Chapter 15 Atlas of the Human Brainstem*
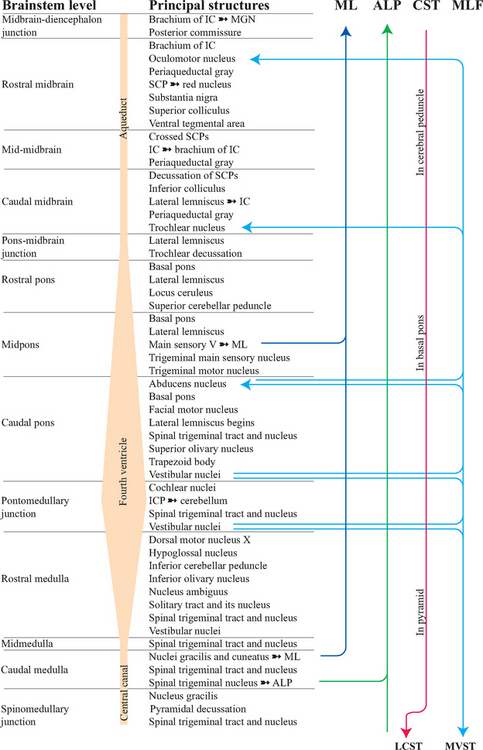
This series of five chapters on the functional anatomy of the brainstem concludes here, with a summary of the principal contents of the brainstem at each level (Figs. 15-1 to 15-3), a series of transverse sections of the brainstem (Figs. 15-4 to 15-9), and brief descriptions of structures that are indicated in these sections.
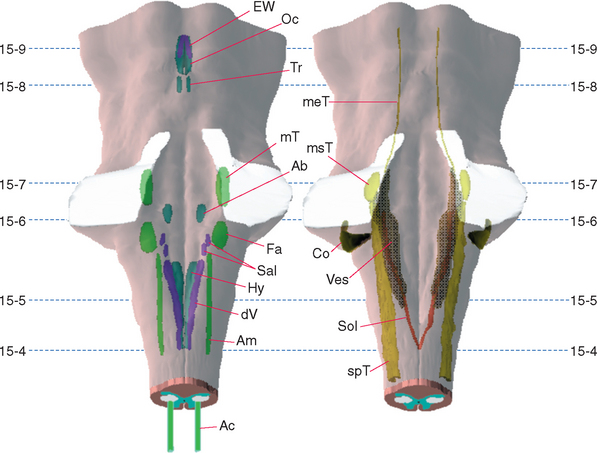
Figure 15-1 Three-dimensional reconstructions of the brainstem, with motor (left) and sensory (right) cranial nerve nuclei indicated. Dashed lines indicate the planes of the sections shown in Figures 15-4 to 15-9. Ab, abducens nucleus; Ac, accessory nucleus; Am, nucleus ambiguus; Co, cochlear nuclei; dV, dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus; EW, Edinger-Westphal nucleus; Fa, facial motor nucleus; Hy, hypoglossal nucleus; meT, mesencephalic nucleus of the trigeminal; msT, trigeminal main sensory nucleus; mT, trigeminal motor nucleus; Oc, oculomotor nucleus; Sal, salivary nuclei; Sol, nucleus of the solitary tract; spT, spinal trigeminal nucleus; Tr, trochlear nucleus; Ves, vestibular nuclei.
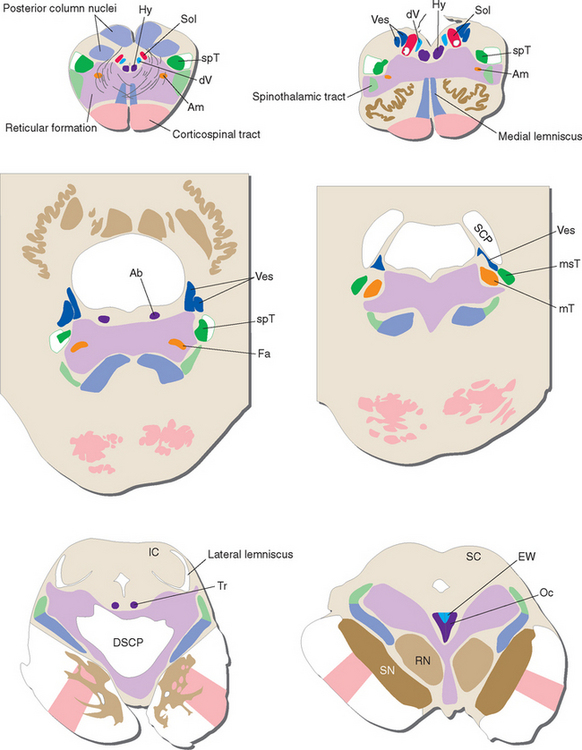
Figure 15-2 Schematic views of the transverse sections of the brainstem shown photographically in Figures 15-4 to 15-9, each enlarged to about three times its actual size. Major tracts and cranial nerve nuclei are indicated. DSCP, decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncles; IC, inferior colliculus; RN, red nucleus; SC, superior colliculus; SCP, superior cerebellar peduncle; SN, substantia nigra; other abbreviations as in Figure 15-1.
(Modified from Nolte J, Angevine JB Jr: The human brain in photographs and diagrams, ed 3, St. Louis, 2007, Mosby.)
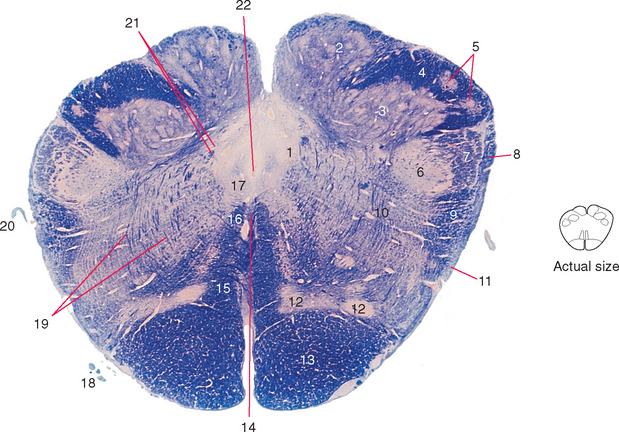
Figure 15-4 Caudal medulla (close to the level of the obex).
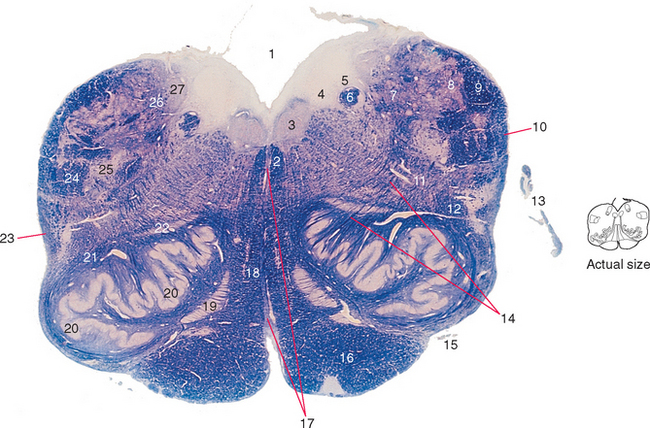
Figure 15-5 Rostral medulla.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree