Case 49 New Trends in Neurotrauma Monitoring
Judith Marcoux and Abdulrazag Ajlan
Fig. 49.1 Computed tomography scan of the head showing a very small intraparenchymal hematoma in the right hippocampal area.
- A 20-year-old man is involved in a high-speed motor vehicle accident. He was the driver and was wearing his seatbelt.
- He is hemodynamically stable and his Glasgow Coma Score (GCS) before intubation is 8.
- A computed tomography (CT) scan of his head is obtained and shown in Fig. 49.1.
- His GCS remains 8 without sedation and he has an intraventricular drain placed to monitor his intracranial pressure (ICP). The opening pressure is 17 mm Hg.
- He is kept normothermic, normocapnic, and with a cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) above 70 mm Hg.
- Over the course of the next 3 days, his ICP rises and he needs heavier sedation, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) drainage, and hyperosmolar therapy.
- A repeat CT scan shows diffuse cerebral edema with effacement of the subarachnoid spaces.
- Transcranial Doppler (TCD) measurements reveal high velocities in both carotid arteries as well as the middle cerebral arteries.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>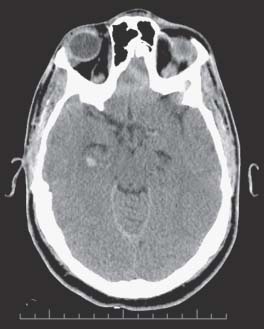
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation Questions
Questions Answers
Answers


