C1-C2 Instability
Julia Crim, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Trauma
Jefferson C1 Fracture
Odontoid C2 Fracture
Hyperflexion Injury, Cervical
Rotary Subluxation, Atlantoaxial
Os Odontoideum
Pathologic Vertebral Fracture
Non-Traumatic
Rheumatoid Arthritis, Adult
Spondyloarthropathy, Seronegative
Less Common
Non-Traumatic
CPPD
Osteomyelitis, C1-C2
Grisel Syndrome
Achondroplasia
Trisomy 21 (10-20%, 1-2% Symptomatic)
Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia
Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS)
Mimics of Instability
Normal Variant
Incomplete Fusion, Posterior Element
Craniovertebral Junction Variants
Calcific Tendinitis, Longus Coli
Pseudosubluxation (Childhood)
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Imaging Evaluation of Instability
Transverse ligament of dens critical to anteroposterior stability
Normal distance from inferior margin C1 arch to dens < 2 mm in adults
Increased distance indicates rupture transverse ligament
Flexion-extension views useful
May be false negative in 1st week after injury
Jefferson fracture unstable if combined lateral displacement of C1 lateral masses relative to articular pillars of C2 ≥ 7 mm
Incomplete fusion of posterior elements does not cause instability because ligaments intact
Grisel syndrome in association with retropharyngeal infection, primarily seen in children
Rheumatoid arthritis often also involves atlanto-axial articulations, lower cervical uncovertebral and facet joints
Will not be present in C-spine unless peripheral involvement also present
RA pannus does not calcify
Calcified inflammatory tissue around dens usually due to CPPD
Other Essential Information
Craniocervical junction injuries often multilevel
Os odontoideum felt to represent nonunited dens fracture
Image Gallery
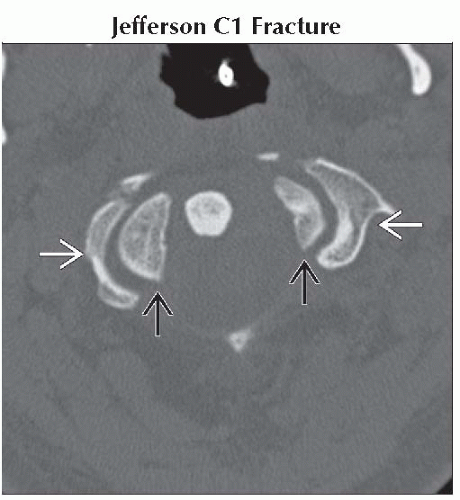 Axial bone CT shows lateral dislocation of lateral masses of C1
 relative to C2 articular pillars relative to C2 articular pillars  . Combined lateral displacement of lateral masses > 7 mm confirms instability. . Combined lateral displacement of lateral masses > 7 mm confirms instability.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|