Cervical, Chronic Post-Traumatic Abnormality
Julia Crim, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Post-Traumatic
Accelerated Degeneration
Os Odontoideum
Post-Operative Spinal Complications
Kyphosis
Scoliosis
Ligament Ossification
Trauma Mimics
Ossification, Anterior Longitudinal Ligament
DISH
Post-Operative Change, Normal
Pathologic Vertebral Fracture
Rheumatoid Arthritis, Adult
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Craniovertebral Junction Variants
Klippel-Feil Spectrum
OPLL
Achondroplasia
Less Common
Osteomyelitis, C1-C2
Crystalline Arthropathies
Gout, calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease, hemodialysis arthropathy
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Single level &/or upper cervical degenerative disease suggests prior injury
Wide surgical decompression without fusion often yields unstable spine with secondary deformity
Ossification of anterior longitudinal ligament (ALL) known as DISH when > 4 adjacent levels affected
May see smaller foci of ossification due to trauma, aging, or seronegative arthropathy
Look for other signs of trauma to help make distinction
Small foci of ossification ALL distinguished from trauma by normal configuration of underlying vertebra
Posterior element injuries not uncommonly missed acutely
Malalignment, focal degenerative disease signs suggest prior injury
Fracture nonunion sometimes difficult to determine
Prolonged failure of bridging callus
Time to healing depends on age, health, and fracture location
Sclerosis of apposing fracture margins
Craniocervical instability due to multiple causes
Trauma
Arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative, calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease
Congenital: Achondroplasia, trisomy 21
Infection
Kyphosis, scoliosis due to many causes
Short curve deformities suggest trauma, infection, congenital, or tumor
Image Gallery
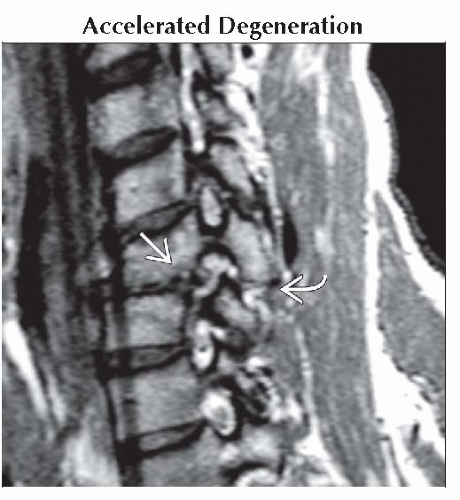 Sagittal oblique T2WI MR shows 25 year old man with post-traumatic disc degeneration
 and uncovertebral arthritis. Chronic facet subluxation and uncovertebral arthritis. Chronic facet subluxation  is easily missed unless oblique views are obtained. is easily missed unless oblique views are obtained.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|