28 Visual pathways
Introduction
The visual system comprises the retinas, the visual pathways from the retinas to the brainstem and visual cortex, and the cortical areas devoted to higher visual functions. The retinas and visual pathways are described in this chapter. Higher visual functions are described in Chapter 29.
Retina
The retina and the optic nerves are part of the central nervous system. In the embryo, the retina is formed by an outgrowth from the diencephalon called the optic vesicle (Ch. 1). The optic vesicle is invaginated by the lens and becomes the two-layered optic cup.
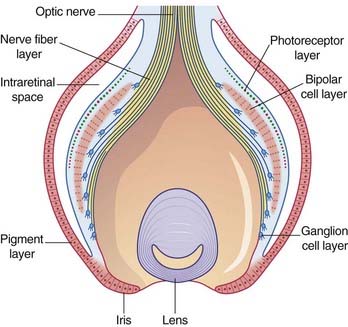
Figure 28.1 shows the general relationships in the developing retina. The nervous layer contains three principal layers of neurons: photoreceptors, which become applied to the pigment layer when the intraretinal space is resorbed; bipolar neurons; and ganglion cells which give rise to the optic nerve and project to the thalamus and midbrain.
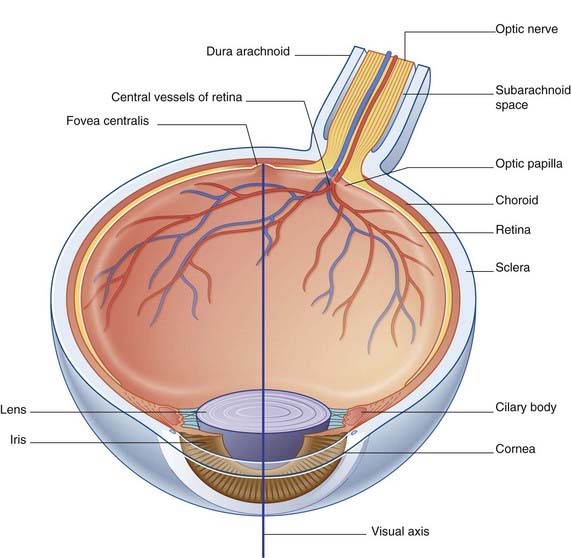
Note that the retina is inverted: light must pass through the layers of optic nerve fibers, ganglion cells, and bipolar neurons to reach the photoreceptors. However, at the point of most acute vision, the fovea centralis, the bipolar and ganglion cell layers lean away all around a central pit (fovea), and light strikes the photoreceptors directly (see Foveal Specialization, later). In the mature eye, the fovea is about 1.5 mm in diameter and occupies the center of the 5 mm wide macula lutea (‘yellow spot’) where many of the photoreceptor cells contain yellow pigment. The fovea is the point of most acute vision and lies in the visual axis – a line passing from the center of the visual field of the eye, through the center of the lens, to the fovea (Figure 28.2). To fixate or foveate an object is to gaze directly at it so that light reflected from its center registers on the fovea.
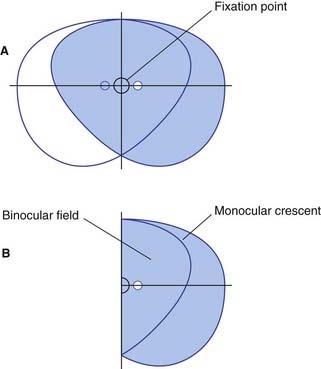
The visual fields of the two eyes overlap across two-thirds of the total visual field. Outside this binocular field is a monocular crescent on each side (Figure 28.3). During passage through the lens, the image of the visual field is reversed, with the result that, e.g., objects in the left part of the binocular visual field register on the right half of each retina, and objects in the upper part of the visual field register on the lower half. This arrangement is preserved all the way to the visual cortex in the occipital lobe.
Structure of the retina
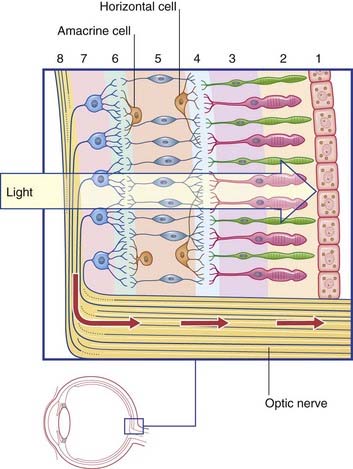
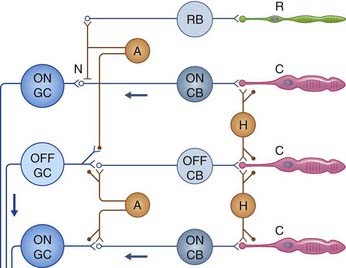
In addition to the serially arranged photoreceptors, bipolar cells, and ganglion cells shown in Figure 28.1, the retina contains two sets of neurons arranged transversely: horizontal cells and amacrine cells (Figure 28.4). A total of eight layers are described for the retina as a whole.
Cone and rod bipolar neurons
Cone bipolar neurons
Cone bipolar neurons are of two types. ON bipolars are switched on (depolarized) by light, being inhibited by transmitter released in the dark. They converge onto ON ganglion cells. OFF bipolars have the reverse response and converge onto OFF ganglion cells (Figure 28.5).