Hyperattenuating (“Dense”) Artery
Sheri L. Harder, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Physiologic Hyperdensity
Cerebral Ischemia-Infarction, Acute
Less Common
Atherosclerosis, Intracranial
Polycythemia
Fusiform Aneurysm (ASVD, Non-ASVD)
Dissection
Pseudoaneurysm
Rare but Important
Devices and Complications
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Presence, localization of focal neurologic findings important
High hematocrit/hemoconcentration can mimic “dense MCA sign”!
Compare to other intracranial vessels!
Diffuse low density brain (anoxia, etc.) makes ALL vessels appear hyperdense, mimics thrombus or SAH!
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Physiologic Hyperdensity
Circulating blood in arteries normally slightly hyperdense to brain
Especially prominent in newborns with unmyelinated, hypodense brain
Diffuse cerebral edema makes vessels appear hyperdense (“false dense MCA sign”)
Cerebral Ischemia-Infarction, Acute
Acute thrombus in affected vessel (e.g., true “dense MCA sign”)
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Atherosclerosis, Intracranial
ASVD with microcalcifications can mimic “dense” MCA
Polycythemia
Can be physiologic (elevated hematocrit in newborns, high altitude, etc.)
Numerous pathologic causes
Fusiform Aneurysm (ASVD, Non-ASVD)
Vertebrobasilar > carotid circulation
Thickened walls may appear hyperdense
Non-ASVD: Younger; inherited vasculopathy, immune disorder
Dissection
Most posterior circulation
Trauma most common etiology
Pseudoaneurysm
Trauma most common etiology
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Devices and Complications
Coils, balloons, stents, methacrylate, etc.
Embolized foreign bodies, calcified atheromata can cause hyperattenuating vessel sign
Image Gallery
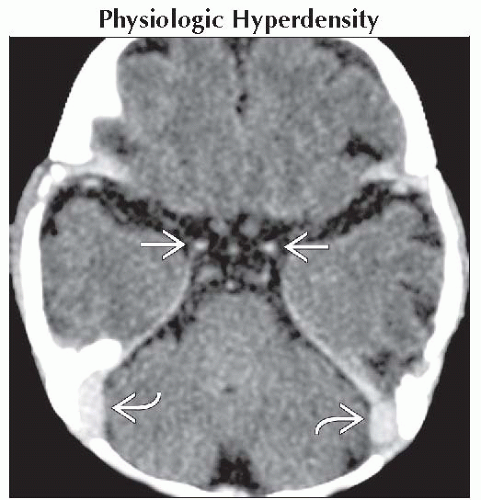 Axial NECT demonstrates relatively hyperdense internal carotid arteries
 in this neonate. Note the corresponding increased density of the transverse sinuses in this neonate. Note the corresponding increased density of the transverse sinuses  . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|