♦ Preoperative
Operative Planning
- Examination
- Physical: assess cutaneous markings, neurologic deficits
- Urodynamic evaluation with post-void residual and/or more comprehensive testing if urological dysfunction is suspected
- Physical: assess cutaneous markings, neurologic deficits
- Imaging
- Plain films: assess vertebral anomalies and deformity
- Ultrasound or head computed tomography if any suggestion of hydrocephalus
- Magnetic resonance imaging: study of choice to evaluate cause of tethering: fatty filum, lipoma, tumor, split cord, dermal sinus
- Plain films: assess vertebral anomalies and deformity
Special Equipment
- Spinal tray
- Operative microscope
- Intraoperative ultrasound
Anesthetic Issues
- General anesthetic without paralytics
- Neurophysiologic monitoring
- Foley catheter
♦ Intraoperative
Positioning
- Prone, transverse rolls tailored to patient to allow abdomen to hang free
- Check pressure points: eyes, arms, genitals, knees, feet
Prep and Drape
- Done widely in case of need for rostrocaudal extension of incision
Exposure
- Midline incision over lumbosacral junction
- Sharp dissection and bipolar cautery, palpating spinous processes; be wary of bifid dorsal elements
- Mobilize paraspinous muscles in subperiosteal plane with small periosteal elevator to minimize blood loss and facilitate healing
- Perform single level laminectomy of L5 in cases of fatty filum with Leksell/Kerrison rongeurs
- Perform further laminectomies in case of dermal sinus tract, lipoma, or tumor to expose entire region of tethering lesion
- Achieve meticulous epidural hemostasis
- Perform further laminectomies in case of dermal sinus tract, lipoma, or tumor to expose entire region of tethering lesion
Intradural Considerations
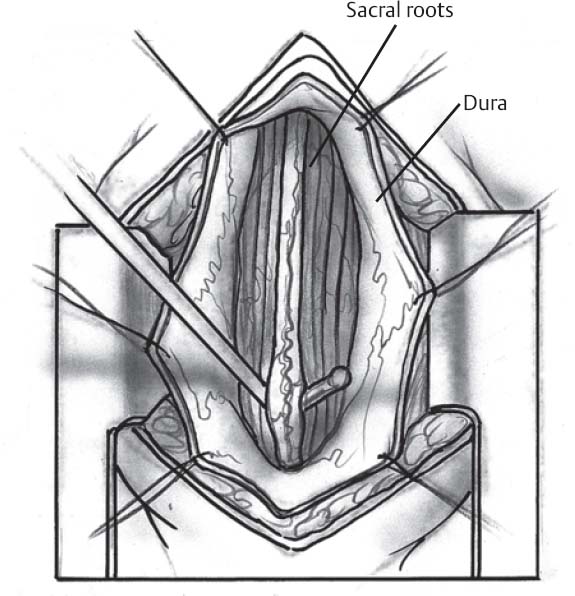
- Incise dura with no. 15 blade and extend with grooved dental instrument
- Avoid incising arachnoid to prevent subdural bleeding which can result in chemical meningitis
- Identify filum terminale, which has a serpiginous vessel on it, cauterize, and divide while gently retracting rostrally to avoid further tension with cautery (Fig. 161.1)
Closure
- 5.0 monofilament (Prolene), running, test with Valsalva maneuver
- Augment with a small piece of dural substitute (Duragen, AlloDerm)
- Watertight fascial closure with heavier absorbable suture (2–0, 3–0 depending on size of patient)
- Running skin closure augmented with cyanoacrylate glue
< div class='tao-gold-member'>Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree