• With the working portal appropriately docked on the level of pathology, an initial exposure can be performed.
• Often there are residual paraspinal muscle fibers that must be removed from the lamina.
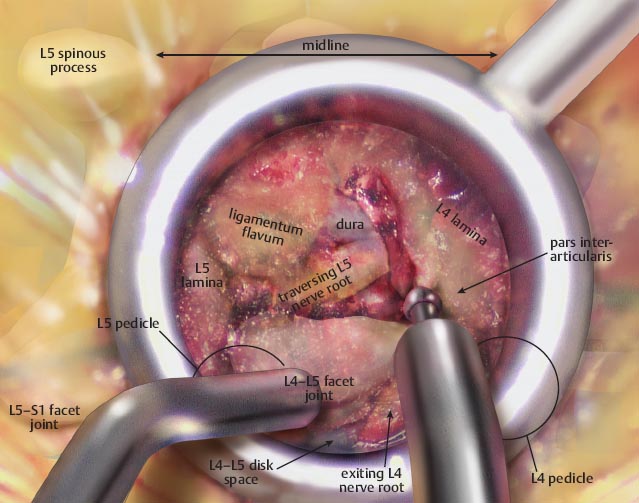
• Once the lamina is exposed, a high-speed burr is used to perform a laminectomy. Bone is removed until only the flavum is visualized.
– The laminectomy is extended laterally through the pars interarticularis.
– Bone is saved in a bone trap.
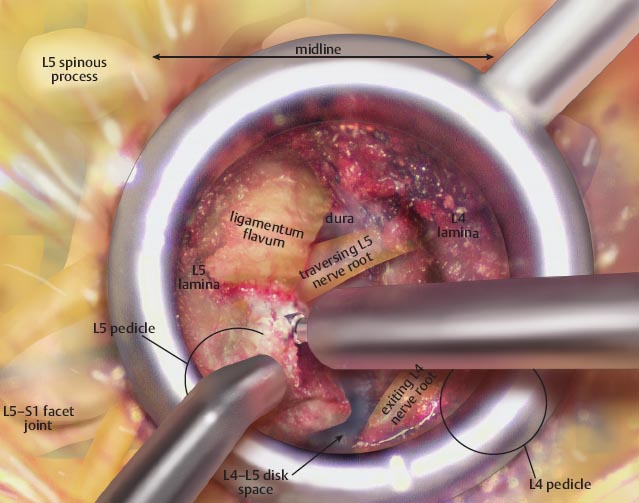
• The laminectomy is extended cranially until the end of the flavum insertion is identified.
– Epidural fat or dura is often seen.
• This marks the cranial extent of the laminectomy.
• The burr is then directed directly laterally through the pars interarticularis.
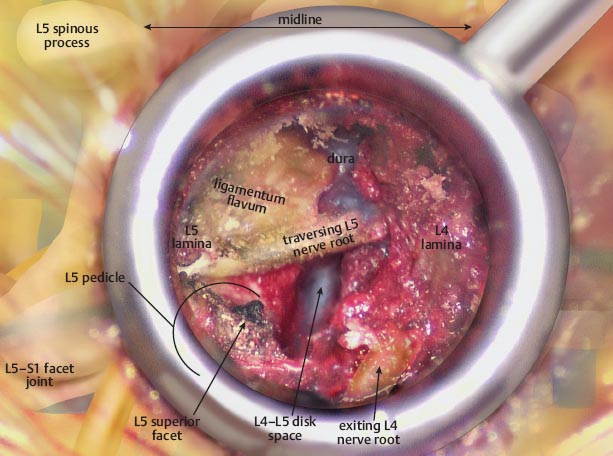
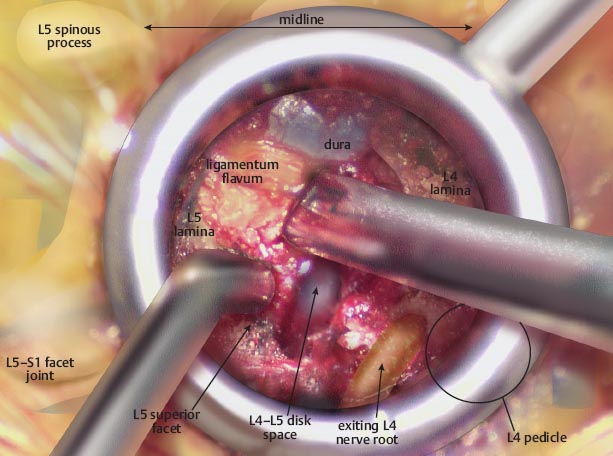
• Once the burr is through the pars, the inferior articular process can be removed, completing the facetectomy and exposing the involved disk space.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








