♦ Preoperative
Operative Planning
- Review imaging: magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Volumetric MRI with fiducials if frameless stereotaxy used for intraoperative guidance
Equipment
- Craniotomy tray
- Mayfield head holder
- High-speed drill
- Frameless stereotaxy
- Microscope (optional)
- Frameless stereotaxy (optional)
Operating Room Set-up
- Headlight
- Loupes
- Bipolar cautery and Bovie cautery
- Three-dimensional reconstructions and coregistrations performed if frameless stereotaxy used
- Micro scope
Anesthetic Issues
- Arterial line blood pressure monitoring
- Intravenous (IV) dexamethasone
- IV antibiotic prophylaxis
- Mannitol for brain relaxation
- Phenytoin load if not already maintained on anticonvulsants
♦ Intraoperative
Positioning
- Sitting slouch, lateral, or three-quarter prone with head in Mayfield three-point fixation
- Head is turned to side opposite lesion, vertex slightly elevated, and neck slightly flexed to allow as much of a straight, vertical approach to the parietal lesion as possible
- Ideally, head should be positioned so that a line drawn through the scalp entry point and the geometric center of the tumor is perpendicular to the floor
Minimal Shave
- Use disposable razor
Sterile Scrub and Prep
- See Chapter 2, General Craniotomy Techniques
Incision
- Depending on size of craniotomy, a linear (preferred) or a U-shaped incision based laterally can be used
Craniotomy
- Size and location of the craniotomy should be guided by frameless stereotaxy
- Single burr hole is usually sufficient
- Medial extent of bone flap should be at least 1 cm away from the midline to avoid the superior sagittal sinus and arachnoid granulations
- Bone flap elevated with Penfield no. 3 and flap elevator
- Holes for dural tenting sutures, central tacking suture, and microplate fixation of bone flap drilled, avoiding the medial edge near sagittal sinus
- Craniotomy edges lined with strips of Surgicel; 4–0 silk dural tenting sutures placed
Dural Opening
- Cruciate or U-shaped dural opening
- Moist “wall-off” cotton sponge is used to prevent drying of dural flap
- Corticectomy is started with pial cauterization using irrigating cautery, sharp division with pinch microscissors, and gentle suction to approach the lesion
- Lesion removal
- Two to four tapered retractors are advanced down to expose the surface of the lesion
- Microscope is useful to provide illumination as well as magnification
- Tumor internally debulked, allowing access to choroidal artery feeding the tumor (Fig. 8.1)
< div class='tao-gold-member'>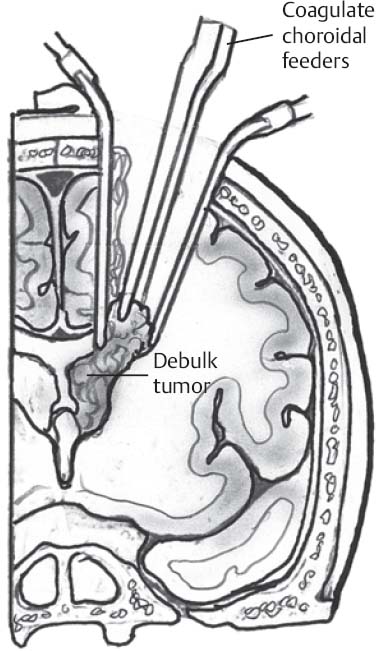
Fig. 8.1 Illustration of superior parietal approach. Debulking of tumor allows rotation to cauterize choroidal arteries.
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
- Two to four tapered retractors are advanced down to expose the surface of the lesion

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







