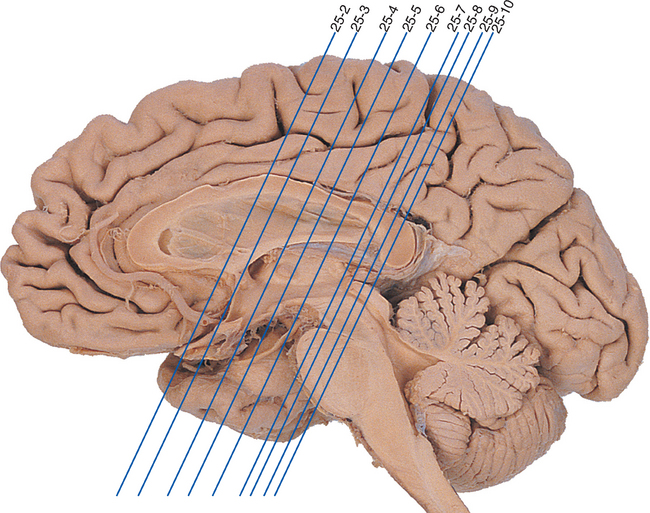
Chapter 25 Atlas of the Human Forebrain*
When the nervous system is discussed in terms of functional subsystems, as in the preceding chapters, it is sometimes difficult to envision how the various parts are related to the whole. Therefore an abbreviated atlas is provided here using the same philosophy as in Chapter 15, with a wide variety of forebrain structures and a few brainstem structures labeled.
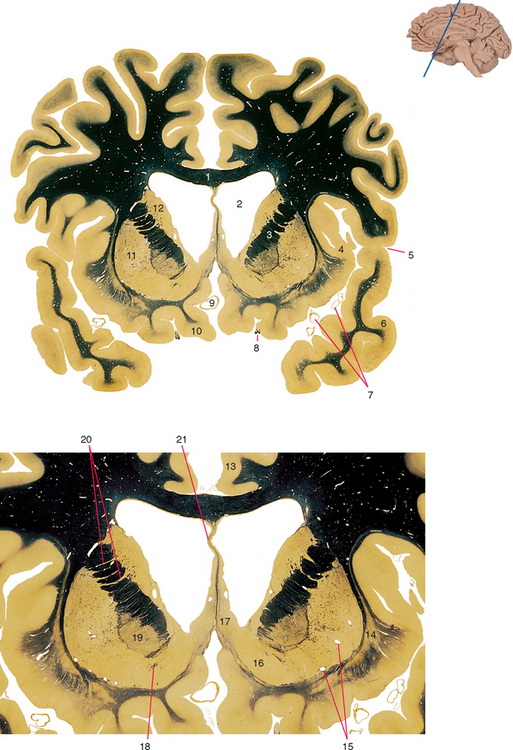
Figure 25-2 Anterior horn of the lateral ventricle.
3. Anterior limb of the internal capsule. Contains projections to and from prefrontal and anterior cingulate cortex, including those from the dorsomedial and anterior nuclei of the thalamus.
7. Branches of the middle cerebral artery. Will emerge from the lateral sulcus and supply the lateral surface of the cerebral hemisphere.
9. Anterior cerebral artery. Branches parallel the corpus callosum and supply the medial surface of the frontal and parietal lobes.
10. Gyrus rectus. Part of orbital frontal cortex; extensive limbic connections, particularly in circuits involving the amygdala.
12. Caudate nucleus (head). The part of the striatum predominantly connected with association cortex.
13. Cingulate gyrus. Extensive limbic connections: anteriorly in circuits involving the amygdala, and posteriorly in circuits involving the hippocampus.
17. Septal nuclei. Reciprocally connected with the amygdala, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and other limbic structures.
19. Globus pallidus (external segment). Afferents from the striatum, efferents to the subthalamic nucleus and other parts of the basal ganglia.
20. Gray bridges between the putamen and caudate nucleus; part of the reason the striatum got its name.
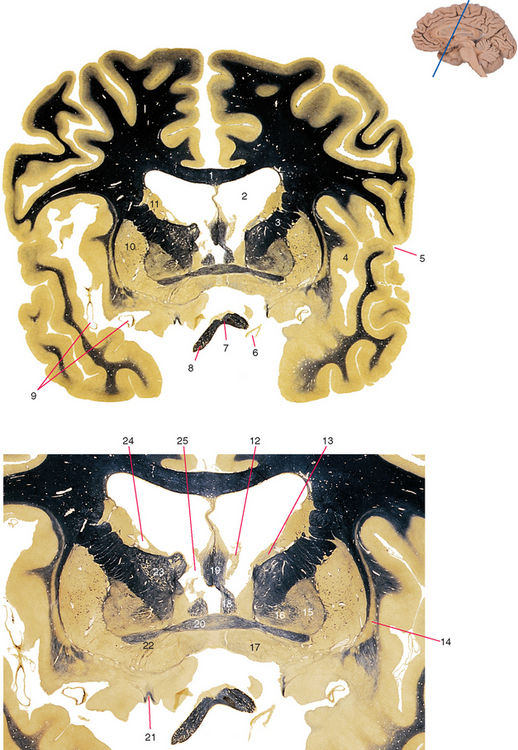
Figure 25-3 Anterior commissure.
6. Internal carotid artery, just before it bifurcates into the anterior and middle cerebral arteries.
8. Optic nerve. Axons of retinal ganglion cells on their way to the lateral geniculate nucleus, superior colliculus, and a few other sites.
9. Branches of the middle cerebral artery. Will emerge from the lateral sulcus and supply the lateral surface of the cerebral hemisphere.
11. Caudate nucleus (junction between the head and body). The part of the striatum predominantly connected with association cortex.
13. Stria terminalis. Efferents from the amygdala to the septal nuclei, basal forebrain, and hypothalamus.
15. Globus pallidus (external segment). Afferents from the striatum, efferents to the subthalamic nucleus and other parts of the basal ganglia.
16. Globus pallidus (internal segment). Afferents from the striatum and subthalamic nucleus, efferents to the thalamus and midbrain reticular formation.
17. Basal forebrain. Includes the basal nucleus (of Meynert), groups of large cholinergic neurons that innervate most forebrain areas.
18. Column of the fornix. Efferents from the hippocampus to the septal nuclei, basal forebrain, and mammillary body.
19. Body of the fornix. Efferents from the hippocampus to the septal nuclei, basal forebrain, and mammillary body.
20. Anterior commissure. Commissural fibers interconnecting the temporal lobes, together with a few crossing olfactory fibers.
23. Reticular nucleus, covering the anterior (and lateral) surface of the thalamus. Afferents from the thalamus and cerebral cortex, GABAergic efferents to the thalamus.
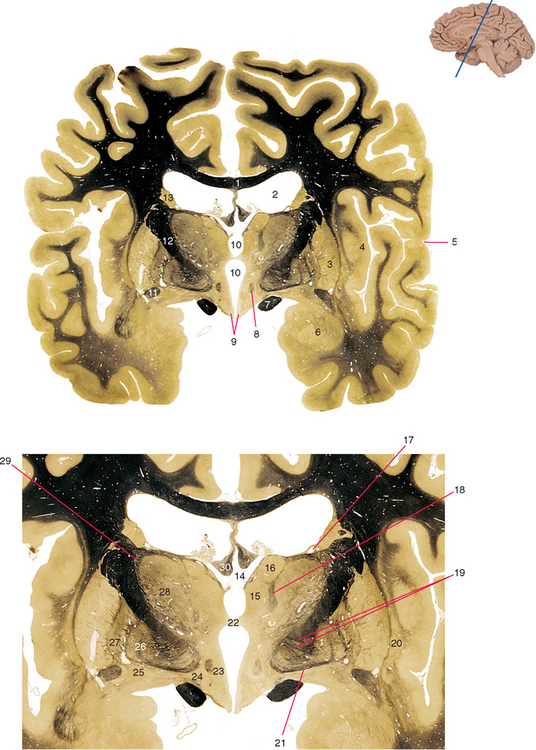
Figure 25-4 Anterior thalamus.
7. Optic tract. Axons of ganglion cells from half of each retina, on their way to the lateral geniculate nucleus, superior colliculus, and a few other sites.
10. Third ventricle. The two portions indicated are separated by the interthalamic adhesion (massa intermedia).
12. Posterior limb of the internal capsule. Contains projections to and from sensorimotor and parietal cortex, including corticospinal fibers and the somatosensory radiation.
13. Caudate nucleus (body). The part of the striatum predominantly connected with association cortex.
14. Transverse cerebral fissure. An extension of subarachnoid space, situated above the roof of the third ventricle and containing the internal cerebral veins.
16. Anterior nucleus. Afferents from the mammillary body (via the mammillothalamic tract), efferents to the cingulate gyrus.
18. Mammillothalamic tract. Projection from the mammillary body to the anterior nucleus of the thalamus. Part of the Papez circuit.
19. Lenticular fasciculus (passing through the internal capsule). Part of the projection from the internal segment of the globus pallidus to the thalamus.
21. Ansa lenticularis. Part of the projection from the internal segment of the globus pallidus to the thalamus.
23. Medial zone of the hypothalamus. At this level, includes the ventromedial and dorsomedial nuclei.
25. Location of the basal nucleus (of Meynert). Groups of large cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain that innervate most forebrain areas.
26. Globus pallidus (internal segment). Afferents from the striatum and subthalamic nucleus, efferents to the thalamus and midbrain reticular formation.
27. Globus pallidus (external segment). Afferents from the striatum, efferents to the subthalamic nucleus and other parts of the basal ganglia.
28. Ventral anterior and ventral lateral (VA/VL) nuclei. Afferents from the cerebellum and basal ganglia, efferents to motor areas of cortex.
29. Reticular nucleus of the thalamus. Afferents from the thalamus and cerebral cortex, GABAergic efferents to the thalamus.
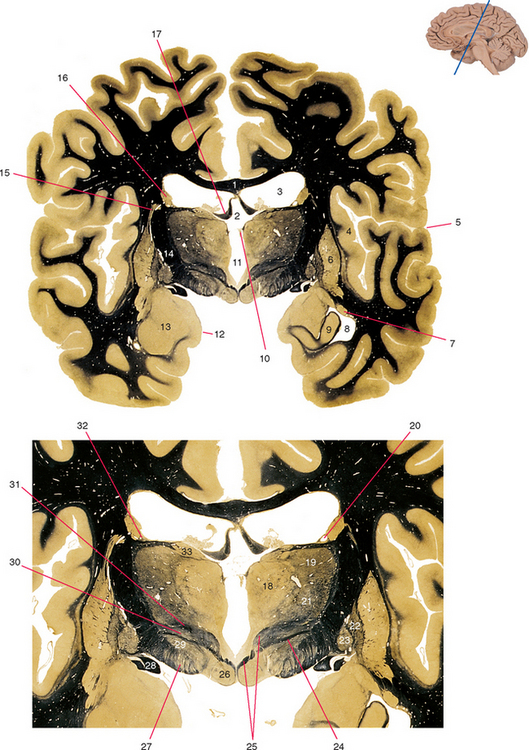
Figure 25-5 Midthalamus; mammillary bodies.
2. Transverse cerebral fissure. An extension of subarachnoid space, situated above the roof of the third ventricle and containing the internal cerebral veins.
7. Caudate nucleus (tail). The part of the striatum predominantly connected with association cortex.
12. Uncus. The proximity of the surface of the uncus to the cerebral peduncle can cause clinical problems.
14. Posterior limb of the internal capsule. Contains projections to and from sensorimotor and parietal cortex, including corticospinal fibers and the somatosensory radiation.
15. Gray bridge between the putamen and caudate nucleus; part of the reason the striatum got its name.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree