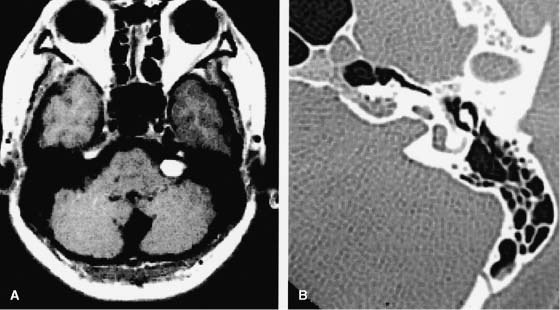
33 Diagnosis Vestibular schwannoma Problems and Tactics Complete removal of the intrameatal portion of a vestibular shwannoma was judged difficult without destroying the inner ear due to drilling the posterior lip of the canal via a lateral suboccipital approach. Direct visualization and removal of the intrameatal tumor was successfully performed with minimum bony drilling by employment of a rigid side-viewing endoscope. Keywords Vestibular shwannoma, internal auditory canal, endoscope This 46-year-old woman had complained of severe hearing disturbance on the left side. The magnetic resonance images (MRIs) showed a tumor in the left cerebellopontine angle. A part of this tumor occupied the internal auditory canal. Computed tomographic (CT) scan showed the widening of the left internal meatus (Fig. 33–1). The surgery was performed via a left lateral suboccipital approach in a park-bench position. The tumor was debulked and removed with standard microsurgical techniques. A small part of the posterior wall of the auditory canal was drilled away. Under the microscope, the tumor seemed to have been completely removed. Then an endoscope was introduced to inspect the inside of the auditory meatus (Fig. 33–2). There was a large amount of residual tumor in the meatus. The tumor was removed under endoscopic view, and the inside of the total auditory canal and the fundus of the inner ear were inspected. After total removal of the tumor, the porus was clearly observed. The anterior–superior quadrant was occupied by the facial nerve. The posterior–inferior quadrant was occupied by the inferior vestibular nerve. The tumor was confirmed to arise from the superior vestibular nerve, and this nerve was completely removed, so that there was a hole at the posterior–superior quadrant. Although the inferior vestibular nerve was preserved, the cochlear nerve could not be preserved (Fig. 33–3). The postoperative course was uneventful. Follow-up MRI study for 8 years after the operation revealed no sign of recurrence of the tumor. FIGURE 33–1 Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT). (A) MRI, axial view, showing a left vestibular shwannoma. (B) Left petrous bone axial CT, showing enlarged left internal meatus due to tumor. The endoscope should be of high resolution.1
Removal of Vestibular Schwannoma in the Internal Auditory Canal with the Aid of Neuroendoscopy
Clinical Presentation
Surgical Technique
Outcome
Endoscopic Instrumentation
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree