly or posteriorly; early access to pericallosal feeders. Enter cingulate gyrus defining anterior and posterior surfaces of AVM, open falx, and identify medial border in splenium; posteromedial choroidal supply then stretched and taken. Deep venous drainage taken last; other option is the contralateral interhemispheric parafalcine approach.
- Anterior (amygdalo-uncal): pterional craniotomy, wide sylvian fissure split, retracting AVM with temporal lobe laterally, stretches feeders to be taken from middle cerebral artery, anterior choroidal artery (AChA), posterior communicating artery, and posterior cerebral artery (PCA). Care to preserve peduncle perforators from AChA.
- Intraventricular
- Head of caudate: frontal craniotomy with transventricular access via either an interhemispheric transcallosal or a frontal transcortical route
- Dorsal thalamus: parietooccipital craniotomy with interhemispheric transcallosal approach; with lateral dorsal pulvinar AVM medial to fornix (with posterolateral choroidal feeders), use parietal transcortical transventricular approach
- Choroid plexus: use temporal craniotomy and inferior gyrus approach for anterior lesions (anterior choroidal supply); use high parietal parasagittal approach to trigone and access posterolateral choroidal feeders early
- Head of caudate: frontal craniotomy with transventricular access via either an interhemispheric transcallosal or a frontal transcortical route
- Basal ganglia: generally considered unresectable unless located laterally or with ventricular surface representation. Case series reported describing transsylvian, transcallosal, or parietal transcallosal interhemispheric approaches.
Closure
- Meticulous, obsessive-compulsive hemostasis, confirmed with 10 to 15 minute period of induced hypertension prior to closure
- Line cavity with Surgicel, Avitene, or similar hemostatic agent
- Standard watertight dural closure
- Intraoperative contrast angiogram if high resolution study available
Postoperative
- Strict systolic blood pressure control with IV nitroprusside to maintain below 110 mm Hg to prevent perfusion pressure breakthrough hemorrhage for 48 to 72 hours, in case of large lesions
- Gastroprotection and anticonvulsant maintenance
- Contrast angiogram if not performed intraoperatively
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue