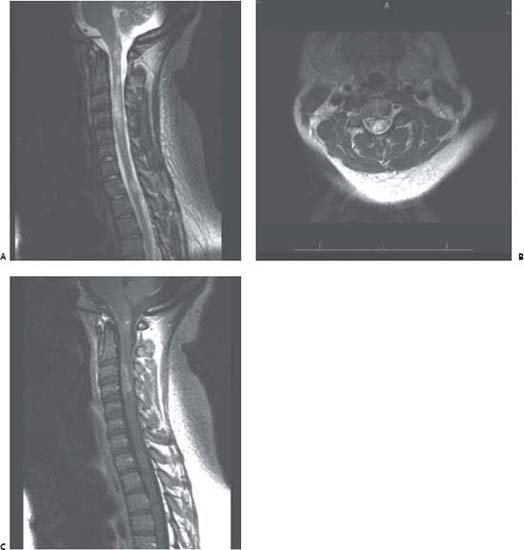
Case 112 Neuromyelitis Optica Fig. 112.1 Magnetic resonance imaging of spine with findings of multilevel increase signal and suggest edema on T2-weighted images within the spinal cord. (A) Sagittal and (B) axial T2-weighted images are demonstrated. The longest extends just below obex to the C5 level. There is second region of increased signal extending from the superior to the inferior margin of the T2 vertebra. (C) Sagittal T1-weighted MRI with contrast: this is a postcontrast view of the same lesion in (A). Note the contrast enhancement at level of C3–C4.
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Questions
Questions
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
112 Neuromyelitis Optica
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


