12 Basic Overview of Electromyography
1. The differential diagnosis, determined by the clinical findings and nerve conduction data.
2. The ease with which the muscle can be located and activated [e.g., although both the tibialis anterior (TA) and medial gastrocnemius (MG) are distal leg muscles, the TA is much easier to activate than the MG].
3. The degree of pain associated with sampling the particular muscle [e.g., both the first dorsal interosseous (FDI) and abductor pollicis brevis (APB) are distal C8–T1 innervated muscles, but the APB is much more painful to sample than the FDI for most patients).
Equipment
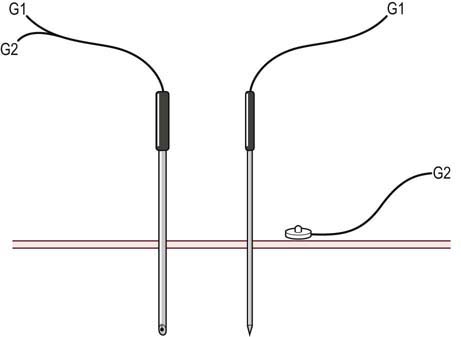
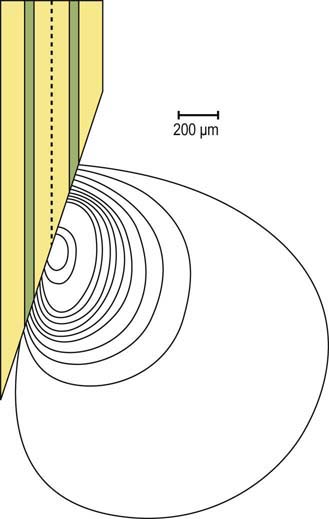
In addition to the EMG machine, an EMG needle, needle cable, ground electrode, and gloves are necessary to perform the needle EMG study. The ground electrode is applied to the limb being studied in order to suppress noise and for electrical safety. Disposable gloves must always be worn to prevent the transmission of bloodborne infections between the patient and the electromyographer. The EMG needle is connected to a cable and then plugged into the EMG machine. Either a concentric or monopolar EMG needle can be used (Figure 12–1). When an electrical potential is measured, including the potentials measured during the needle EMG study, voltage is measured as the difference between the active and reference recording electrodes. The concentric needle contains both the active and reference electrodes in the needle itself (Figure 12–2). The shaft of the needle serves as the reference electrode, whereas the active electrode runs as a very small wire through the center of the needle and is exposed at the needle tip. The end of the concentric needle is beveled, resulting in a recording area that has a “teardrop” configuration (Figure 12–3). In contrast, the monopolar needle is Teflon coated, and its exposed end serves as the active recording electrode. Its recording area is that of a sphere around the tip of the needle. For the monopolar needle montage, an additional surface disc electrode is required as the reference electrode.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree