Autoantibodies to gangliosides
By an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) as described elsewhere,1 IgM and IgG antibodies against ganglioside GM1, GM1b, GD1a, GalNAc-GD1a, GD1b, GT1a, or GQ1b were investigated in serum obtained on day 2. IgG antibodies reacted with GD1b and GD1a (each titer, 800 and 200) but not with GM1. An absorption study was performed as reported elsewhere,2 but it could not show the presence of cross-reactive anti-GD1b antibodies with GD1a.
CONCLUSION
Kaida and his coworkers6 examined sera from 17 patients with GBS (nine with ataxia and eight without ataxia) who had monospecific anti-GD1b IgG antibodies, with the use of an ELISA in which wells were coated with a mixture of GD1b and each of nine gangliosides (GM1, GM2, GM3, GD1a, GD3, GT1a, GT1b, GQ1b, and GalNAc-GD1a). The binding activities of the anti-GD1b IgG antibodies against such mixture antigens were compared between ataxic and nonataxic patients. The reactivity to antigens, such as GD1b combined with GD1a, GalNAc-GD1a, GT1b, and GQ1b were significantly reduced in ataxic compared with nonataxic patients.
We performed similar studies using serum from the presented AMAN patient who had monospecific anti-GD1b IgG antibodies. Moreover, we compared the results with those in three patients with AMAN who had anti-GM1 and anti-GD1b IgG antibodies and three ASAN who had monospecific anti-GD1b IgG antibodies. Two of the ASAN patients were reported elsewhere.4 The assays were performed in triplicate and twice or more. The representative results are shown in Figure 45-1. As reported by Kaida et al.,6 binding activity of anti-GD1b IgG antibodies was inhibited by adding GD1a, GalNAc-GD1a, GT1b, or GQ1b in sera from ASAN patients, whereas it was not by adding them in sera from AMAN patients who had both anti-GM1 and anti-GD1b IgG antibodies. The binding activity, however, was reduced by adding GalNAc-GD1a and GQ1b, but not by adding in GD1a and GT1b in serum from the presented patient who did not show ataxia. These results suggest anti-GD1b IgG antibodies, which are inhibited by GD1a and GT1b and are associated with ataxia. In other words, the anti-GD1b antibodies, which are inhibited by GalNAc-GD1a and GQ1b, may not be responsible for the development of ataxia. The hypothesis should be tested in a large series.
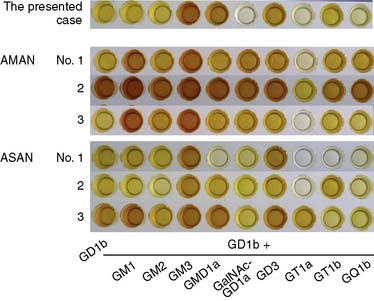
Figure 45-1 Inhibition of binding activity of anti-GD1b immunogoblin G (IgG) antibodies by various gangliosides. The binding activity of anti-GD1b IgG antibodies was decreased by adding GalNAc-GD1a, GT1a, and GQ1b in serum from the presented patients with acute motor axonal neuropathy (AMAN) and by adding GT1a in sera from three AMAN patients (Numbers 1–3). In sera from three patients with acute sensory ataxic neuropathy (ASAN), the binding activity was inhibited by GD1a, GalNAc-GD1a, GT1a, GT1b, and GQ1b (Number 1), by GT1a and GQ1b (Number 2), and by GalNAc-GD1a, GT1b, and GQ1b (Number 3). ASAN patients Numbers 1 and 2, respectively, were reported elsewhere.4
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








