Fig. 28.1
Trigonocephaly. Axial (a) and 3D volume-rendered (b) CT images show prominence of the fused metopic suture (arrows)
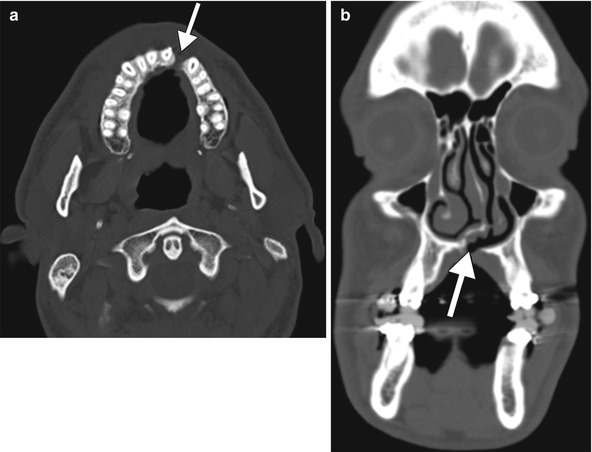
Fig. 28.2
Cleft palate. Axial (a) and coronal (b) CT images show a defect in the left parasagittal hard palate (arrows)
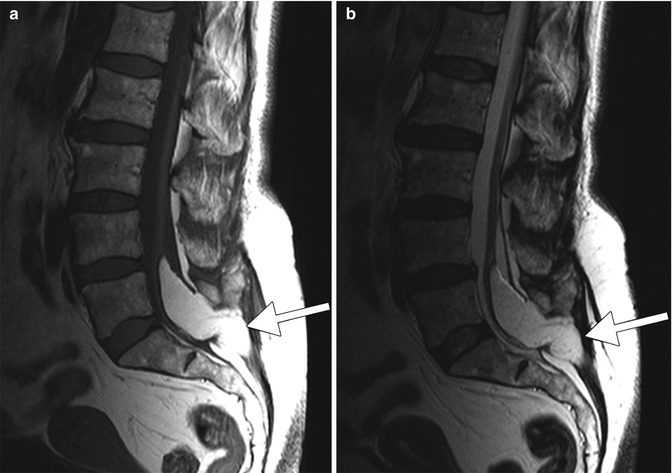
Fig. 28.3
Spina bifida. Sagittal T1-weighted (a) and T2-weighted (b) MR images show lumbosacral dysraphism associated with a lipomyelomeningocele (arrows)
28.4 Differential Diagnosis
Hyperammonemic encephalopathy can be caused by other drugs, such as Tylenol overdose, with identical imaging findings. The imaging findings in congenital valproate-induced malformations are rather characteristic, although there may be confounders in terms of the etiology. While the combination of anomalies and appropriate history may implicate valproate, there are many other potential causes of the associated anomalies.
Suggested Reading
Carter BS, Stewart JM. Valproic acid prenatal exposure. Association with lipomyelomeningocele. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1989;28(2):81–5.CrossRef
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








