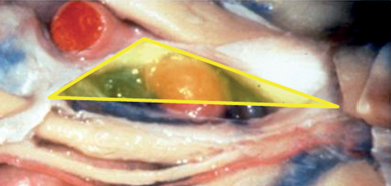
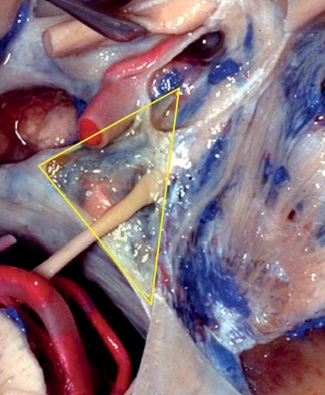
43 What groups of anatomical triangles exist in the skull base?1 Parasellar group: includes the anteromedial (clinoidal), oculomotor (paramedial), supratrochlear, and infratrochlear (Parkinson’s triangle) Middle fossa group: anterolateral, lateral, posterolateral (Glasscock’s) and posteromedial (Kawase’s) Paraclival group: inferomedial and inferolateral (trigeminal) triangles How many triangles are there in the roof of the cavernous sinus? Two, clinoidal and oculomotor How many triangles are there in the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus? Two as well, supratrochlear and infratrochlear Fig. 43.1 Lateral view of the parasellar/cavernous sinus region. Right parasellar anteromedial triangle. Note the entry of the third nerve in the superior aspect of the cavernous sinus. Note CN VI lateral to CN III and in contact with the lateral aspect of the ICA. What are the limits of the anteromedial (clinoidal) triangle? Medial border is the optic nerve. Lateral border is CN III. Posterior border is the dural between both, which relates to the distal dural ring of the ICA. What structure needs to be drilled to access this triangle? The anterior clinoid process (ACP) What are its contents? • Anterior loop and horizontal segment of the parasellar ICA • Venous trabeculae • Fibrous tissue related to the proximal ring of the carotid artery What are the limits of the oculomotor triangle? Medial border: interclinoidal dural fold Posteromedial border: posterior petroclival ligament Anteromedial border: anterior petroclival ligament Fig. 43.2 Superior view of the oculomotor triangle. The ACP has been drilled to expose the carotid artery.
Skull Base Triangles
Skull Base Triangles
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue

Full access? Get Clinical Tree






