Chronic Back Pain/Radiculopathy, Post-Operative
Kevin R. Moore, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Failed Back Surgery Syndrome
Peridural Fibrosis
Intervertebral Disc Herniation, Recurrent
Degenerative Disc Disease
Instability
Post-Laminectomy Spondylolisthesis
Accelerated Degeneration
Less Common
Hardware Failure
Bone Graft Complications
Vertebroplasty Complications
Post-Operative Infection
Scoliosis, Degenerative
Rare but Important
Arachnoiditis, Lumbar
Arachnoiditis Ossificans, Lumbar
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Careful clinical exam will often distinguish radiculopathy from mechanical back pain, enabling a tailored differential list
Carefully consider hardware failure or indolent infection in post-operative implant patients presenting with chronic back pain
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Failed Back Surgery Syndrome
Continued low back pain ± radicular pain following lumber spinal surgery
Myriad etiologies manifest clinically as failed back surgery syndrome (FBSS)
Look for specific abnormal imaging findings that may be addressed clinically
Peridural Fibrosis
Scar formation within epidural space following lumbar spinal surgery
Subset of FBSS
T1 C+ FS MR imaging increases sensitivity for detecting peridural fibrosis and permits differentiation of fibrosis from disc herniation
Intervertebral Disc Herniation, Recurrent
Focal extension of disc material beyond endplate margins at previously operated intervertebral disc level
Subset of FBSS
T1 C+ FS MR imaging increases sensitivity for detecting peridural fibrosis and permits differentiation of fibrosis from disc herniation
Degenerative Disc Disease
Generalized and multifactorial process affecting discovertebral unit leading to biomechanical/morphologic alterations
Imaging diagnosis of degenerative disc disease does not distinguish symptomatic from asymptomatic levels
May be asymptomatic or associated with back/neck pain ± radiculopathy
Instability
Loss of spine motion segment stiffness, where applied force produces greater displacement than normal, producing pain/deformity
Deformity increases with motion and increases over time
Any spinal motion segment (comprised of two adjacent vertebrae, disc and connecting spinal ligaments) may be involved
Most common at post-operative levels, particularly if posterior elements removed by laminectomy
AP translation at unstable level may vary from few mm to entire width of vertebral body
Post-Laminectomy Spondylolisthesis
Loss of spine motion segment stiffness, where applied force produces greater displacement than normal, producing pain/deformity
AP canal diameter narrows at subluxation level, distinguishing from spondylolysis where the AP canal diameter is increased
Accelerated Degeneration
Synonyms include spinal “transitional degenerative syndrome” and “accelerated segmental degeneration”
Degeneration of disc space/facets at level(s) adjacent to spinal fusion 2° to altered biomechanical forces → degenerative disc changes, disc herniation, and/or subluxation
Identical changes occur at motion segments above or below congenital segmentation anomaly levels
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Hardware Failure
Mechanical breakdown or malfunction of spinal fusion hardware
Malposition of spinal fusion hardware without mechanical failure of implant
Presentation symptoms range from indolent with chronic pain to calamitously with acute pain
Bone Graft Complications
Abnormal alignment, position, or placement of graft or hardware ± associated neurologic deficit, instability, infection
Graft migration, graft displacement, or graft extrusion
Cervical > thoracic > lumbar
Vertebroplasty Complications
Complication types include
Extravasation of cement into spinal canal, neural foramen, or vertebral venous plexus
Pulmonary embolization of cement
Vertebral osteomyelitis
“Bounce back” fracture adjacent to vertebroplasty level
Post-Operative Infection
Infectious sequelae following operative procedures
Most frequently begins in intervertebral disc space => discitis, epidural abscess, subdural abscess, &/or paraspinal abscess
Look for unexpected abnormal MR enhancement post-spinal surgery imaging
Scoliosis, Degenerative
“De novo” scoliosis
Lateral spinal curvature due to degenerative disc and facet disease
Radiculopathy secondary to foraminal narrowing and nerve root compression
Usually seen in older patients
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Arachnoiditis, Lumbar
Post-inflammatory adhesion and clumping of cauda equina nerve roots in thecal sac
Imaging shows either absence of discrete nerve roots (“empty sac”) or peripheral displacement of nerve roots in thecal sac
Arachnoiditis Ossificans, Lumbar
Intradural ossification associated with post-inflammatory adhesion and clumping of lumbar nerve roots
Look for focal calcific density on CT or hyperintensity on T1WI and T2WI within lumbar nerve root aggregate
Image Gallery
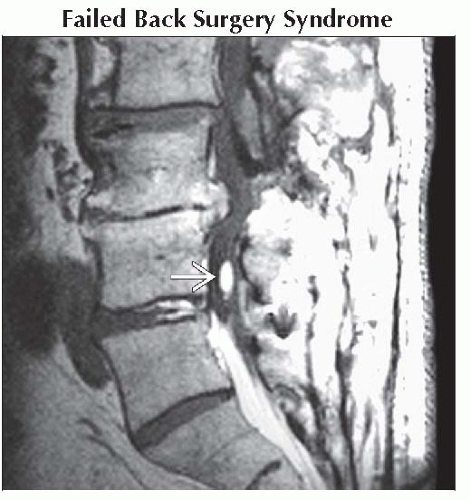
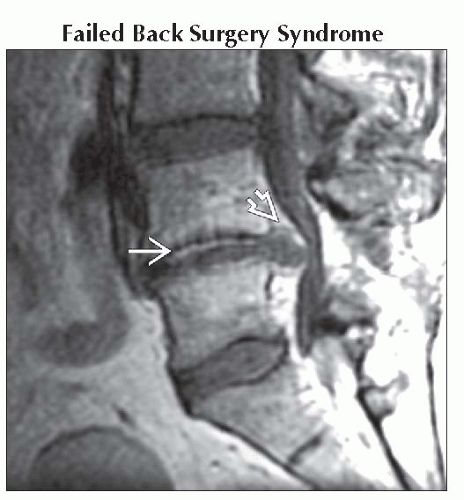 Sagittal T1 C+ MR shows large recurrent L4-5 disc herniation compressing thecal sac
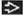 with thin peripheral enhancement. Note linear enhancement within disc due to disc degeneration with thin peripheral enhancement. Note linear enhancement within disc due to disc degeneration  . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|