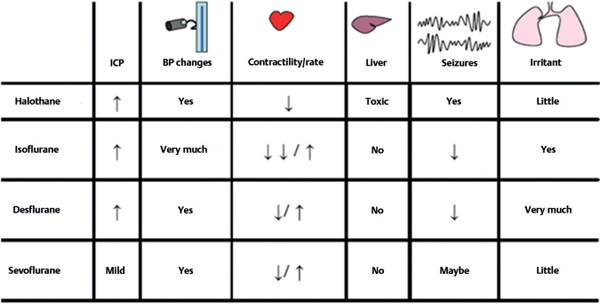
59 Name some of the intravenous anesthetics. • Barbiturates: thiopental • Benzodiazepines: midazolam • Etomidate • Ketamine • Propofol • Opioids: fentanyl What is a potential complication of barbiturate use? Hypotension or tachycardia; ensure adequate fluid balance and volume. Which barbiturate can lower seizure threshold (make seizure more likely)? Methohexital (Brevital®) Brevis = short (lasts a few minutes)1 Which is the preferred benzodiazepine for conscious sedation and induction? Midazolam (Versed®) Why is etomidate good for neurosurgery patients? Cardiovascular stability and rapid recovery (important so that we can get an exam soon after surgery) What is a potential complication of its use? Adrenal suppression and myoclonus (not to be confused with seizure activity)2 Which induction agent can increase CBF and ICP? Ketamine. The rest essentially reduce ICP, metabolism, and flow. What are potential complications of propofol use? • Propofol-related infusion syndrome (PRIS) • Hypotension (more with bolus) • Apnea • Hypertriglyceridemia (>500 mg/dL) An otherwise unexplained severe metabolic acidosis (usually lactic) associated with either cumulative high-dose propofol or long infusion time; potentially fatal (in approximately 60%) Is there anything else other than metabolic acidosis that occur with PRIS? Yes, cardiac failure, enlarged liver (children), and rhabdomyolysis may occur. What is the incidence of this complication? Unknown. No registry is available. Fewer than 100 cases have been described in the medical literature so far. How can you prevent it and monitor its appearance? 1. Avoid more than 5 mg/kg/h for longer than 48 hours or short-term administration of large doses. 2. Consider other sedative if vasopressor requirements during propofol infusion are increasing! 3. Monitor arterial blood gases (ABGs), blood pressure (BP), electrocardiograms (ECGs), creatine kinase (CK), and lactic acid levels. What is the treatment? Supportive. Stop infusion of propofol. Pressors and bicarbonate may be required. What is a common characteristic of volatile (inhaled) anesthetics? They are vasodilators and therefore can increase CBF and ICP. Is there any other way they can increase ICP? Most of them are respiratory irritants and can trigger a sympathetic response during induction, increasing BP and ICP. Do they present any other common advantage with regard to cerebral protection? They tend to decrease the metabolic consumption of oxygen. Which one is particularly irritant? Isoflurane (Isoflurane = Irritant) Which provide cerebral protection5? Isoflurane, desflurane, and sevoflurane Which one of them is the choice for long procedures in obese patients? Desflurane, because it has the lowest fat-to-blood solubility Fig. 59.1 Table of neuroanesthetics, their actions, and their impact on body systems.
Pharmacological Aspects
59.1 Systemic Effects
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree






