Cervical, Lower, Post-Traumatic Bony Abnormality
Julia Crim, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Subaxial Cervical Spine Fractures
Hyperflexion Injury, Cervical
Posterior Column Injury, Cervical
Burst Fracture, Cervical
Hyperflexion-Rotation Injury, Cervical
Lateral Flexion Injury, Cervical
Hyperextension Injury, Cervical
Hyperextension-Rotation, Cervical
Pathologic Vertebral Fracture
Shear Injury
Post-Traumatic Deformity
Accelerated Degeneration
Facet Arthropathy, Cervical
Kyphosis
Scoliosis
Nontraumatic Entities that Mimic Trauma
Ossification of Anterior Longitudinal Ligament
Metastases, Lytic Osseous
Rheumatoid Arthritis, Adult
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Klippel-Feil Spectrum
Post-Operative Change, Normal
Facet Arthropathy, Cervical
Incomplete Fusion, Posterior Element
Osteomyelitis, Pyogenic
Less Common
Spondyloarthropathy, Seronegative
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Evaluate for post-traumatic instability with flexion/extension views
Not accurate in 1st week after injury
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Signs of acute injury
Malalignment, focal kyphosis, or lordosis
Soft tissue swelling (not always present)
Fracture line
Signs of remote trauma
Cervical deformity
Single level facet osteoarthritis
MR very helpful in questions of acuity of injury, and distinguishing trauma from trauma mimics
Look for bone marrow edema on fluid sensitive sequences
Trauma mimics
Ossification of anterior longitudinal ligament: No bone donor site visible
Growth disturbance in congenital and childhood disorders
Infection: Vertebral endplates eroded
Metastatic disease
May see round or oval bone lesion, or involvement of entire vertebral body
Cortex destroyed not just disrupted as in trauma
Incomplete fusion shows smoothly contoured margins, unlike trauma
Image Gallery
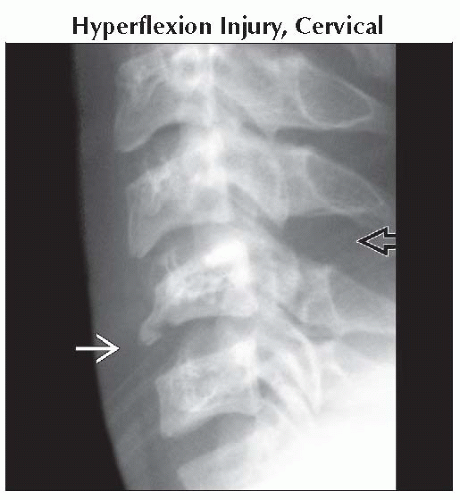 Lateral radiograph shows flexion teardrop fracture
 due to anterior compression, and widened interspinous distance due to anterior compression, and widened interspinous distance  due to posterior distraction. due to posterior distraction.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|