Acute Upper Extremity Pain/Weakness
Kevin R. Moore, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Intervertebral Disc Herniation
Intervertebral Disc Herniation, Cervical
Intervertebral Disc Herniation, Traumatic
Cervical Fracture with Nerve Compression
Burst Fracture, Cervical
Hyperflexion Injury, Cervical
Lateral Flexion Injury, Cervical
Hyperflexion-Rotation Injury, Cervical
Pathologic Vertebral Fracture
Less Common
Syringomyelia
Traumatic Dural AV Fistula
Peripheral Neuropathy
Brachial Plexus Traction Injury
Radial Neuropathy
Ulnar Neuropathy
Median Nerve Entrapment
Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment
Infection
Abscess, Paraspinal
Abscess, Epidural
Osteomyelitis, Granulomatous
Osteomyelitis, Pyogenic
Rare but Important
Idiopathic Brachial Plexus Neuritis
Acute Transverse Myelitis, Idiopathic
Secondary Acute Transverse Myelitis
ADEM, Spinal Cord
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Careful clinical exam distinguishes radiculopathy from mechanical back pain or myelopathy, limiting pertinent differential diagnosis list
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Intervertebral Disc Herniation
Intervertebral Disc Herniation, Cervical
Localized (< 50% of disc circumference) displacement of disc material beyond edges of vertebral ring apophyses
Clinical symptoms affected by level, location, herniation size
Intervertebral Disc Herniation, Traumatic
Disc herniation following trauma
Muscle, ligamentous injuries suggest etiology
Cervical Fracture with Nerve Compression
Burst Fracture, Cervical
Typically mid- or lower cervical spine
Axial compression → comminuted fracture extending through both endplates
Hyperflexion Injury, Cervical
Typically mid or lower cervical spine
Flexion force disrupts capsular & posterior ligaments → anterior vertebral displacement/angulation, focal kyphosis, ↑ space between spinous processes
Lateral Flexion Injury, Cervical
Typically mid or lower cervical spine
Articular mass fracture ± fractures of transverse and uncinate processes, vertebral body
Hyperflexion-Rotation Injury, Cervical
Typically mid or lower cervical spine
Traumatic disruption of cervical spine (ligaments ± bony elements) → facet subluxation, focal vertebral angulation, rotation
Pathologic Vertebral Fracture
Fracture through abnormal bone weakened by tumor or infection
Search for trabecular and cortical bone destruction, spinal cord &/or nerve root compression
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Syringomyelia
Expanded spinal cord with central dilated, beaded, or sacculated cystic cavity
Traumatic Dural AV Fistula
AVF nidus with enlarged draining veins
Radiculopathy 2° to nerve compression by enlarged epidural veins
Peripheral Neuropathy
Brachial Plexus Traction Injury
Stretch injury or avulsion of ≥ 1 cervical roots, brachial plexus elements
Denervation changes in dorsal paraspinal muscles, arm and forearm muscles innervated by terminal peripheral nerve branches
Radial Neuropathy
Focal radial nerve enlargement, abnormal T2 hyperintensity
Characteristic entrapment locations include mid humeral shaft or fibrous arch of Frohse
Ulnar Neuropathy
Focal ulnar nerve enlargement, abnormal T2 hyperintensity
Most common in cubital tunnel (elbow); uncommon in Guyon tunnel (wrist) or brachial plexus
Median Nerve Entrapment
Focal median nerve enlargement, abnormal T2 hyperintensity
Entrapment most common at carpal tunnel or pronator teres muscle
Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment
Mass impinges nerve at spinoglenoid or suprascapular notch
Abnormal T2 hyperintensity in denervated muscles
Infection
Abscess, Paraspinal
Paravertebral enhancing phlegmon or peripherally enhancing liquified pus collection
Abscess, Epidural
Spondylodiscitis with adjacent enhancing epidural phlegmon ± peripherally enhancing fluid collection
May extend over many vertebral segments
Osteomyelitis, Granulomatous
Tuberculosis or brucellosis most common
May produce spinal cord, nerve compression
Osteomyelitis, Pyogenic
Ill-defined abnormal vertebral marrow signal centered at disc with loss of adjacent endplate definition
May produce spinal cord, nerve compression
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Idiopathic Brachial Plexus Neuritis
Parsonage-Turner syndrome
Immune-mediated neuropathy of brachial plexus
Smooth enlargement of brachial plexus elements, mild diffuse nerve and muscle enhancement
Acute Transverse Myelitis, Idiopathic
Inflammatory lesion involving both spinal hemicords → bilateral motor, sensory, and autonomic dysfunction
Lesion extent > 2 vertebral segments + eccentric enhancement
Secondary Acute Transverse Myelitis
Inflammatory disorder of spinal cord associated with many etiologies
T2 hyperintense lesion with mild cord expansion, minimal to no enhancement
ADEM, Spinal Cord
Para/postinfectious immune-mediated inflammatory disorder of spinal cord white matter
Multiple sclerosis mimic
Image Gallery
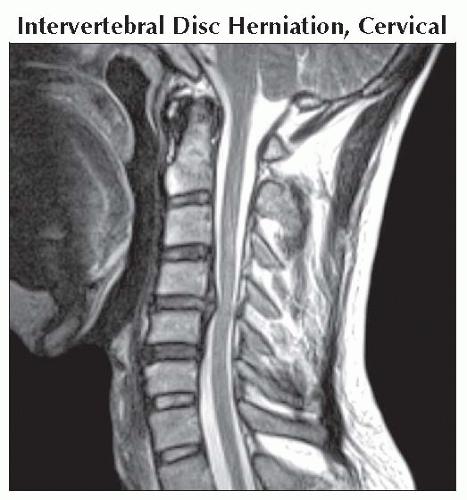 Sagittal T2WI MR demonstrates a C4-5 cervical disc herniation with spinal cord deformation. Location corresponds with left arm pain. |
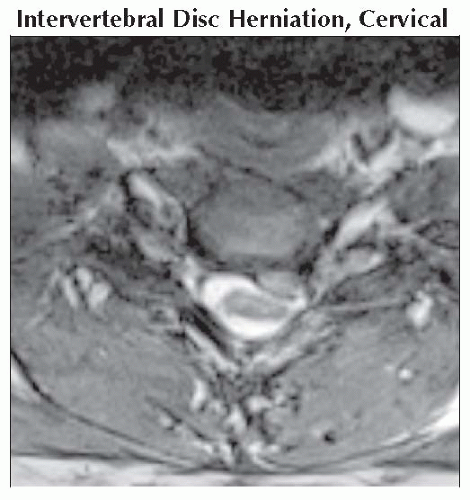 Axial T2* GRE MR shows a large left C6-7 cervical disc herniation with deformation of the spinal cord concordant with clinical localization of left arm pain. |
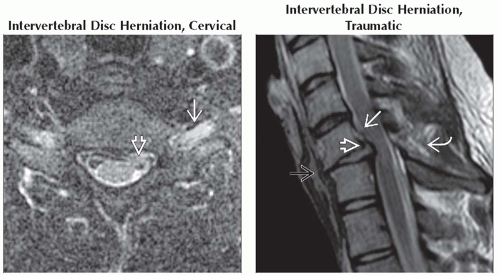 (Left) Axial T2WI FS MR in a patient with left arm pain shows a small cervical HNP
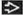 with abnormal asymmetric T2 hyperintensity of the irritated left C7 nerve root with abnormal asymmetric T2 hyperintensity of the irritated left C7 nerve root  . (Right) Sagittal T2WI MR shows ligamentous injury with herniated C6-7 disc . (Right) Sagittal T2WI MR shows ligamentous injury with herniated C6-7 disc 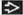 , disruption of anterior longitudinal , disruption of anterior longitudinal  , posterior longitudinal , posterior longitudinal  , and interspinous ligaments , and interspinous ligaments 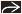 . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|