♦ Preoperative
Operative Planning
- Resuscitate according to Advanced Trauma Life Support and traumatic brain injury guidelines
- Review imaging (usually computed tomography [CT] scan, may include magnetic resonance imaging, CT-angiogram, and angiogram)
- Extent, size, and location of hematoma(s)
- Amount of midline shift
- Other cranial pathology; in particular, is there a fracture overlying a major venous sinus or the frontal sinus; skull or orbital fractures
- Hydrocephalus
- Extent, size, and location of hematoma(s)
- Identify location and extent of scalp loss or lacerations
- Cervical spine: if feasible after trauma, clear cervical spine; if not, maintain collar
- Surgical evacuation or decompression should be performed as soon as possible when indicated
- Check coagulation status
Routine Equipment
- Major craniotomy tray with minor set-up
- Subdural head holder (e.g., donut)
- Mayfield head holder may be needed if a ruptured aneurysm is cause of pathology
- High-speed drill
- Headlamp and loupes
- Bipolar cautery
- Intracranial pressure and brain oxygen monitor
- Hemovac drain
- Ventricular drain for hydrocephalus (large bore if intraventricular hemorrhage)
- Dural substitutes (e.g., DuraGen, Dura-Guard [Synovis Surgical Innovations, St. Paul, MN])
- Aneurysm clips if ruptured aneurysm or AVM part of pathology
- Rapid infuser if venous sinus involved
- Leyla (Yasargil) bar can be used to help hold back scalp
Anesthetic Issues
- Major goals
- Prevention of secondary cerebral insults (e.g., hypoxia, hypotension, hyperglycemia)
- Prevent and reduce brain swelling
- Prevention of secondary cerebral insults (e.g., hypoxia, hypotension, hyperglycemia)
- Airway control; no tape or ties around the neck
- Ventilate to maintain PaO2 > 100 mm Hg and PaCO2 25 to 30 mm Hg
- Two large bore intravenous (IV) needles
- Arterial catheter: maintain normotension (appropriate for patient)
- Transfusion products and replacement factors should be available particularly if there is a fracture over a major venous sinus
- Administer IV cefazolin 1 g (also 500 mg metronidazole if air sinus involved)
- IV mannitol 1 g/kg before skin incision
- Load with anticonvulsants: 1 g phenytoin (slow IV)
♦ Intraoperative (Fig. 20.1)
Positioning
- Supine with an ipsilateral shoulder roll
- Head supported on donut, turned to contralateral side, and elevated just above heart level (for ruptured aneurysms, Mayfield head holder, and position for pterional craniotomy see Chapter 5, Pterional Approach).
- If spine is not cleared, position in lateral position on a bean bag with neck in neutral position and sagittal sinus parallel to ground
Sterile Prep and Drape
- See Chapter 2, General Craniotomy Techniques
Scalp Incision
- Shave
- Identify midline and contralateral frontal burr hole for ventricular catheter or intracranial pressure (ICP) monitor
- Incorporate scalp lacerations if feasible
- Start 1 cm anterior to the tragus at the root of the zygoma. Continue in a large reverse question mark fashion. Course just superior to the pinna, extend posterior ~4 to 5 cm, across the parietal region to the midline, then carry forward to the hairline and cross over to the opposite frontal region in a curvilinear fashion along the hairline for ~3 to 4 cm.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>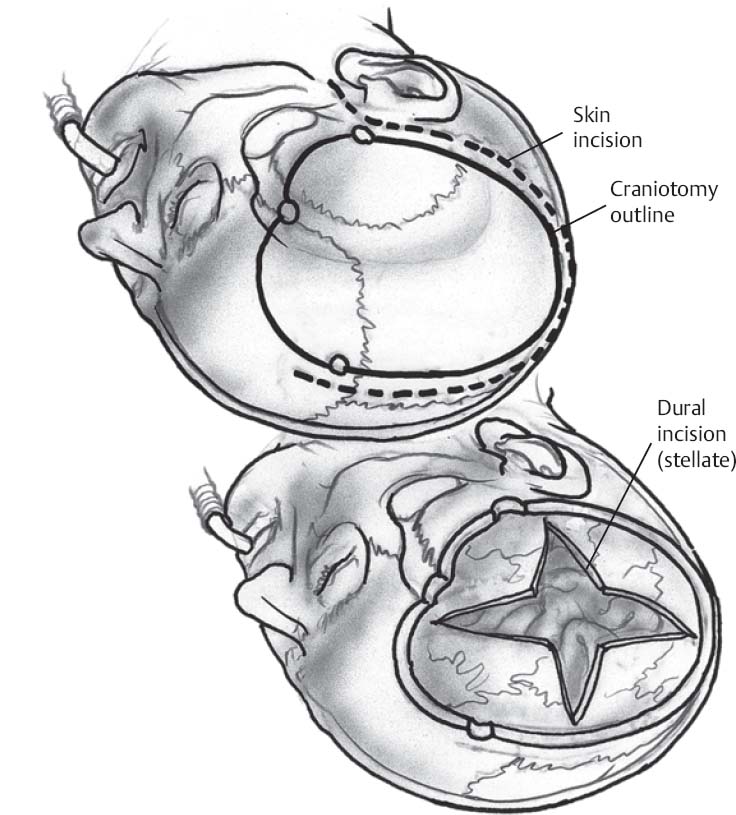 Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue








