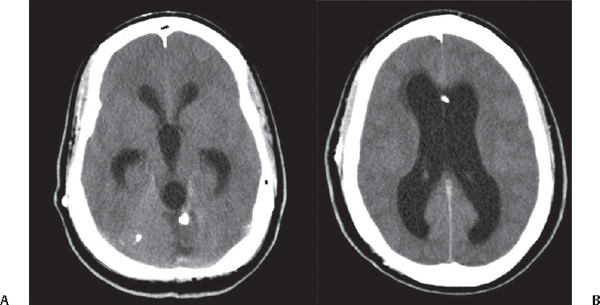
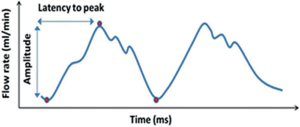
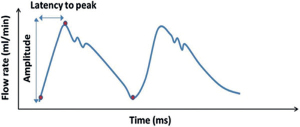
76 What is hydrocephalus? An abnormal accumulation of CSF volume in the ventricular system that is disproportionate to the brain volume How can hydrocephalus be classified? 1. Idiopathic (e.g., without apparent cause) 2. Secondary (e.g., to tumor mass, blood, inflammation) 3. Progressive (active)/arrested (inactive)/compensated 4. High/normal/low pressure 5. High/normal/low volume 6. Adult/infant/neonatal/in utero 7. Obstructive/communicating/combined (both) 8. Functional (hypersecretion/decreased absorption) 9. Compensatory or “ex vacuo” (e.g., brain atrophy) 10. Complex (associated with multicompartments, cysts) Is it curable? To this day, very few cases can be considered “cured” after surgery (unless secondary to a curable condition, see below). It is a condition that is, in most cases, temporarily controlled with CSF diversion techniques. Fig. 76.1 (A,B) CT scan with contrast demonstrating hydrocephalus with involvement of all four ventricles and associated posterior fossa mass. Resection of the mass is believed possibly to be able to control (and potentially “cure”) the hydrocephalus. Note the radiographic CT signs of hydrocephalus including dilatation of the temporal horns, rounding of the third ventricles, effacement of the convexity sulci, enlargement of the lateral ventricles, and transependymal CSF flow (seen around frontal horns of lateral ventricles). What is the incidence of hydrocephalus at birth? Approximately 0.7 to 0.8 per 1000 live births How can neonatal hydrocephalus be detected? By ultrasound in utero or after birth What segment of the lateral ventricles is typically increased in size in neonatal hydrocephalus? Atrium and occipital horns of the lateral ventricles What are the three most common causes?1 1. Intraventricular hemorrhage 2. Spina bifida 3. Tumors What are three most common symptoms?2 1. Irritability 2. Nausea/vomiting 3. Headache What are the three most common signs?2 1. Increased head circumference 2. Bulging fontanelle 3. Delayed development What are some indicators of negative prognosis for shunts in neonates? • Age <6 months • Cortical mantle <1 cm at the coronal suture • Complex hydrocephalus • Association with congenital anomalies What is one of the mechanisms of hydrocephalus in achondroplasia (dwarfism)? Venous obstruction Why is the mechanism stated above important? Because ventricular volume decreases rapidly after shunting What happens to patients with the above problem when they grow older? Shunt obstruction may not be manifested by increased ventricular volume, making diagnosis of shunt failure difficult What is that situation called? Normal volume hydrocephalus (ICP will be elevated) What is the equivalent situation in the adult? Pseudotumor cerebri Is pseudotumor a form of hydrocephalus? No. What should you always inquire about when evaluating shunts in the pediatric population? • Developmental milestones • Performance in school and social behavior as a measure of cognitive development Can cognitive development be normal if the ventricle size does not completely return to normal? Yes What is “arrested-hydrocephalus”? When a patient with adequately treated hydrocephalus has reached a point where the ventricles are stable in size, with equilibrium in the pathology and compensatory mechanisms3 No. A patient can progress to increased ICP and shunt failure after being diagnosed with “arrested” hydrocephalus. How long do you have to follow someone to say that the HCP has arrested? The time to follow up and diagnose this condition is unclear but it is more than just a few years, and, even then, patients still can decompensate.4 What is “compensated hydrocephalus”? A state of stable ventriculomegaly in the absence of a functioning shunt Can these patients decompensate or deteriorate in intellectual development? Yes. This is why it is recommended to “err on the side of shunt” in patients younger than 3 years of age.5 With what is the CSF pulse waveform pattern in Fig. 76.2 associated? Communicating hydrocephalus.6 Note the amplitude is up to three times higher than normal and the latency is reduced to approximately half of normal. Fig. 76.2 Why is the latency to peak decreased? Due to the lack of venous outflow and CSF distensibility, i.e., lack of compliance What are some of the common causes for communicating hydrocephalus? Leptomeningeal inflammation due to infections/meningitis, subarachnoid hemorrhage, idiopathic What tumor is associated with communicating hydrocephalus? Choroid plexus papilloma What skull base bony anomaly is associated with communicating hydrocephalus? Platybasia What do we typically find in obstructive hydrocephalus caused by atresia of the foramen of Luschka and Magendie? Selective enlargement of the posterior fossa With what is the CSF pulse waveform pattern in Fig. 76.3 associated? Hydrocephalus due to aqueductal stenosis (AS).7 Note the amplitude is high and the latency significantly reduced, to almost one third of normal. Fig. 76.3
Types of Hydrocephalus
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree






