Cord Lesion, T2 Hyperintense, Ventral
Lubdha M. Shah, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
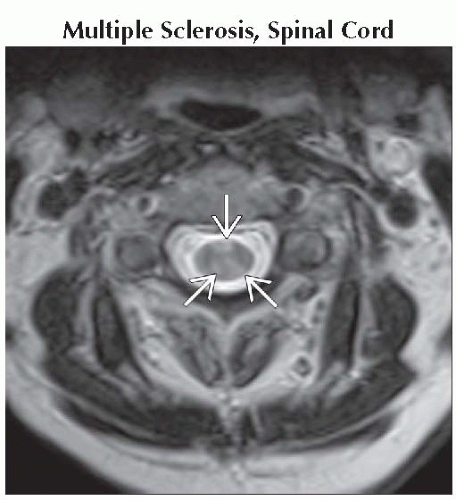
Multiple Sclerosis, Spinal Cord
Contusion-Hematoma, Spinal Cord
Infarction, Spinal Cord
Spondylotic Myelopathy
Less Common
Spinal Cord Herniation
Rare but Important
Viral Myelitis
Toxin Exposure
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Axial T2WI: Useful to localize lesion center in relationship to spinal cord long tracts
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Multiple Sclerosis, Spinal Cord
STIR MR is sensitive for detecting demyelinating lesions
Ill-defined = partial demyelination; well-defined = complete demyelination
Contusion-Hematoma, Spinal Cord
Acute contusion shows T2 hyperintensity with susceptibility artifact from blood products on GRE
STIR detects marrow edema & ligamentous injury
Infarction, Spinal Cord
T2 hyperintensity in gray matter ± adjacent white matter, classically anterior horn cells
Vertebral body infarct with increased T2 marrow signal in the anterior vertebral body/deep medullary portion near the endplate
Spondylotic Myelopathy
Pathophysiologic factors may be static mechanical, dynamic mechanical, & spinal cord ischemia
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Spinal Cord Herniation
Focal anterior cord displacement through a ventral dural defect with expansion of dorsal subarachnoid space
Often in mid-thoracic spine with cord deformity
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Viral Myelitis
Disease of lower motor neurons that affects the gray matter of the spinal cord, specifically ventral horns
Includes poliomyelitis
Toxin Exposure
Reported cases of T2 hyperintensity & enhancement in the anterior horns & lumbar nerve roots after heroin & amphetamine exposure
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Earliest manifestations of ALS on imaging may be diffusion restriction
Image Gallery